Staff demonstrating hours for level-3 Inorganic Lab
... EXAMPLE trans-(Et3P)2PtHCl + C2H4 trans-(Et3P)2PtCl(C2H5) In this example the resulting ethyl complex is stable because the d 8 platinum Pt(2+) atom strongly prefers square-planar geometry. A related route is insertion of a carbene into a TM-H bond EXAMPLE CpMo(CO)3H + CH2N2 CpMo(CO)3(CH3) CH2N2 ...
... EXAMPLE trans-(Et3P)2PtHCl + C2H4 trans-(Et3P)2PtCl(C2H5) In this example the resulting ethyl complex is stable because the d 8 platinum Pt(2+) atom strongly prefers square-planar geometry. A related route is insertion of a carbene into a TM-H bond EXAMPLE CpMo(CO)3H + CH2N2 CpMo(CO)3(CH3) CH2N2 ...
Depending on C, where the
... Contains -OH hydroxyl group • Common formula is R-OH – alcohols: R is alkyl group (e. g. methyl, ethyl...) – phenols: R is aryl (e. g. phenyl) ...
... Contains -OH hydroxyl group • Common formula is R-OH – alcohols: R is alkyl group (e. g. methyl, ethyl...) – phenols: R is aryl (e. g. phenyl) ...
Unit 5 and 6 revsion - Deans Community High School
... Q14. The burning of fossil fuels is a major source of air pollution. (a) Name the acidic gas formed when air in a car engine is sparked. (b) Name the acidic gas formed when coal with a high sulphur content is burned. (c) Name the toxic gas formed when methane is burned in a limited supply of air. (d ...
... Q14. The burning of fossil fuels is a major source of air pollution. (a) Name the acidic gas formed when air in a car engine is sparked. (b) Name the acidic gas formed when coal with a high sulphur content is burned. (c) Name the toxic gas formed when methane is burned in a limited supply of air. (d ...
Chemistry 101 H Introduction to Organic Chemistry Chapter 6
... Before 19th Century, belief was: Compounds present in plants and animals required a “vital (life) force” for their creation. 1828, Friedrich Wohler carried out a laboratory synthesis of urea, a biological product formerly believed to be a product of the “vital force”. Wohler’s laboratory synthesis o ...
... Before 19th Century, belief was: Compounds present in plants and animals required a “vital (life) force” for their creation. 1828, Friedrich Wohler carried out a laboratory synthesis of urea, a biological product formerly believed to be a product of the “vital force”. Wohler’s laboratory synthesis o ...
CoordinationCompounds
... Coordination Compounds • Transition metals have s, d and p orbitals all available for bonding • Don’t obey the octet rule • They are most stable with filled d, s and p orbitals – s2d10p6 (18 e-) • Transition metals act like a Lewis acid (electron pair acceptor) so as to fill valence orbitals • Tran ...
... Coordination Compounds • Transition metals have s, d and p orbitals all available for bonding • Don’t obey the octet rule • They are most stable with filled d, s and p orbitals – s2d10p6 (18 e-) • Transition metals act like a Lewis acid (electron pair acceptor) so as to fill valence orbitals • Tran ...
Bimolecular reactions of the chromium
... The study of the gas-phase reactions of bare transition-metal cations with organic substrates during the last few years has given a wealth.of information about organometallic chemistry.’ A typical gas-phase reaction of a transition-metal ion with a hydrocarbon is the oxidative insertion into C-H and ...
... The study of the gas-phase reactions of bare transition-metal cations with organic substrates during the last few years has given a wealth.of information about organometallic chemistry.’ A typical gas-phase reaction of a transition-metal ion with a hydrocarbon is the oxidative insertion into C-H and ...
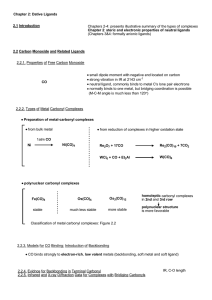
Chapter 2: Dative Ligands 2.1 Introduction 2.2.1. Properties of Free
... H2-complexes: arrested oxidative addition of dihidrogen metal backbonds to H2 *, but cleaves H-H only partially most metal: in low oxidation state (backbonding) many of these low-valent complexes are cationic (neutral, low-valent metal is too much electron-rich) neutral H2 complexes have -accepting ...
... H2-complexes: arrested oxidative addition of dihidrogen metal backbonds to H2 *, but cleaves H-H only partially most metal: in low oxidation state (backbonding) many of these low-valent complexes are cationic (neutral, low-valent metal is too much electron-rich) neutral H2 complexes have -accepting ...
Kazzie`s Guide to Orgo 2
... General Note: Some of these questions have been previously used in examples, etcetera, but they cover the things that I think are important to know from this semester. Try to work through them with as few resources as possible, and we will go through this at the final review. Chem 210 Stuff Identify ...
... General Note: Some of these questions have been previously used in examples, etcetera, but they cover the things that I think are important to know from this semester. Try to work through them with as few resources as possible, and we will go through this at the final review. Chem 210 Stuff Identify ...
索书号:O62 /C713p (MIT) Principles and Applications Of
... 13 Synthetic Applications of Transition-Metal Hydrides 14 Synthetic Applications of Complexes Containing Metal-Carbon σBonds 15 Synthetic Applications of Transition-Metal Carbonyl Compounds 16 Synthetic Applications of Transition-Metal Carbenes and Metallacycles 17 Synthetic Applications of Transiti ...
... 13 Synthetic Applications of Transition-Metal Hydrides 14 Synthetic Applications of Complexes Containing Metal-Carbon σBonds 15 Synthetic Applications of Transition-Metal Carbonyl Compounds 16 Synthetic Applications of Transition-Metal Carbenes and Metallacycles 17 Synthetic Applications of Transiti ...
File
... • A series of compound of uniform chemical type • Showing gradations in physical properties • Having a general formula for its members • Each member having a similar method of ...
... • A series of compound of uniform chemical type • Showing gradations in physical properties • Having a general formula for its members • Each member having a similar method of ...
pdfInt 2 Homework Unit 2 1 MB
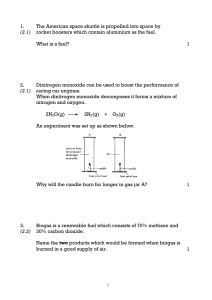
... Scientists have been experimenting to find ways of reducing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. One of these ways involves placing concrete balls on the sea bed. They hope that green plants called algae will grow on the balls and this will help to reduce the carbon dioxide level. Give a reason why the ...
... Scientists have been experimenting to find ways of reducing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. One of these ways involves placing concrete balls on the sea bed. They hope that green plants called algae will grow on the balls and this will help to reduce the carbon dioxide level. Give a reason why the ...
Chemistry
... 16. Chlorobenzene preferentially gives o- or p- derivatives on electrophilic substitution. Explain this with the concept of resonance 17. Why Sandmeyer’s reaction is considered to be an effective method in organic synthesis? ...
... 16. Chlorobenzene preferentially gives o- or p- derivatives on electrophilic substitution. Explain this with the concept of resonance 17. Why Sandmeyer’s reaction is considered to be an effective method in organic synthesis? ...
Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
... brought by the ligands plus the valence electrons of the metal equals 18. When the electron-count is less than 18, metal is said to be coordinatively unsaturated and can take on additional ligands. 18-Electron rule is to transition metals as the octet rule is to second-row elements. ...
... brought by the ligands plus the valence electrons of the metal equals 18. When the electron-count is less than 18, metal is said to be coordinatively unsaturated and can take on additional ligands. 18-Electron rule is to transition metals as the octet rule is to second-row elements. ...
... N are the same as in the amide group, sp2 hybridized. The lonepair electrons in the p z orbital are delocalized and would not be available to accept a hydrogen bond. The same is true about the NH group in a peptide bond. 5. (4 pts) What is the most stable form of Mg? Is it ionized and if so what is ...
Name……………………………………............................. Index number
... Write your name, index number class and admission number in the spaces provided Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided. Answer all the questions in the spaces provided. Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators may be used. All working must be clearly shown where n ...
... Write your name, index number class and admission number in the spaces provided Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided. Answer all the questions in the spaces provided. Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators may be used. All working must be clearly shown where n ...
Chapter 14…Kinetic Theory
... 7. Indicate the relationship between the variables in each of the equations above. 8. Indicate what each variable stands for in each of the equations above. 9. Temperature is in what unit for gas laws? 10. STP stands for: 11. Standard temperature = __________ 12. Standard pressure = __________ atm, ...
... 7. Indicate the relationship between the variables in each of the equations above. 8. Indicate what each variable stands for in each of the equations above. 9. Temperature is in what unit for gas laws? 10. STP stands for: 11. Standard temperature = __________ 12. Standard pressure = __________ atm, ...
Introduction to Homogenous Catalysis with Ruthenium
... molybdenum, tungsten, and rhenium metal complexes have also been reported for catalytic dehydrogenation. (7) In a homogeneous hydrogen transfer oxidation reaction, acetone is utilized as both a solvent and a hydrogen acceptor (equation 2). ...
... molybdenum, tungsten, and rhenium metal complexes have also been reported for catalytic dehydrogenation. (7) In a homogeneous hydrogen transfer oxidation reaction, acetone is utilized as both a solvent and a hydrogen acceptor (equation 2). ...
Final Exam Review
... What are the products of free radical halogenation of an alkane (ex: Cl2/hv light)? What is the electivity for brominations vs. chlorinations? How are alkyne anions formed from terminal alkynes? Which radical or anion is most stable? Proper names for compounds containing functional groups covered th ...
... What are the products of free radical halogenation of an alkane (ex: Cl2/hv light)? What is the electivity for brominations vs. chlorinations? How are alkyne anions formed from terminal alkynes? Which radical or anion is most stable? Proper names for compounds containing functional groups covered th ...
Slide 1 - Alfred State College intranet site
... Carbonyl and Carboxyl Compounds III. Interesting Carbonyl Compounds Formaldehyde (CH2═O) is the simplest aldehyde: •It is sold as formalin, a 37% aqueous solution used to preserve biological specimens. ...
... Carbonyl and Carboxyl Compounds III. Interesting Carbonyl Compounds Formaldehyde (CH2═O) is the simplest aldehyde: •It is sold as formalin, a 37% aqueous solution used to preserve biological specimens. ...
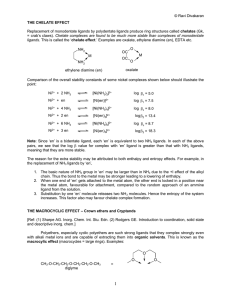
© Ravi Divakaran THE CHELATE EFFECT Replacement of
... and acting as donor ligand atoms. The sequence of equilibrium constants for this ether is Li+ < Na+ < K+ > Rb+ > Cs+. Other crown ethers which have cavities of different sizes give different sequences of equilibrium constants so that selective complex formation with a particular metal ion is possibl ...
... and acting as donor ligand atoms. The sequence of equilibrium constants for this ether is Li+ < Na+ < K+ > Rb+ > Cs+. Other crown ethers which have cavities of different sizes give different sequences of equilibrium constants so that selective complex formation with a particular metal ion is possibl ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... 11. When H2SO4 and Ba(OH)2 are reacted in a double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2 ...
... 11. When H2SO4 and Ba(OH)2 are reacted in a double replacement reaction, one of the products of the reaction is… a) H2 d) BaH2 b) H2O e) SO2 c) BaS 12. In the double replacement reaction between the weak acid, HC2H3O2 and strong base, NaOH, which ion(s) are spectator ions? a) Na+, C2H3O2– d) H+, C2 ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.