Introduction to Alkyl Halides, Alcohols, Ethers, Thiols
... (b) A chlorine contributes about the same molecular mass (35 units) as an ethyl group (29 units), and alkyl chlorides have about the same boiling points as alkanes of the same molecular mass. Hence, chloromethane has about the same boiling point as propane, which has a lower boiling point than the f ...
... (b) A chlorine contributes about the same molecular mass (35 units) as an ethyl group (29 units), and alkyl chlorides have about the same boiling points as alkanes of the same molecular mass. Hence, chloromethane has about the same boiling point as propane, which has a lower boiling point than the f ...
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids
... There will be two features in the IR spectrum of a carboxylic acid: the intense carbonyl stretching absorption (1710 cm-1) and the OH absorption ...
... There will be two features in the IR spectrum of a carboxylic acid: the intense carbonyl stretching absorption (1710 cm-1) and the OH absorption ...
Activity 1: Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds
... Alkyl halide = a hydrocarbon having at least one halide connected to a carbon atom. Alkene = a hydrocarbon having at least one double bond between carbon atoms. Alkyne = a hydrocarbon having at least one triple bond between carbon atoms. Alcohol = a hydrocarbon containing an “O-H” functional group c ...
... Alkyl halide = a hydrocarbon having at least one halide connected to a carbon atom. Alkene = a hydrocarbon having at least one double bond between carbon atoms. Alkyne = a hydrocarbon having at least one triple bond between carbon atoms. Alcohol = a hydrocarbon containing an “O-H” functional group c ...
Nucleophilic Substitution on the Carbonyl Group
... By altering the reaction conditions of a reaction, you change the equilibrium position of that reaction. By changing the equilibrium position of a reaction, you control which product forms in the greater amount. In an esterification reaction, chemists want to maximize the amount of ester obtained by ...
... By altering the reaction conditions of a reaction, you change the equilibrium position of that reaction. By changing the equilibrium position of a reaction, you control which product forms in the greater amount. In an esterification reaction, chemists want to maximize the amount of ester obtained by ...
Palladium-Catalyzed Synthesis and Transformation of Organoboranes
... amounts of Pd2(dba)3. By employment of commercially available chiral diboronates enantioenriched homoallyl alcohols could be obtained. We have also developed a palladium-catalyzed method for synthesis of functionalized allylboronic acids from vinyl cyclopropane, vinyl aziridine, allyl acetate and al ...
... amounts of Pd2(dba)3. By employment of commercially available chiral diboronates enantioenriched homoallyl alcohols could be obtained. We have also developed a palladium-catalyzed method for synthesis of functionalized allylboronic acids from vinyl cyclopropane, vinyl aziridine, allyl acetate and al ...
Chapter 4- Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of
... arrangement with both Xs on the same side of the double bond is called a cis isomer, and the arrangement with the Xs on opposite sides is called a trans isomer. The subtle difference in shape between geometric isomers can dramatically affect the biological activities of organic molecules. For exampl ...
... arrangement with both Xs on the same side of the double bond is called a cis isomer, and the arrangement with the Xs on opposite sides is called a trans isomer. The subtle difference in shape between geometric isomers can dramatically affect the biological activities of organic molecules. For exampl ...
Chapter 2 Phenols
... 1-The OH group of phenols allows hydrogen bonding to other phenol molecules and to water. 2-Compared to compounds of similar size and molecular weight, hydrogen bonding in phenol raises its melting point, boiling point, and solubility in water. ...
... 1-The OH group of phenols allows hydrogen bonding to other phenol molecules and to water. 2-Compared to compounds of similar size and molecular weight, hydrogen bonding in phenol raises its melting point, boiling point, and solubility in water. ...
Properties of amines
... Amines are compounds based on an ammonia molecule (NH3), where one or more of the hydrogen atoms is replaced by a carbon chain. Thus R—NH2 is a primary amine, while R—NH—R’ is a secondary amine, and R—N(R’)—R’’ is a tertiary amine. You will only be asked to name primary amines. Note that 2-aminopro ...
... Amines are compounds based on an ammonia molecule (NH3), where one or more of the hydrogen atoms is replaced by a carbon chain. Thus R—NH2 is a primary amine, while R—NH—R’ is a secondary amine, and R—N(R’)—R’’ is a tertiary amine. You will only be asked to name primary amines. Note that 2-aminopro ...
Chapter in Zumdahl: Chapter #12 Kinetics (2
... draw Lewis electron dot structures for main group elements use Lewis structures to predict oxidation numbers and formal charge on an atom. explain the relationship between the enthalpy of dissociation of an ionic bond and it’s bond strength. predict relative differences in melting point and solubili ...
... draw Lewis electron dot structures for main group elements use Lewis structures to predict oxidation numbers and formal charge on an atom. explain the relationship between the enthalpy of dissociation of an ionic bond and it’s bond strength. predict relative differences in melting point and solubili ...
Radical reactions with metal complexes in aqueous solutions
... radicals will be converted into charged entities due to the electron transfer and thus intrinsically have distinctly higher solvation energy ...
... radicals will be converted into charged entities due to the electron transfer and thus intrinsically have distinctly higher solvation energy ...
$doc.title
... Genera1ng Alkoxides from Alcohols • Alcohols are weak acids – requires a strong base to form an alkoxide such as NaH, sodium amide NaNH2, and Grignard reagents (RMgX) • Alkoxides are bases used as ...
... Genera1ng Alkoxides from Alcohols • Alcohols are weak acids – requires a strong base to form an alkoxide such as NaH, sodium amide NaNH2, and Grignard reagents (RMgX) • Alkoxides are bases used as ...
NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL CHEMISTRY EXAMINATION (1995
... From these data, she can conclude that a) both Ba(IO 3 ) 2 and Mg(ClO3 ) 2 are insoluble in water. b) both PbCrO4 and Mg(ClO3 ) 2 are insoluble in water. c) Ba(IO 3 ) 2 , Pb(IO 3 ) 2 , and PbCrO4 are insoluble in water. d) all of Ba(IO 3 ) 2 , Mg(ClO 3 ) 2 , Pb(IO 3 ) 2 , PbCrO4 , and CaCrO 4 are in ...
... From these data, she can conclude that a) both Ba(IO 3 ) 2 and Mg(ClO3 ) 2 are insoluble in water. b) both PbCrO4 and Mg(ClO3 ) 2 are insoluble in water. c) Ba(IO 3 ) 2 , Pb(IO 3 ) 2 , and PbCrO4 are insoluble in water. d) all of Ba(IO 3 ) 2 , Mg(ClO 3 ) 2 , Pb(IO 3 ) 2 , PbCrO4 , and CaCrO 4 are in ...
Cobalt-Ammine complexes handout
... In this model, each metal center has a total of 6 ligands bound to it, creating a coordination sphere with octahedral geometry. Some ligands form simple covalent bonds through sharing of electrons, while others donate a lone pair to form a coordinate covalent bond. Any charge that is not balanced by ...
... In this model, each metal center has a total of 6 ligands bound to it, creating a coordination sphere with octahedral geometry. Some ligands form simple covalent bonds through sharing of electrons, while others donate a lone pair to form a coordinate covalent bond. Any charge that is not balanced by ...
Notes
... 3. Esterification - organic acid and alcohol forms an ester and water • e.g. acetic acid and ethanol : CH3COOH + C2H5OH CH3COOC2H5 + H2O 4. Addition : A C=C bond is broken and atoms are attached to the carbon atoms ...
... 3. Esterification - organic acid and alcohol forms an ester and water • e.g. acetic acid and ethanol : CH3COOH + C2H5OH CH3COOC2H5 + H2O 4. Addition : A C=C bond is broken and atoms are attached to the carbon atoms ...
Chemistry 3
... This is an exothermic reaction that creates liquid ammonia on condensing. From an industrial point of view, a lower temperature would cause the process to be too slow. This explains the moderately high temperature chosen. A pressure of 150-200 atmospheres is used as creating equipment to maintain a ...
... This is an exothermic reaction that creates liquid ammonia on condensing. From an industrial point of view, a lower temperature would cause the process to be too slow. This explains the moderately high temperature chosen. A pressure of 150-200 atmospheres is used as creating equipment to maintain a ...
Organic - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... quite likely that the transition state leading to 5a should reflect at least some of this energy difference and therefore be more stable than that leading to 5b. (5) Mori, K.; Uede, H. Tetrahedron 1981,37, 2581. ...
... quite likely that the transition state leading to 5a should reflect at least some of this energy difference and therefore be more stable than that leading to 5b. (5) Mori, K.; Uede, H. Tetrahedron 1981,37, 2581. ...
Ligand Exchange Mechanisms
... Even though BDE's of C-C bonds are lower than those of analogous C-H bonds (e.g. C6H 5-CH3:100 kcal/mol vs. C6H 5-H: 110 kcal/mol), transition metal mediated OA's into C-C bonds are much more rare than those for analogous C-H bonds. Formation of the σ-complex is kinetically disfavored by steric repu ...
... Even though BDE's of C-C bonds are lower than those of analogous C-H bonds (e.g. C6H 5-CH3:100 kcal/mol vs. C6H 5-H: 110 kcal/mol), transition metal mediated OA's into C-C bonds are much more rare than those for analogous C-H bonds. Formation of the σ-complex is kinetically disfavored by steric repu ...
Ch 12- Transition Metales and coordination compound
... (monodentate ligand ): — the ligands possess a single donor atom and are able to occupy only one site in a coordination sphere ...
... (monodentate ligand ): — the ligands possess a single donor atom and are able to occupy only one site in a coordination sphere ...
Chemical Reactions
... 1. Add a small amount of ammonium carbonate to a test tube. 2. Pass the sample around for the students to make observations. (Smell, appearance) 3. Using test tube clamps, hold the test tube over the flame of a Bunsen burner. 4. Allow the solid to completely disappear. 5. Have a student waft a sampl ...
... 1. Add a small amount of ammonium carbonate to a test tube. 2. Pass the sample around for the students to make observations. (Smell, appearance) 3. Using test tube clamps, hold the test tube over the flame of a Bunsen burner. 4. Allow the solid to completely disappear. 5. Have a student waft a sampl ...
Basic definitions for organic chemistry
... composition The percentage composition by mass is found by dividing the mass of an element present by the mass of the compound present, then multiplying by 100. Elemental mass of C and H can be found by allowing the substance to undergo complete combustion. • mass of carbon • mass of hydrogen ...
... composition The percentage composition by mass is found by dividing the mass of an element present by the mass of the compound present, then multiplying by 100. Elemental mass of C and H can be found by allowing the substance to undergo complete combustion. • mass of carbon • mass of hydrogen ...
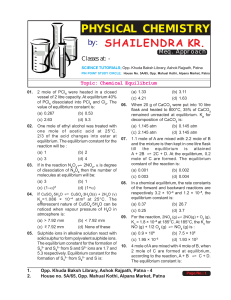
Chemical Equilibrium - Shailendra Kumar Chemistry
... temperature and 0.50 atm pressure. NH4HS decomposes to give NH3 and H2S and total equilibrium pressure in flask is 0.84 atm. The equilibrium constant for the reaction is: (a) 0.30 ...
... temperature and 0.50 atm pressure. NH4HS decomposes to give NH3 and H2S and total equilibrium pressure in flask is 0.84 atm. The equilibrium constant for the reaction is: (a) 0.30 ...
Exam 3 Answer Key
... 6. (2.5) True or False? A molecule with a non-superimposable mirror image must be chiral. 7. (2.5) True or False? A hydrogen attached to a carbon of a triple bond can be abstracted using a base, the conjugate acid of which is stronger than the alkyne. ...
... 6. (2.5) True or False? A molecule with a non-superimposable mirror image must be chiral. 7. (2.5) True or False? A hydrogen attached to a carbon of a triple bond can be abstracted using a base, the conjugate acid of which is stronger than the alkyne. ...
Study of complexes of platinum group metals containing nitrogen
... isopropyl groups of this complex. In addition to the ligand peaks, complexes 3 and 8 show a pair of singlets each between 2.18 and 2.02 ppm respectively corresponding to the eighteen protons of the hexamethlybenzene group of these complexes. It is difficult to assign the exact structure of these comp ...
... isopropyl groups of this complex. In addition to the ligand peaks, complexes 3 and 8 show a pair of singlets each between 2.18 and 2.02 ppm respectively corresponding to the eighteen protons of the hexamethlybenzene group of these complexes. It is difficult to assign the exact structure of these comp ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.