Exam 3 Review Sheet
... o Friedel-Crafts acylation: acid chloride, AlCl3 Can be followed by Wolff-Kishner (N2H4, KOH) or Clemmenson (Zn(Hg), HCl) reduction to eliminate oxygen. • Addition of the second and third groups o ortho/para vs. meta directors. Resonance structures, inductive effects. Activating the ring. • Sy ...
... o Friedel-Crafts acylation: acid chloride, AlCl3 Can be followed by Wolff-Kishner (N2H4, KOH) or Clemmenson (Zn(Hg), HCl) reduction to eliminate oxygen. • Addition of the second and third groups o ortho/para vs. meta directors. Resonance structures, inductive effects. Activating the ring. • Sy ...
Ch 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I
... – This vinylic alcohol can rearrange to form a ketone – The rearrangement is acid catalyzed and involves the loss of a proton from the hydroxyl group, the addition of a hydrogen to the other carbon of the double bond and the relocation of the double bond. ...
... – This vinylic alcohol can rearrange to form a ketone – The rearrangement is acid catalyzed and involves the loss of a proton from the hydroxyl group, the addition of a hydrogen to the other carbon of the double bond and the relocation of the double bond. ...
2.10 Alcohols notes - A
... polymers to be produced without using crude oil (assuming that the original ethanol was produced by fermentation). The dehydration of alcohols is favoured by acidic conditions, as the -OH group becomes protonated by H+ ions which produces a water molecule which then leaves. The acid acts as a cataly ...
... polymers to be produced without using crude oil (assuming that the original ethanol was produced by fermentation). The dehydration of alcohols is favoured by acidic conditions, as the -OH group becomes protonated by H+ ions which produces a water molecule which then leaves. The acid acts as a cataly ...
Mill Hill County High School
... polymers to be produced without using crude oil (assuming that the original ethanol was produced by fermentation). The dehydration of alcohols is favoured by acidic conditions, as the -OH group becomes protonated by H+ ions which produces a water molecule which then leaves. The acid acts as a cataly ...
... polymers to be produced without using crude oil (assuming that the original ethanol was produced by fermentation). The dehydration of alcohols is favoured by acidic conditions, as the -OH group becomes protonated by H+ ions which produces a water molecule which then leaves. The acid acts as a cataly ...
alcohol - Portal UniMAP
... is one which electron transfer occurs In organic chemistry this tends to have a significance more on par of oxygen content Oxidation reactions as ones in which carbon gains bonds to oxygen Reduction reactions as ones in which carbon atoms lose bonds to oxygen. ...
... is one which electron transfer occurs In organic chemistry this tends to have a significance more on par of oxygen content Oxidation reactions as ones in which carbon gains bonds to oxygen Reduction reactions as ones in which carbon atoms lose bonds to oxygen. ...
Lecture 14 Organic and Biological Chemistry 1
... Solubility “Like dissolves like” To determine the solubility of organic compounds consider: The number and types of functional groups (Identify ...
... Solubility “Like dissolves like” To determine the solubility of organic compounds consider: The number and types of functional groups (Identify ...
File
... Dehydration (in concentrated sulfuric or phosphoric acid) – produces a double bond (opposite of addition of water) ...
... Dehydration (in concentrated sulfuric or phosphoric acid) – produces a double bond (opposite of addition of water) ...
File
... Identify one isomer that will react with aqueous sodium hydroxide almost exclusively by an SN2 mechanism. Draw the mechanism for this reaction using curly arrows to represent the movement of electron pairs. Include the structural formulas of the transition state and the organic product. ...
... Identify one isomer that will react with aqueous sodium hydroxide almost exclusively by an SN2 mechanism. Draw the mechanism for this reaction using curly arrows to represent the movement of electron pairs. Include the structural formulas of the transition state and the organic product. ...
136KB - NZQA
... however, is an unsaturated molecule / hydrocarbon, because it has a double C=C bond, which breaks, allowing two extra atoms to bond to the structure, resulting in the formation of 1,2-dibromoethane, CH2BrCH2Br. This is an addition reaction. ...
... however, is an unsaturated molecule / hydrocarbon, because it has a double C=C bond, which breaks, allowing two extra atoms to bond to the structure, resulting in the formation of 1,2-dibromoethane, CH2BrCH2Br. This is an addition reaction. ...
ch22 lecture 7e
... for the reaction between N2(g) and O2(g). – Industrial fixation results from the production of NH3, which is used to make fertilizers. – Biological fixation involves the conversion of atmospheric N2 to NO3– by blue-green algae and nitrogen-fixing bacteria. ...
... for the reaction between N2(g) and O2(g). – Industrial fixation results from the production of NH3, which is used to make fertilizers. – Biological fixation involves the conversion of atmospheric N2 to NO3– by blue-green algae and nitrogen-fixing bacteria. ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... Pages 199-203; Text section 7.2 Types of Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions can be classified into one of four categories depending on what type and how many reactants are present. We can use a generalized equation to represent each. In the generalized equation, the letters A and B represent posi ...
... Pages 199-203; Text section 7.2 Types of Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions can be classified into one of four categories depending on what type and how many reactants are present. We can use a generalized equation to represent each. In the generalized equation, the letters A and B represent posi ...
Chapter 5 – Chemical Reactions
... Increase concentration of solution (a more concentrated acid will react faster than a dilute acid) Add a catalyst – a catalyst is a chemical that speeds up a reaction but does not get used up by the reaction ...
... Increase concentration of solution (a more concentrated acid will react faster than a dilute acid) Add a catalyst – a catalyst is a chemical that speeds up a reaction but does not get used up by the reaction ...
Summary of Reactions Which Will Appear on Exams
... 42. REACTIONS OF GRIGNARD REAGENTS AND ORGANOLITHIUM COMPOUNDS WITH ESTERS TO FORM TERTIARY ALCOHOLS ...
... 42. REACTIONS OF GRIGNARD REAGENTS AND ORGANOLITHIUM COMPOUNDS WITH ESTERS TO FORM TERTIARY ALCOHOLS ...
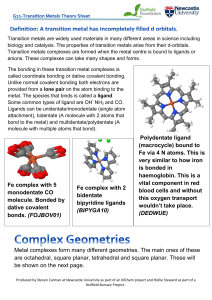
Polydentate ligand (macrocycle) bound to Fe via 4 N atoms. This is
... Transition metals are widely used materials in many different areas in science including biology and catalysis. The properties of transition metals arise from their d-orbitals. Transition metals complexes are formed when the metal centre is bound to ligands or anions. These complexes can take many s ...
... Transition metals are widely used materials in many different areas in science including biology and catalysis. The properties of transition metals arise from their d-orbitals. Transition metals complexes are formed when the metal centre is bound to ligands or anions. These complexes can take many s ...
File
... • A protein with a D amino acid instead of L will have its R group sticking out in the wrong direction. • Many other kinds of organic molecules exist as enantiomers. Usually only one form is active in biological systems. For example, if one form binds to a receptor protein on the surface of a cell, ...
... • A protein with a D amino acid instead of L will have its R group sticking out in the wrong direction. • Many other kinds of organic molecules exist as enantiomers. Usually only one form is active in biological systems. For example, if one form binds to a receptor protein on the surface of a cell, ...
Higher Chemistry
... Naming compounds with no more than eight carbon atoms in their longest chain. For straight and branch chained aldehydes and ketones systematic names, structural formulae and isomers. c) Oxidation reactions of aldehydes and ketones. d) Effect of heat on proteins, denature of proteins. 4. Oxidation of ...
... Naming compounds with no more than eight carbon atoms in their longest chain. For straight and branch chained aldehydes and ketones systematic names, structural formulae and isomers. c) Oxidation reactions of aldehydes and ketones. d) Effect of heat on proteins, denature of proteins. 4. Oxidation of ...
Hydrogen Bonding • Aldehydes and ketones don`t hydrogen bond
... The (a) ketone and (b) aldehyde have lost an αhydrogen. In the resulting molecule, the ketone has an alkyl group, while the aldehyde has a hydrogen. Alkyl groups are electron donors, and so it tries to push more electrons to the negative carbanion (red arrow). This makes the molecule less stable tha ...
... The (a) ketone and (b) aldehyde have lost an αhydrogen. In the resulting molecule, the ketone has an alkyl group, while the aldehyde has a hydrogen. Alkyl groups are electron donors, and so it tries to push more electrons to the negative carbanion (red arrow). This makes the molecule less stable tha ...
Chemistry Carbon
... nitrogen atom attached to two hydrogen atoms and the carbon skeleton. Amines - Organic compounds with amino groups. ...
... nitrogen atom attached to two hydrogen atoms and the carbon skeleton. Amines - Organic compounds with amino groups. ...
1 - Wikispaces
... (b) Propanoic acid can be prepared from propanal, CH3CH2CHO. State the reagents for this conversions. Reagents……………………………………………………………………………………………….. ...
... (b) Propanoic acid can be prepared from propanal, CH3CH2CHO. State the reagents for this conversions. Reagents……………………………………………………………………………………………….. ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.