Practice Exam 2
... a) there are no oxygen atoms to remove from the alcohol carbon. b) there are no hydrogen atoms attached to the alcohol carbon. c) the alcohol carbon is bonded to four groups so no oxygen can be added to it. d) the alcohol carbon is bonded to four groups so no hydrogen can be added to it. e) the alco ...
... a) there are no oxygen atoms to remove from the alcohol carbon. b) there are no hydrogen atoms attached to the alcohol carbon. c) the alcohol carbon is bonded to four groups so no oxygen can be added to it. d) the alcohol carbon is bonded to four groups so no hydrogen can be added to it. e) the alco ...
From Organometallic Zinc and Copper Complexes to Highly
... activity system prepared by the addition of diethyl zinc to a hot (200 C) solution of a copper(II) alkoxide precursor. This system formed small, unsupported nanoparticles of both Cu and ZnO and showed up to 85% of the activity, in a squalane suspension, of the ternary reference.11i Other alkylzinc ...
... activity system prepared by the addition of diethyl zinc to a hot (200 C) solution of a copper(II) alkoxide precursor. This system formed small, unsupported nanoparticles of both Cu and ZnO and showed up to 85% of the activity, in a squalane suspension, of the ternary reference.11i Other alkylzinc ...
Chapter 21: Carboxylic acid Derivatives I. Introduction
... The word anhydride literally means without water, and an acid anhydride is the combination of two molecules of carboxylic acid with the elimination of one molecule of water. ...
... The word anhydride literally means without water, and an acid anhydride is the combination of two molecules of carboxylic acid with the elimination of one molecule of water. ...
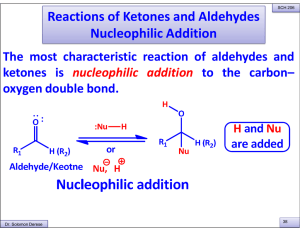
Reactions of Ketones and Aldehydes Nucleophilic Addition
... If the cassava is crushed with water and allowed to stand (‘ferment’), enzymes in the cassava will do the same job and then the HCN can be washed out before the cassava is cooked and eaten. The cassava is now safe to eat but it still contains some glucoside. Some diseases found in eastern Nigeria ca ...
... If the cassava is crushed with water and allowed to stand (‘ferment’), enzymes in the cassava will do the same job and then the HCN can be washed out before the cassava is cooked and eaten. The cassava is now safe to eat but it still contains some glucoside. Some diseases found in eastern Nigeria ca ...
Carbonyl Compounds notes
... This reaction is known as alkaline hydrolysis. It is also known as saponification. It is not readily reversible, so results in a better yield of the alcohol and carboxylate than the acid hydrolysis of the same ester. The NaOH in this reaction is not a catalyst; it is a reactant. The equilibrium can ...
... This reaction is known as alkaline hydrolysis. It is also known as saponification. It is not readily reversible, so results in a better yield of the alcohol and carboxylate than the acid hydrolysis of the same ester. The NaOH in this reaction is not a catalyst; it is a reactant. The equilibrium can ...
7. Organic halides
... isomers and configurational isomers. Types of configurational isomers are geometric isomers and optical isomers. Conformation of alkanes Groups connected by a bond in a molecule can undergo rotation about it. The different arrangements of the atoms in space that results are called conformations of ...
... isomers and configurational isomers. Types of configurational isomers are geometric isomers and optical isomers. Conformation of alkanes Groups connected by a bond in a molecule can undergo rotation about it. The different arrangements of the atoms in space that results are called conformations of ...
OXIDATION - REDUCTION
... dioxide CO2. Its anion is the oxalate ion C2O42, found in salts such as sodium oxalate. 9. Hydrogen sulfide, H2S – This gas can be used as a reductant as it can be oxidised to sulfur species in a higher oxidation state eg SO2. 10. Hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 – When acting as a reductant it is oxidised ...
... dioxide CO2. Its anion is the oxalate ion C2O42, found in salts such as sodium oxalate. 9. Hydrogen sulfide, H2S – This gas can be used as a reductant as it can be oxidised to sulfur species in a higher oxidation state eg SO2. 10. Hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 – When acting as a reductant it is oxidised ...
Chapter 19 d-block metal chemistry: general considerations
... charge distribution on molecules and complex ions. It states that the distribution of charge in a molecule or ion is such that the charge on a single atom is within the range +1 to -1 (ideally close to zero). ...
... charge distribution on molecules and complex ions. It states that the distribution of charge in a molecule or ion is such that the charge on a single atom is within the range +1 to -1 (ideally close to zero). ...
5. Bonding in Complexes
... ligands and the type of the coordination polyhedra depend on the size of the central atom or ion, the identity of the ligands and their steric interactions, and the electronic interactions between the central atom or ion and the ligands. Coordination numbers can vary between 2 and 12. Those with 4, ...
... ligands and the type of the coordination polyhedra depend on the size of the central atom or ion, the identity of the ligands and their steric interactions, and the electronic interactions between the central atom or ion and the ligands. Coordination numbers can vary between 2 and 12. Those with 4, ...
Lab 6
... which the acyl group is the acetyl group. Such reactions are called acetylation reactions. These reactions involve the transfer of an acetyl acyl group to an oxygen atom (i.e., the substitution of an acetyl group for an H atom bonded to oxygen). When alcohols or phenols are acylated, the products ar ...
... which the acyl group is the acetyl group. Such reactions are called acetylation reactions. These reactions involve the transfer of an acetyl acyl group to an oxygen atom (i.e., the substitution of an acetyl group for an H atom bonded to oxygen). When alcohols or phenols are acylated, the products ar ...
Aspirin - Community Colleges of Spokane
... Aspirin, acetylsalicylic acid, has been used as an antipyretic (fever reducer), an analgesic (pain reliever), an antirheumatic, and recently as an anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory drug. Aspirin is truly a wonder drug, an achievement to modern medicine. In this experiment, you will synthesize acet ...
... Aspirin, acetylsalicylic acid, has been used as an antipyretic (fever reducer), an analgesic (pain reliever), an antirheumatic, and recently as an anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory drug. Aspirin is truly a wonder drug, an achievement to modern medicine. In this experiment, you will synthesize acet ...
d_block - ilc.edu.hk
... 2. m.p. from Fe to Zn due to the of unpaired d-electrons (from 4 to 0) ...
... 2. m.p. from Fe to Zn due to the of unpaired d-electrons (from 4 to 0) ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... Now, let us continue this motion further and then you end up with a molecule in which these two axial ligands have an angle of 120 degrees. The equatorial ligands have an angle of 180 degrees and this brings us to another trigonal bipyramidal geometry. This trigonal bipyramidal geometry can be rota ...
... Now, let us continue this motion further and then you end up with a molecule in which these two axial ligands have an angle of 120 degrees. The equatorial ligands have an angle of 180 degrees and this brings us to another trigonal bipyramidal geometry. This trigonal bipyramidal geometry can be rota ...
Alcohols, Phenols , Phenols and Ethers Alcohols
... According to IUPAC system (Unit 12, Class XI), the name of an alcohol is derived from the name of the alkane from which the alcohol is derived, by substituting ‘e’ of alkane with the suffix ‘ol’. The position of substituents are indicated by numerals. For this, the longest carbon chain (parent chai ...
... According to IUPAC system (Unit 12, Class XI), the name of an alcohol is derived from the name of the alkane from which the alcohol is derived, by substituting ‘e’ of alkane with the suffix ‘ol’. The position of substituents are indicated by numerals. For this, the longest carbon chain (parent chai ...
msc_pre_chemistry_pap1_bl3
... the detection of complexes can also be used to determine their stability constants. The study of the complexes is supposed to be incomplete without finding the stability or formation constants, because most of the properties and utility of the complexes depend on it. The value of stability constant ...
... the detection of complexes can also be used to determine their stability constants. The study of the complexes is supposed to be incomplete without finding the stability or formation constants, because most of the properties and utility of the complexes depend on it. The value of stability constant ...
Synthesis of Alcohols Using Grignard Reagents Grignard reagents
... O What remains is the combination of Grignard reagent and carbonyl compound that can be used to prepare the alcohol. ...
... O What remains is the combination of Grignard reagent and carbonyl compound that can be used to prepare the alcohol. ...
Slajd 1 - Lublin
... General properties and applies of phthalocyanine dotted sol-gel materials For over 30 years phthalocyanine dyes have been extensively studied due to their spectroscopic and photoelectric properties and can be applied in many branches: in the field of physics, in technique, medicine, chemistry and ot ...
... General properties and applies of phthalocyanine dotted sol-gel materials For over 30 years phthalocyanine dyes have been extensively studied due to their spectroscopic and photoelectric properties and can be applied in many branches: in the field of physics, in technique, medicine, chemistry and ot ...
Chemistry Chapter 14 Notes
... the complex ion forms. • For example, when the cobalt ion, Co2+, bonds with four Cl− ligands, the total charge is (+2) + 4(−1) = −2. • Metal ions and ligands can form complexes that have no charge. These are not complex ions. • Complex ions often form in systems that reach equilibrium. • Consider zi ...
... the complex ion forms. • For example, when the cobalt ion, Co2+, bonds with four Cl− ligands, the total charge is (+2) + 4(−1) = −2. • Metal ions and ligands can form complexes that have no charge. These are not complex ions. • Complex ions often form in systems that reach equilibrium. • Consider zi ...
Chapters E-18 review - Bakersfield College
... 14. Which compound bas cis and trans isomer? If it bas, draw its cis and trans isomer. Which one bas higher boiling point (cis or trans)? a)2-methyl-2-butene b) 2-chloro-2-butene ...
... 14. Which compound bas cis and trans isomer? If it bas, draw its cis and trans isomer. Which one bas higher boiling point (cis or trans)? a)2-methyl-2-butene b) 2-chloro-2-butene ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.