ch15 lecture 7e
... Organic Compounds and the Atomic Properties of Carbon 15.1 The Special Nature of Carbon and the Characteristics of Organic Molecules 15.2 The Structures and Classes of Hydrocarbons 15.3 Some Important Classes of Organic Reactions 15.4 Properties and Reactivities of Common Functional Groups 15.5 The ...
... Organic Compounds and the Atomic Properties of Carbon 15.1 The Special Nature of Carbon and the Characteristics of Organic Molecules 15.2 The Structures and Classes of Hydrocarbons 15.3 Some Important Classes of Organic Reactions 15.4 Properties and Reactivities of Common Functional Groups 15.5 The ...
Chapter 1 Notes
... - compounds are called amines - compounds that have both amino and carboxyl groups are called amino acids ...
... - compounds are called amines - compounds that have both amino and carboxyl groups are called amino acids ...
Document
... Anhydrous magnesium sulphate solid is much ___________ than its hydrated form (MgSO4.7H2O), this is because in anhydrous form, the cations and anions are linked by _________________________; while in the hydrated form, water molecules are present between the ions and linked by hydrogen bonds only, h ...
... Anhydrous magnesium sulphate solid is much ___________ than its hydrated form (MgSO4.7H2O), this is because in anhydrous form, the cations and anions are linked by _________________________; while in the hydrated form, water molecules are present between the ions and linked by hydrogen bonds only, h ...
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Notes Sheet
... In an alkyl halide, one of the hydrogen atoms in an alkane has been replaced by a halogen. – What are halogens again? Alkyl halides are easy to name; – name of the alkane is preceded by the number of the carbon on which the halogen is substituted and the name of the halogen, – modified so that -ine ...
... In an alkyl halide, one of the hydrogen atoms in an alkane has been replaced by a halogen. – What are halogens again? Alkyl halides are easy to name; – name of the alkane is preceded by the number of the carbon on which the halogen is substituted and the name of the halogen, – modified so that -ine ...
Abstract Substituted phenyl carbametes and. Isomeric azepines
... Substituted phenyl carbametes and. Isomeric azepines were synthesised by methods reported in literature. The product of thermolysis of ethylazidoformate and toluene was analyzed on capillary SE-54. column GC-MS. The analysis reveal that all the three methyl substituted (2, 3 and 4) isomers are forme ...
... Substituted phenyl carbametes and. Isomeric azepines were synthesised by methods reported in literature. The product of thermolysis of ethylazidoformate and toluene was analyzed on capillary SE-54. column GC-MS. The analysis reveal that all the three methyl substituted (2, 3 and 4) isomers are forme ...
File
... are soluble in water. • Higher molecular weight alcohols (6 Cs or more) are not soluble in water. ...
... are soluble in water. • Higher molecular weight alcohols (6 Cs or more) are not soluble in water. ...
Making Connections - SCH4U1-CCVI
... Enthalpy Change, ∆H Results in the difference in enthalpies of the reactants and the products during a change, due to: - breakage of bonds or intermolecular forces ∆H = +ve (endo) - formation of bonds or intermolecular forces ∆H = -ve (exo) Determination of Enthalpy Change, ∆H - H and ∆H cannot be d ...
... Enthalpy Change, ∆H Results in the difference in enthalpies of the reactants and the products during a change, due to: - breakage of bonds or intermolecular forces ∆H = +ve (endo) - formation of bonds or intermolecular forces ∆H = -ve (exo) Determination of Enthalpy Change, ∆H - H and ∆H cannot be d ...
Acids and Bases
... A protic solvent is one in which hydrogen is attached to a highly electronegative atom such as oxygen or nitrogen e.g. water Solvation of both acetic acid and acetate ion occurs in water although the acetate is more stabilized by this solvation ...
... A protic solvent is one in which hydrogen is attached to a highly electronegative atom such as oxygen or nitrogen e.g. water Solvation of both acetic acid and acetate ion occurs in water although the acetate is more stabilized by this solvation ...
PowerPoint
... Polymers are extremely long molecule chains that consist of repeated molecular units called monomers. Each monomer can be made up of anywhere from four to 100 atoms, and when chained together they can form polymers made up of hundreds or thousands of atoms total. These polymer molecules are still to ...
... Polymers are extremely long molecule chains that consist of repeated molecular units called monomers. Each monomer can be made up of anywhere from four to 100 atoms, and when chained together they can form polymers made up of hundreds or thousands of atoms total. These polymer molecules are still to ...
Slide 1
... In metal-free Arduengo carbenes interaction of empty p-orbital of the carbene carbon with filled p-orbitals of the adjacent atoms raises the energy of the former. It matches the energy of filled metal orbitals only poorly now and thus is a week acceptor . So, the metal-to-carbene bonding can be bett ...
... In metal-free Arduengo carbenes interaction of empty p-orbital of the carbene carbon with filled p-orbitals of the adjacent atoms raises the energy of the former. It matches the energy of filled metal orbitals only poorly now and thus is a week acceptor . So, the metal-to-carbene bonding can be bett ...
Organic Chemistry - Moorpark College
... 1) The first word comes from the Alcohol part of the word (The R' which is connected to by a single bond to an oxygen.) Name it as the alkyl group i.e. methyl 2) The second word is from the carboxylic part of the word ( the R which has the C=O carbonyl group) the "ic acid" in the common form becomes ...
... 1) The first word comes from the Alcohol part of the word (The R' which is connected to by a single bond to an oxygen.) Name it as the alkyl group i.e. methyl 2) The second word is from the carboxylic part of the word ( the R which has the C=O carbonyl group) the "ic acid" in the common form becomes ...
Reactions to functionalize benzene
... Due to the stability of aromatic system, addition reactions aren’t favored. Electrophilic aromatic substitution is the predominant reaction mechanism Hydrogens are easily replaced by electrophilic substituent groups H ...
... Due to the stability of aromatic system, addition reactions aren’t favored. Electrophilic aromatic substitution is the predominant reaction mechanism Hydrogens are easily replaced by electrophilic substituent groups H ...
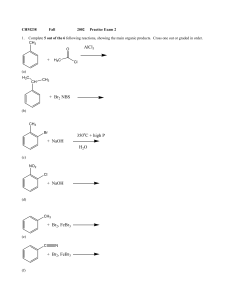
+ NaOH 350 C + high P H2O + H3C AlCl3 + NaOH + Br2, FeBr3
... Starting with toluene, design syntheses, providing the correct reagents for the following transformations. Both processes can be accomplished with 2 steps, but there is more than one correct answer for each. Assume that ortho and para isomers can be separated. OH O CH3 ...
... Starting with toluene, design syntheses, providing the correct reagents for the following transformations. Both processes can be accomplished with 2 steps, but there is more than one correct answer for each. Assume that ortho and para isomers can be separated. OH O CH3 ...
Organic Chemistry
... What does it mean to be organic? To be an organic compound means that you contain carbon ...
... What does it mean to be organic? To be an organic compound means that you contain carbon ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 PART-A
... 11. Give an example for α, β, γ and δ-elimination reaction. 12. State and explain the Hammond postulate to the bromination of n-propane. 13. How will you determine the reaction mechanism of hydrolysis of an ester using isotoping labeling method? 14. Write and explain the Steven’s rearrangement. 15. ...
... 11. Give an example for α, β, γ and δ-elimination reaction. 12. State and explain the Hammond postulate to the bromination of n-propane. 13. How will you determine the reaction mechanism of hydrolysis of an ester using isotoping labeling method? 14. Write and explain the Steven’s rearrangement. 15. ...
Whitten, Davis, and Peck, General Chemistry, 6th Edition
... Recommended CER Experiments to accompany Hornback’s Organic Chemistry, Second Edition The table below matches sections from the book with recommended CER labs. Click on the experiment title to view a PDF of each lab. Go to www.CERLabs.com to search the complete CER database and to learn more about c ...
... Recommended CER Experiments to accompany Hornback’s Organic Chemistry, Second Edition The table below matches sections from the book with recommended CER labs. Click on the experiment title to view a PDF of each lab. Go to www.CERLabs.com to search the complete CER database and to learn more about c ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.