Document
... A negative ion or a molecule with a lone pair of electrons Attracted to a positive/electron deficient centre Donates a pair of electrons to form a dative covalent bond. ...
... A negative ion or a molecule with a lone pair of electrons Attracted to a positive/electron deficient centre Donates a pair of electrons to form a dative covalent bond. ...
ch22_lecture_6e_final
... for the reaction between N2(g) and O2(g). – Industrial fixation results from the production of NH3, which is used to make fertilizers. – Biological fixation involves the conversion of atmospheric N2 to NO3- by blue-green algae and nitrogen-fixing bacteria. ...
... for the reaction between N2(g) and O2(g). – Industrial fixation results from the production of NH3, which is used to make fertilizers. – Biological fixation involves the conversion of atmospheric N2 to NO3- by blue-green algae and nitrogen-fixing bacteria. ...
+ Y
... has an electron-poor atom (e.g H+, CH3+ ) and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile ...
... has an electron-poor atom (e.g H+, CH3+ ) and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile ...
ClickHere - KV HVF , AVADI Chennai
... 13 What are interstitial compounds? Why are such compounds well known for transition metals? 14 Draw a figure to show splitting of degenerate d-orbitals in an octahedral field. How does the magnitude of the ∆o decides the high spin and low spin complexes. 15 The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqu ...
... 13 What are interstitial compounds? Why are such compounds well known for transition metals? 14 Draw a figure to show splitting of degenerate d-orbitals in an octahedral field. How does the magnitude of the ∆o decides the high spin and low spin complexes. 15 The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqu ...
10. Alkyl Halides - University of West Alabama
... 10.7 Preparing Alkyl Halides from Alcohols • Reaction of tertiary C-OH with HX is fast and effective – Add HCl or HBr gas into ether solution of tertiary alcohol • Primary and secondary alcohols react very slowly and often rearrange, so alternative methods are used ...
... 10.7 Preparing Alkyl Halides from Alcohols • Reaction of tertiary C-OH with HX is fast and effective – Add HCl or HBr gas into ether solution of tertiary alcohol • Primary and secondary alcohols react very slowly and often rearrange, so alternative methods are used ...
BITSAT Chemistry
... velocity and root mean square of a gas at a particular A mixture of C6H6 and excess H2 has a pressure of 60 mm of Hg in an unknown volume. After the gas had been passed over a nickel catalyst and all the benzene converted to cyclohexane, the pressure of the gas was 30 mm of Hg in the same volume at ...
... velocity and root mean square of a gas at a particular A mixture of C6H6 and excess H2 has a pressure of 60 mm of Hg in an unknown volume. After the gas had been passed over a nickel catalyst and all the benzene converted to cyclohexane, the pressure of the gas was 30 mm of Hg in the same volume at ...
Chapter 10 for 302
... There cannot be any acidic protons in the solvent, as the Grignard is such a strong base. There cannot be any pi bonds in the solvent as those are sites of reactivity that the Grignard will attack. From here on, I will use Grignard to refer to both Grignard reagents and organolithiums, as they ...
... There cannot be any acidic protons in the solvent, as the Grignard is such a strong base. There cannot be any pi bonds in the solvent as those are sites of reactivity that the Grignard will attack. From here on, I will use Grignard to refer to both Grignard reagents and organolithiums, as they ...
Organic Reactions
... • Note that you will see full structural formulas and condensed structural formulas. • Table R has partially condensed formulas. You need to be able to discern between these different ways of describing molecules. ...
... • Note that you will see full structural formulas and condensed structural formulas. • Table R has partially condensed formulas. You need to be able to discern between these different ways of describing molecules. ...
Chemistry Crunch #12.2: Organic Reactions KEY Why? Learning
... 3. Summarize. In a characteristic addition reaction: a) There will always be 2 reactant(s) and 1 product(s). b) The hydrocarbon reactant will always have a double or triple bond, or in other words, the hydrocarbon will be unsaturated. c) We learned how to classify many non-organic chemical reactions ...
... 3. Summarize. In a characteristic addition reaction: a) There will always be 2 reactant(s) and 1 product(s). b) The hydrocarbon reactant will always have a double or triple bond, or in other words, the hydrocarbon will be unsaturated. c) We learned how to classify many non-organic chemical reactions ...
I (21 points) Complete the following reactions by providing starting
... A. (JOC, 2008, ASAP, Loh) Chemists have been studying the Barbier-Grignard reactions with the goal of affecting the carbon-carbon bond forming reaction in solvents like water. Recent developments include the use of indium metal catalysts that react through single electron transfer mechanisms. Show t ...
... A. (JOC, 2008, ASAP, Loh) Chemists have been studying the Barbier-Grignard reactions with the goal of affecting the carbon-carbon bond forming reaction in solvents like water. Recent developments include the use of indium metal catalysts that react through single electron transfer mechanisms. Show t ...
Organic Reactions Worksheet
... 2. The formation of 2-hexanol from an alkene. 3. The formation of 2,2-pentanediol. 4. The reaction between 3-hexanol and potassium dichromate. What would you visually observe? 5. The reaction between trans-2-hexene with hydrogen bromide. 6. The reaction that would occur if isopropanol was heated at ...
... 2. The formation of 2-hexanol from an alkene. 3. The formation of 2,2-pentanediol. 4. The reaction between 3-hexanol and potassium dichromate. What would you visually observe? 5. The reaction between trans-2-hexene with hydrogen bromide. 6. The reaction that would occur if isopropanol was heated at ...
PPT: Intro to Organic Chemistry
... H H H H H –C–C–H + Cl2 H–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H If more chlorine is provided, the reaction will produce... H H H H H –C–C–Cl + Cl2 Cl–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H ...
... H H H H H –C–C–H + Cl2 H–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H If more chlorine is provided, the reaction will produce... H H H H H –C–C–Cl + Cl2 Cl–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H ...
C h e m g u i d e ... CARBOXYLIC ACIDS: PREPARATION
... 1. Carboxylic acids are commonly made from primary alcohols. The alcohol is heated under reflux with an excess of sodium or potassium dichromate(VI) solution acidified with sulphuric acid. When the reaction is complete, the carboxylic acid can be distilled off. a) Describe what you would see during ...
... 1. Carboxylic acids are commonly made from primary alcohols. The alcohol is heated under reflux with an excess of sodium or potassium dichromate(VI) solution acidified with sulphuric acid. When the reaction is complete, the carboxylic acid can be distilled off. a) Describe what you would see during ...
1. Which of the following amino acids contains sulfur? a
... 1. Which of the following amino acids contains sulfur? a) asparagine b) methionine + c) histidine d) threonine 2. What is the symbol of the element that is classified as an alkali metal and is in the fourth period of the periodic table? a) Ca b) K + c) Br d) Na 3. A silver atom is converted to a sil ...
... 1. Which of the following amino acids contains sulfur? a) asparagine b) methionine + c) histidine d) threonine 2. What is the symbol of the element that is classified as an alkali metal and is in the fourth period of the periodic table? a) Ca b) K + c) Br d) Na 3. A silver atom is converted to a sil ...
CLASS-X SC (Chemical Reactions and Equations)
... 17. (a) An aqueous solution has a PH value of 7.0. Is this solution acidic, basic or neutral? (b) If H+ concentration of a solution is 1×10-2mol L-1what will be its P4 value? (c) Which has higher PH value: 1−M HCl or 1−M NaOH 18. What will you observe when: (i) Red litmus is introduced into a soluti ...
... 17. (a) An aqueous solution has a PH value of 7.0. Is this solution acidic, basic or neutral? (b) If H+ concentration of a solution is 1×10-2mol L-1what will be its P4 value? (c) Which has higher PH value: 1−M HCl or 1−M NaOH 18. What will you observe when: (i) Red litmus is introduced into a soluti ...
N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but
... i) React with aldehydes and ketones forming secondary and tertiary alcohols respectively. ii) React with carbon dioxide. RMgBr + CO2 ...
... i) React with aldehydes and ketones forming secondary and tertiary alcohols respectively. ii) React with carbon dioxide. RMgBr + CO2 ...
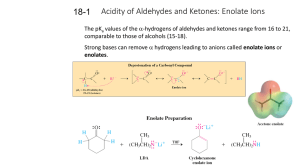
18-1 Enolates (PPT)
... The enolate resonance hybrid possesses partial negative charges on both carbon and oxygen and may attack electrophiles at either position. ...
... The enolate resonance hybrid possesses partial negative charges on both carbon and oxygen and may attack electrophiles at either position. ...
FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
... • Aromatic compounds derive their names from the fact that many of these compounds in the early days of discovery were grouped because they were oils with fragrant odors, hence the name aromatic. • The current definition of aromatic compounds includes only those with a benzene ring, which is a speci ...
... • Aromatic compounds derive their names from the fact that many of these compounds in the early days of discovery were grouped because they were oils with fragrant odors, hence the name aromatic. • The current definition of aromatic compounds includes only those with a benzene ring, which is a speci ...
File - chemistryattweed
... once some ammonia is produced, some nitrogen and hydrogen are formed from the ammonia (the reverse reaction). When nitrogen and hydrogen are initially added to a reaction vessel, the reaction is slow. Equilibrium is reached when the rate of the forward reaction is the same as the rate of the reverse ...
... once some ammonia is produced, some nitrogen and hydrogen are formed from the ammonia (the reverse reaction). When nitrogen and hydrogen are initially added to a reaction vessel, the reaction is slow. Equilibrium is reached when the rate of the forward reaction is the same as the rate of the reverse ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.