CHAPTER-6 DEHYDROHALOGENATION OF ALKYL HALIDES
... – Approach to carbon is extremely hindered and elimination predominates especially at high temperatures ...
... – Approach to carbon is extremely hindered and elimination predominates especially at high temperatures ...
CHEMISTRY
... (2) The system is at equilibrium (3) A catalyst is added (4) The reactants are initially mixed 19. For the reaction CI2(g) + 2 NO (g) 2 NOCI (g) doubling the concentration of both reactants increases the rate by a factor of eight. If only the concentration of CI2 is doubled, the rate increases by ...
... (2) The system is at equilibrium (3) A catalyst is added (4) The reactants are initially mixed 19. For the reaction CI2(g) + 2 NO (g) 2 NOCI (g) doubling the concentration of both reactants increases the rate by a factor of eight. If only the concentration of CI2 is doubled, the rate increases by ...
DEHYDRATION - ALKENE TEST EXERCISES
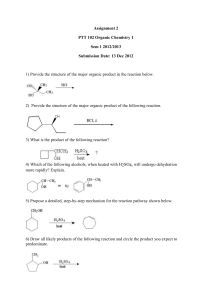
... 1. Give a detailed mechanism for the acid-catalyzed dehydration of cyclohexanol to cyclohexene. ...
... 1. Give a detailed mechanism for the acid-catalyzed dehydration of cyclohexanol to cyclohexene. ...
Chapter 8_part 1
... produces two products: 2-chloro-3-methylbutane and 2chloro-2-methylbutane Give the structure and name of the product that would be obatained from ionic addition of IBr to propene ...
... produces two products: 2-chloro-3-methylbutane and 2chloro-2-methylbutane Give the structure and name of the product that would be obatained from ionic addition of IBr to propene ...
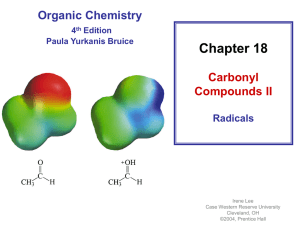
Nucleophilic Addition to Carbonyl Groups
... Because a carbon-carbon double bond is not readily attacked by nucleophiles, metal hydrides can be used to reduce a carbon-oxygen double bond to the corresponding alcohol without reducing the alkene. ...
... Because a carbon-carbon double bond is not readily attacked by nucleophiles, metal hydrides can be used to reduce a carbon-oxygen double bond to the corresponding alcohol without reducing the alkene. ...
Organic Reactions 1
... Plants are the ultimate chemists. In order for scientists to recreate compounds we must be able to take a starting compound and manipulate it until we have created the compound we are interested in. There are certain types of reactions in organic chemistry. These will provide us with the different p ...
... Plants are the ultimate chemists. In order for scientists to recreate compounds we must be able to take a starting compound and manipulate it until we have created the compound we are interested in. There are certain types of reactions in organic chemistry. These will provide us with the different p ...
Chap Thirteen: Alcohols
... iii. reaction with acid chlorides or esters (double addition) iv. reaction with epoxides (Anti stereoselective; SN2-like regioselectivity) v. Side reactions with acidic compounds d. Via reduction of carbonyls or epoxides with Hydride Reducing reagents i. Reduction of Ketones, Aldehydes and Epoxides ...
... iii. reaction with acid chlorides or esters (double addition) iv. reaction with epoxides (Anti stereoselective; SN2-like regioselectivity) v. Side reactions with acidic compounds d. Via reduction of carbonyls or epoxides with Hydride Reducing reagents i. Reduction of Ketones, Aldehydes and Epoxides ...
AMINO ACIDS Ethan Secor, John N. Gitua (Mentor)
... carbon atom the compound is known as an -amino acid. ...
... carbon atom the compound is known as an -amino acid. ...
Assignment 2 Group A and B
... 9) Which of the following alcohols can be prepared by the reaction of methyl formate with excess Grignard reagent? A) 1-pentanol B) 2-pentanol C) 3-pentanol D) 2-methyl-2-pentanol E) 3-methyl-3-pentanol 10) What reagent(s) would you use to accomplish the following conversion? ...
... 9) Which of the following alcohols can be prepared by the reaction of methyl formate with excess Grignard reagent? A) 1-pentanol B) 2-pentanol C) 3-pentanol D) 2-methyl-2-pentanol E) 3-methyl-3-pentanol 10) What reagent(s) would you use to accomplish the following conversion? ...
types of organic reactions
... One product will be there in greater amounts than the other and is called the major product (the other is called the minor product). To decide which is the major product, Markovnikov’s rule is used: The hydrogen atom of the addition reagent goes to the carbon atom of the double bond, that is attache ...
... One product will be there in greater amounts than the other and is called the major product (the other is called the minor product). To decide which is the major product, Markovnikov’s rule is used: The hydrogen atom of the addition reagent goes to the carbon atom of the double bond, that is attache ...
Slide 1
... If a compound has two functional groups, the one with the lowest priority is indicated by its prefix ...
... If a compound has two functional groups, the one with the lowest priority is indicated by its prefix ...
Jeopardy
... nucleophilic part of the reagent will bind with the most stable carbon of the substrate? ...
... nucleophilic part of the reagent will bind with the most stable carbon of the substrate? ...
Developing Binuclear Metal Complexes for Catalysis
... Some homodinuclear complexes are far more catalytically active than their mononuclear counterparts. Stanley’s Rh2(norbornadiene)(P4) complex, where P4 is (PEt2CH2CH2PPhCH2)2,3 catalyzes the hydroformylation of terminal olefins at a rate of 640 h-1 with a linear:branched selectivity of 27.5 for the a ...
... Some homodinuclear complexes are far more catalytically active than their mononuclear counterparts. Stanley’s Rh2(norbornadiene)(P4) complex, where P4 is (PEt2CH2CH2PPhCH2)2,3 catalyzes the hydroformylation of terminal olefins at a rate of 640 h-1 with a linear:branched selectivity of 27.5 for the a ...
Carboxylic Acid
... You know Alkanes and Benzenes, and Alkynes and Alkenes, Amines and Alcohols, Aldehydes and Ketones...... But do you recall, the most famous functional group of all Carboxylic Acid, Has a carbonyl and a hydroxyl It loves to donate protons Then an anion is formed Of all the other acids It’s the most c ...
... You know Alkanes and Benzenes, and Alkynes and Alkenes, Amines and Alcohols, Aldehydes and Ketones...... But do you recall, the most famous functional group of all Carboxylic Acid, Has a carbonyl and a hydroxyl It loves to donate protons Then an anion is formed Of all the other acids It’s the most c ...
Honors Chemistry Organic Chemistry
... _____ 1. amines _____ 2. addition reaction _____ 3. phenyl group _____ 4. benz(a)anthracene _____ 5. structural isomers _____ 6. aromatic hydrocarbon _____ 7. –COOH _____ 8. –OH _____ 9. functional group common to aldehydes and ketones _____ 10. methanol _____ 11. C6H5OH _____ 12. condensation react ...
... _____ 1. amines _____ 2. addition reaction _____ 3. phenyl group _____ 4. benz(a)anthracene _____ 5. structural isomers _____ 6. aromatic hydrocarbon _____ 7. –COOH _____ 8. –OH _____ 9. functional group common to aldehydes and ketones _____ 10. methanol _____ 11. C6H5OH _____ 12. condensation react ...
Transition Metal Chemistry 2 2011.12.2 Ⅰ Fundamental
... person who introduced sex in catalysis. ...
... person who introduced sex in catalysis. ...
C1_5_products_from_oils_crossword
... 11. Polymers that change in response to changes in their environment. 12. A hydrocarbon whose molecules contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. Down 1. Something that cannot be replaced once it is used up. 2. An alkene with the formula C2H4. 3. The reaction used in the oil industry to break ...
... 11. Polymers that change in response to changes in their environment. 12. A hydrocarbon whose molecules contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond. Down 1. Something that cannot be replaced once it is used up. 2. An alkene with the formula C2H4. 3. The reaction used in the oil industry to break ...
10.4b Organic Practice Test Version 2
... 3. Which one of the following statements best describes an elimination reaction? a) Carbon atoms in the organic product are bonded to fewer atoms than the carbon atoms in the organic reactant. b) A hydrogen atom or functional group is replaced with a different atom or functional group. c) Atoms are ...
... 3. Which one of the following statements best describes an elimination reaction? a) Carbon atoms in the organic product are bonded to fewer atoms than the carbon atoms in the organic reactant. b) A hydrogen atom or functional group is replaced with a different atom or functional group. c) Atoms are ...
reactions of the carbonyl group in aldehydes and ketones
... KETONES L.O.: Outline the mechanism for nucleophilic addition reaction of aldehydes and ketones with hydrides. ...
... KETONES L.O.: Outline the mechanism for nucleophilic addition reaction of aldehydes and ketones with hydrides. ...
PART 3 Principles and Applications of Organometallics in Catalysis
... The effect of a catalyst is to change the rate of conversion of a substrate into products, but they do not change the position of an equilibrium. The thermodynamics of the reaction concerned have to be favourable at the outset; catalysts can't perform the miracle of pushing a reaction up the thermod ...
... The effect of a catalyst is to change the rate of conversion of a substrate into products, but they do not change the position of an equilibrium. The thermodynamics of the reaction concerned have to be favourable at the outset; catalysts can't perform the miracle of pushing a reaction up the thermod ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.