List of Objectives for Chem52
... Name aromatic compounds (and their derivatives) by their IUPAC-accepted common names. You should know the structures of benzene, toluene, the xylenes, phenol, aniline, benzaldehyde, and benzoic acid. (See Table 15.1.) You should also know the structure of pyridine, pyrrole, and ...
... Name aromatic compounds (and their derivatives) by their IUPAC-accepted common names. You should know the structures of benzene, toluene, the xylenes, phenol, aniline, benzaldehyde, and benzoic acid. (See Table 15.1.) You should also know the structure of pyridine, pyrrole, and ...
Chem 322 - Exam #3 - Spring 2003
... (b) Based on the mechanisms for the formation of the major (56%) and minor (6%) products above (which are the same except for the hydrogen replaced), explain why the amount of 2,6dimethylcyclohexanone produced is about 10 times greater than that of 2,2dimethylcyclohexanone. The first step in this me ...
... (b) Based on the mechanisms for the formation of the major (56%) and minor (6%) products above (which are the same except for the hydrogen replaced), explain why the amount of 2,6dimethylcyclohexanone produced is about 10 times greater than that of 2,2dimethylcyclohexanone. The first step in this me ...
Final Sc. Ed. 423. Chemistry II
... This course is designed with the aim of providing theoretical and practical knowledge and skills in the area of Chemistry Education. The course is divided into two parts i.e., theoretical part and practical part. The theoretical part comprise of different units from physical, inorganic and organic c ...
... This course is designed with the aim of providing theoretical and practical knowledge and skills in the area of Chemistry Education. The course is divided into two parts i.e., theoretical part and practical part. The theoretical part comprise of different units from physical, inorganic and organic c ...
DISTINGUISH TESTS
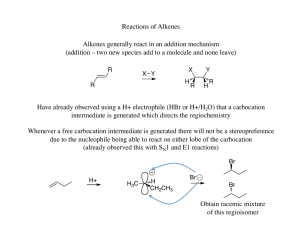
... In a molecule if Carbon atom is surrounded by four different groups called asymmetric carbon or chiral carbon which is must for optical active compound. 1:1 ratio of dextro and leavo mixture is known as racemic mixture. The process of conversion of enantiomer into a racemic mixture is known as ...
... In a molecule if Carbon atom is surrounded by four different groups called asymmetric carbon or chiral carbon which is must for optical active compound. 1:1 ratio of dextro and leavo mixture is known as racemic mixture. The process of conversion of enantiomer into a racemic mixture is known as ...
Chapter 11
... Similar to reactions with alkenes, when alkynes react with hydrohalic acid (e.g. HBr) the proton reacts with the π bond and the positively charged intermediate is reacted with the halide ...
... Similar to reactions with alkenes, when alkynes react with hydrohalic acid (e.g. HBr) the proton reacts with the π bond and the positively charged intermediate is reacted with the halide ...
CHM230 - Preparation of Methyl Benzoate Preparation of Methyl
... 4. Wash the organic layer with water 5. Drain the organic layer into a dry erlenmeyer flask and dry with magnesium sulfate 6. The aqueous layer from the sodium carbonate wash should be acidified with concentrated HCl. When this aqueous material is made strongly acidic with hydrochloric acid, unreact ...
... 4. Wash the organic layer with water 5. Drain the organic layer into a dry erlenmeyer flask and dry with magnesium sulfate 6. The aqueous layer from the sodium carbonate wash should be acidified with concentrated HCl. When this aqueous material is made strongly acidic with hydrochloric acid, unreact ...
Extremely Facile Template Synthesis of Gold(III)
... seldom synthesized by the template condensation reaction. The Au(III) complex of 1 is the only one so far which has been prepared by the template reaction.15,16 In most cases it is probable that Au(III) is reduced to metallic gold or Au2O3‚nH2O, in a basic solution. The Au(III) complexes of macrocyc ...
... seldom synthesized by the template condensation reaction. The Au(III) complex of 1 is the only one so far which has been prepared by the template reaction.15,16 In most cases it is probable that Au(III) is reduced to metallic gold or Au2O3‚nH2O, in a basic solution. The Au(III) complexes of macrocyc ...
Coordination_networks_of_Cu2
... are versatile ligands for constructing MOFs and coordination networks [1–20]. Such ligands can yield networks that can clathrate guest species because the flexible ligand may be able to ‘breathe’ to accommodate the guest, whilst maintaining its crystalline structure [21]. This might be termed an ‘in ...
... are versatile ligands for constructing MOFs and coordination networks [1–20]. Such ligands can yield networks that can clathrate guest species because the flexible ligand may be able to ‘breathe’ to accommodate the guest, whilst maintaining its crystalline structure [21]. This might be termed an ‘in ...
Gas phase chemistry of neutral metal clusters
... Kappes and Staley’s experimental investigation of CO oxidation by N2 O catalyzed by isolated FeO+ (or Fe+ ) in 1981 started the study of gas phase molecular heterogeneous catalysis [41]. After more than two decades, many examples of catalytic cycles facilitated by metal atoms [42–45], metal clusters ...
... Kappes and Staley’s experimental investigation of CO oxidation by N2 O catalyzed by isolated FeO+ (or Fe+ ) in 1981 started the study of gas phase molecular heterogeneous catalysis [41]. After more than two decades, many examples of catalytic cycles facilitated by metal atoms [42–45], metal clusters ...
What Should Be Impossible: Resolution of the Mononuclear Gallium
... Figure 1. Λ-fac (left) and ∆-fac (right) geometries of tris(benzohydroxamato) complexes. ...
... Figure 1. Λ-fac (left) and ∆-fac (right) geometries of tris(benzohydroxamato) complexes. ...
Organometallic Chemistry
... reaction for C-C bond formation, it is often accompanied by competing side reactions such as enolization, reduction, or aldol condensation of the carbonyl substrate. • Organomagnesium compounds can act not only as nucleophiles, but also as bases • It can convert ketones with enolizable hydrogens to ...
... reaction for C-C bond formation, it is often accompanied by competing side reactions such as enolization, reduction, or aldol condensation of the carbonyl substrate. • Organomagnesium compounds can act not only as nucleophiles, but also as bases • It can convert ketones with enolizable hydrogens to ...
Presentation
... (B) a mixture of benzene and Mg(OMe)Br (C) a mixture of toluene and Mg (OH)Br (D) a mixture of phenol and Mg(OH)Br ...
... (B) a mixture of benzene and Mg(OMe)Br (C) a mixture of toluene and Mg (OH)Br (D) a mixture of phenol and Mg(OH)Br ...
THE ELECTROCHEMISTRY OF STRAPPED AND CAPPED PORPHYRIN
... may be explained by two plausible mechanisms: an EE reaction to form radical-cation and dlcationic species or an ECE mechanism in which the chemical process (e.g. a cleavage of the strap and/or loss of the conjugation in the porphyrin ring) is very fast relative to the scan rate [13]. In this case t ...
... may be explained by two plausible mechanisms: an EE reaction to form radical-cation and dlcationic species or an ECE mechanism in which the chemical process (e.g. a cleavage of the strap and/or loss of the conjugation in the porphyrin ring) is very fast relative to the scan rate [13]. In this case t ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.