
Unit 15 Organics Day 2 Cyclic Hydrocarbons: If you remove 2
... Unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons: the arenes ...
... Unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons: the arenes ...
Controlling Rate - Lesmahagow High School
... Sometimes the collisions do not result in a reaction, despite having the minimum kinetic energy. This is thought to be because the particles have not collided with the correct geometry (angle) to allow the activated complex to be formed. In the above reaction of hydrogen and bromine the particles co ...
... Sometimes the collisions do not result in a reaction, despite having the minimum kinetic energy. This is thought to be because the particles have not collided with the correct geometry (angle) to allow the activated complex to be formed. In the above reaction of hydrogen and bromine the particles co ...
Rates of Hydrolysis of Some Halogeno-compounds
... In this experiments we are going to study the effect of the structure of the halogeno-compounds on the rate of hydrolysis. 1-chlorobutane, 1-bromobutane and 1iodobutane can be classified as 'Haloalkanes' while bromobenzen can be classified as 'Halobenzenes'. Haloalkanes (鹵烷) (also known as alkyl hal ...
... In this experiments we are going to study the effect of the structure of the halogeno-compounds on the rate of hydrolysis. 1-chlorobutane, 1-bromobutane and 1iodobutane can be classified as 'Haloalkanes' while bromobenzen can be classified as 'Halobenzenes'. Haloalkanes (鹵烷) (also known as alkyl hal ...
Chapter 2 Key Terms: element, atom, proton, neutron, electron
... Chapter 3 Key Terms: surface tension, specific heat, hydrophilic, hydrophobic, hydrogen ion, hydroxide ion, pH scale, buffer Chapter 4 Key Terms: organic chemistry, isomer, functional group hydrocarbon, and hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino groups Chapter 5 Key Terms: polymer, dehydration or conde ...
... Chapter 3 Key Terms: surface tension, specific heat, hydrophilic, hydrophobic, hydrogen ion, hydroxide ion, pH scale, buffer Chapter 4 Key Terms: organic chemistry, isomer, functional group hydrocarbon, and hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino groups Chapter 5 Key Terms: polymer, dehydration or conde ...
Indian Journal of Chemistry
... and excess energies of activation (G*E) for viscous flow have been calculated. These values are negative over the entire range of composition. The results for VmE, , and G*E are discussed in terms of interaction between components. The viscosity data have been correlated with the equations of Mc ...
... and excess energies of activation (G*E) for viscous flow have been calculated. These values are negative over the entire range of composition. The results for VmE, , and G*E are discussed in terms of interaction between components. The viscosity data have been correlated with the equations of Mc ...
Yearly Lesson Plan 2007
... increase in the number of carbon atoms in alkene molecules, explain the effects on boiling points of alkenes due to increase in the number of carbon atoms in alkene molecules, describe chemical properties of alkenes, compare and contrast alkanes with alkenes. relate the reactivities of alkan ...
... increase in the number of carbon atoms in alkene molecules, explain the effects on boiling points of alkenes due to increase in the number of carbon atoms in alkene molecules, describe chemical properties of alkenes, compare and contrast alkanes with alkenes. relate the reactivities of alkan ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... two alkyl groups bonded to the carbonyl carbon followed by the word ketone. • Ketones are named systematically by replacing the final -e of the alkane name with -one. The numbering of the chain begins at the end nearest the carbonyl group. The location of the carbonyl group is indicated by placing t ...
... two alkyl groups bonded to the carbonyl carbon followed by the word ketone. • Ketones are named systematically by replacing the final -e of the alkane name with -one. The numbering of the chain begins at the end nearest the carbonyl group. The location of the carbonyl group is indicated by placing t ...
Excercises 6-10
... 1. The following chemical transformation of 2-‐bromo-‐1-‐phenylpropane to (E)-‐1-‐ phenylprop-‐1-‐ene is an elimination reaction. These β-‐hydrogen eliminations can proceed via three different mechanisms. Please p ...
... 1. The following chemical transformation of 2-‐bromo-‐1-‐phenylpropane to (E)-‐1-‐ phenylprop-‐1-‐ene is an elimination reaction. These β-‐hydrogen eliminations can proceed via three different mechanisms. Please p ...
1 NEUTRON DIFFRACTION STUDIES OF METAL
... Hydrogen atoms have the ability to occupy interstitial cavities in metal lattices. It is well known that hydrogen can occupy interstitial sites in non-stoichiometric hydrides of metals leading to high coordination [9]. These materials have historically been studied with surface diffraction technique ...
... Hydrogen atoms have the ability to occupy interstitial cavities in metal lattices. It is well known that hydrogen can occupy interstitial sites in non-stoichiometric hydrides of metals leading to high coordination [9]. These materials have historically been studied with surface diffraction technique ...
sn2 reactions of alkyl halides
... of a large number of functional groups. These syntheses are often carried out by nucleophilic substitution reactions in which the halide is replaced by some nucleophile. These substitution reactions can occur in one smooth step, or in two discrete steps, depending primarily on the structure of the a ...
... of a large number of functional groups. These syntheses are often carried out by nucleophilic substitution reactions in which the halide is replaced by some nucleophile. These substitution reactions can occur in one smooth step, or in two discrete steps, depending primarily on the structure of the a ...
Organic Chemistry
... If there is a limited supply of oxygen incomplete combustion occurs and carbon monoxide or carbon are formed instead of carbon dioxide. e.g. CH4 + 1½O2 CO + 2H2O CH4 + O2 C + 2H2O What problems do the gases released on combustion of alkanes cause? ...
... If there is a limited supply of oxygen incomplete combustion occurs and carbon monoxide or carbon are formed instead of carbon dioxide. e.g. CH4 + 1½O2 CO + 2H2O CH4 + O2 C + 2H2O What problems do the gases released on combustion of alkanes cause? ...
Equilibrium (Sheet 1)
... Section III La Chatelier's principle states that if a stress such as a change in concentration, pressure or temperature is applied to a system in equilibrium, the equilibrium will shift in a way that tends to undo the effect of the stress. For example: H2O + CO H2 + CO2 + heat. If no stress is intro ...
... Section III La Chatelier's principle states that if a stress such as a change in concentration, pressure or temperature is applied to a system in equilibrium, the equilibrium will shift in a way that tends to undo the effect of the stress. For example: H2O + CO H2 + CO2 + heat. If no stress is intro ...
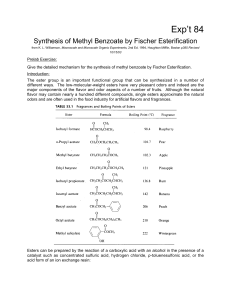
Synthesis of Methyl Benzoate by Fisher Esterification
... For primary alcohols reacting with unhindered carboxylic acids, Keq ~4. If equal quantities of 1butanol and acetic acid are allowed to react, the theoretical yield of ester is only 67% at equilibrium. To upset the equilibrium we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either ...
... For primary alcohols reacting with unhindered carboxylic acids, Keq ~4. If equal quantities of 1butanol and acetic acid are allowed to react, the theoretical yield of ester is only 67% at equilibrium. To upset the equilibrium we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either ...
CONDENSATION POLYMERS
... In the jargon of synthetic organic chemistry, an ester is a functional group. It is a site on the molecule at which reactions take place. It is also a site on the molecule that is easily subject to synthetic transformations. In other words, one functional group might easily be converted into another ...
... In the jargon of synthetic organic chemistry, an ester is a functional group. It is a site on the molecule at which reactions take place. It is also a site on the molecule that is easily subject to synthetic transformations. In other words, one functional group might easily be converted into another ...
Homogeneous Catalysis with Metal Complexes in
... Pantothenic acid is being manufactured from (R)-pantolactone and ,B-alanine (Scheme 3). Most processes for (R)-pantolactone are based on resolution procedures, the resolution being carried out at the stage of the open-chain hydroxy-acid equi valent and the undesired stereoisomer being recycled by ra ...
... Pantothenic acid is being manufactured from (R)-pantolactone and ,B-alanine (Scheme 3). Most processes for (R)-pantolactone are based on resolution procedures, the resolution being carried out at the stage of the open-chain hydroxy-acid equi valent and the undesired stereoisomer being recycled by ra ...
conversion of the OH group into a better leaving group, and
... Williamson ether synthesis can occur to form epoxides. ...
... Williamson ether synthesis can occur to form epoxides. ...
Theoretical problems (official version)
... Much of the photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts – organelles found in plant cells and containing chlorophyll – the light-absorbing substance. Hill isolated chloroplasts from the cells by grinding the leaves in the sucrose solutions. The cell-free chloroplasts did not produce oxygen under illu ...
... Much of the photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts – organelles found in plant cells and containing chlorophyll – the light-absorbing substance. Hill isolated chloroplasts from the cells by grinding the leaves in the sucrose solutions. The cell-free chloroplasts did not produce oxygen under illu ...
Dehydration of Cyclohexanol
... acid and concentrated sulfuric acid is used to prepare cyclohexene from cyclohexanol via an E1 reaction. The mechanism of this E1 reaction involves three steps. First, is the rapid (and reversible) protonation of the alcohol, followed by the much slower rate-determining step, the loss of water to gi ...
... acid and concentrated sulfuric acid is used to prepare cyclohexene from cyclohexanol via an E1 reaction. The mechanism of this E1 reaction involves three steps. First, is the rapid (and reversible) protonation of the alcohol, followed by the much slower rate-determining step, the loss of water to gi ...
Optical Isomers or Enantiomers
... • If the analyzer has to be rotated clockwise, the enantiomer is dextrorotatory (D), or dextro for short. From the Latin word meaning “right”. • If the analyzer has to be rotated counterclockwise, then the enantiomer is laevorotatory (L), or levo for short. From the Latin word ...
... • If the analyzer has to be rotated clockwise, the enantiomer is dextrorotatory (D), or dextro for short. From the Latin word meaning “right”. • If the analyzer has to be rotated counterclockwise, then the enantiomer is laevorotatory (L), or levo for short. From the Latin word ...
Metal Organic Frameworks (MOFs) are 3-dimensional
... hexanuclear ZrO clusters like the ones found in the UiO-66 structure are chemical and thermally quite stable compounds, due to the high coordination number of the zirconium atoms. Defects within the structure have been found as one important feature to enhance catalytic activity and to create Lewis- ...
... hexanuclear ZrO clusters like the ones found in the UiO-66 structure are chemical and thermally quite stable compounds, due to the high coordination number of the zirconium atoms. Defects within the structure have been found as one important feature to enhance catalytic activity and to create Lewis- ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.
















![Coordination Compounds [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000678035_1-c20c75fd4abb97d3ba4a0b0fce26e10b-300x300.png)





