National 5 Chemistry
... I can explain why alcohols are used as fuels and solvents I can represent the formation of ethanol by fermentation as a balanced formula equation I can compare advantages and disadvantages of fermentation and catalytic hydration of ethene as methods of producing ethanol I can state that alcohols rea ...
... I can explain why alcohols are used as fuels and solvents I can represent the formation of ethanol by fermentation as a balanced formula equation I can compare advantages and disadvantages of fermentation and catalytic hydration of ethene as methods of producing ethanol I can state that alcohols rea ...
Final Exam, Chem 111 2012 Study Guide (labs)
... 1. Be familiar with the structure and nomenclature of organic compounds. a. Explain the origin of steric repulsion, with examples (e.g., eclipsed vs staggered) b. Explain how to tell when two structures are different conformations of the same molecule, vs when they are different constitutional isome ...
... 1. Be familiar with the structure and nomenclature of organic compounds. a. Explain the origin of steric repulsion, with examples (e.g., eclipsed vs staggered) b. Explain how to tell when two structures are different conformations of the same molecule, vs when they are different constitutional isome ...
Chapter_Sixteen_lecture
... Be able to recognize the carbonyl group and describe its polarity and shape. Be able to name the members of these families and write their structures, given the names. Be able to describe such properties as polarity, hydrogen bonding, and water solubility. Be able to specify where aldehydes and keto ...
... Be able to recognize the carbonyl group and describe its polarity and shape. Be able to name the members of these families and write their structures, given the names. Be able to describe such properties as polarity, hydrogen bonding, and water solubility. Be able to specify where aldehydes and keto ...
Document
... Ketones if the carbonyl group is Carboxylic acids, or organic within a carbon skeleton acids Aldehydes if the carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon ...
... Ketones if the carbonyl group is Carboxylic acids, or organic within a carbon skeleton acids Aldehydes if the carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon ...
Ch. 4 Carbon
... Ketones if the carbonyl group is Carboxylic acids, or organic within a carbon skeleton acids Aldehydes if the carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon ...
... Ketones if the carbonyl group is Carboxylic acids, or organic within a carbon skeleton acids Aldehydes if the carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon ...
15 - MSU Chemistry
... The starting material in the first reaction has a plane of symmetry so it is achiral: the stereochemistry shows only which diastereoisomer we have. Attack by the amine nucleophile at either end ...
... The starting material in the first reaction has a plane of symmetry so it is achiral: the stereochemistry shows only which diastereoisomer we have. Attack by the amine nucleophile at either end ...
nomenclature continued… - Turner Fenton Secondary School
... Are like aldehydes except the carbonyl group (C=O) is located somewhere in the middle of the chain (not at terminal end). Generally written as RR`C=O. Ketones like aldehydes do not exhibit hydrogen bonding. There are common names for ketones, for example, acetone. Acetone is the key ingredient in na ...
... Are like aldehydes except the carbonyl group (C=O) is located somewhere in the middle of the chain (not at terminal end). Generally written as RR`C=O. Ketones like aldehydes do not exhibit hydrogen bonding. There are common names for ketones, for example, acetone. Acetone is the key ingredient in na ...
Chem 150 Unit 4 - Chemical Properties I Chemical Reactions
... * The elements in Group IIA form compounds (such as Mg3N2 and CaCO3) in which the metal atom is in the +2 oxidation state. * Oxygen usually has an oxidation number of -2. Exceptions include molecules and polyatomic ions that contain O-O bonds, such as O2, O3, H2O2, and the O22- ion. * The nonmetals ...
... * The elements in Group IIA form compounds (such as Mg3N2 and CaCO3) in which the metal atom is in the +2 oxidation state. * Oxygen usually has an oxidation number of -2. Exceptions include molecules and polyatomic ions that contain O-O bonds, such as O2, O3, H2O2, and the O22- ion. * The nonmetals ...
Guide_to_Life_in_Orgo_Ib
... Convert a stereoview into a conventional drawing of a molecule using wedged, dashed, and normal lines. Identify the number of covalent bonds an atom forms to reach an octet. Given a molecular or ionic formula, draw a Lewis and line-bond structure. Describe electron sharing according to valence bond ...
... Convert a stereoview into a conventional drawing of a molecule using wedged, dashed, and normal lines. Identify the number of covalent bonds an atom forms to reach an octet. Given a molecular or ionic formula, draw a Lewis and line-bond structure. Describe electron sharing according to valence bond ...
Alcohols, Phenols , Ethers And Thiols
... alcohol is oxidized by enzymes in the body to start the metabolic process. Alcohol dehydrogenase is the catalyst in the conversion of ethyl alcohol to acetaldehyde, a toxic substance. Cytochrome p-450, that is the oxidizing agent. Thus toxic acetaldehyde cannot accumulate in the body. One treatment ...
... alcohol is oxidized by enzymes in the body to start the metabolic process. Alcohol dehydrogenase is the catalyst in the conversion of ethyl alcohol to acetaldehyde, a toxic substance. Cytochrome p-450, that is the oxidizing agent. Thus toxic acetaldehyde cannot accumulate in the body. One treatment ...
This exam will consist of 30-35 multiple choice or short answer
... What is the solvent in the reaction? What are the starting materials? Product? What are the structures? What are some physical properties of the starting materials and product? What is petroleum ether? What is the purpose of using pet ether in this experiment? What is the mechanism of the reaction? ...
... What is the solvent in the reaction? What are the starting materials? Product? What are the structures? What are some physical properties of the starting materials and product? What is petroleum ether? What is the purpose of using pet ether in this experiment? What is the mechanism of the reaction? ...
Chemistry - Tiwariacademy.net
... SN1 reaction proceeds via the formation of carbocation. The alkyl halide (I) is 3° while (II) is 2°. Therefore, (I) forms 3° carbocation while (II) forms 2° carbocation. Greater the stability of the carbocation, faster is the rate of SN1 reaction. Since 3° carbocation is more stable than 2° carbocat ...
... SN1 reaction proceeds via the formation of carbocation. The alkyl halide (I) is 3° while (II) is 2°. Therefore, (I) forms 3° carbocation while (II) forms 2° carbocation. Greater the stability of the carbocation, faster is the rate of SN1 reaction. Since 3° carbocation is more stable than 2° carbocat ...
Reductions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives - IDC
... Catalytic Hydrogenation : As a rule, the carbonyl group does not add hydrogen as readily as do the carbon-carbon double and triple bonds. Thus, it is fairly easy to reduce an alkene or alkyne function without affecting any carbonyl functions in the same molecule. By using a platinum catalyst and inc ...
... Catalytic Hydrogenation : As a rule, the carbonyl group does not add hydrogen as readily as do the carbon-carbon double and triple bonds. Thus, it is fairly easy to reduce an alkene or alkyne function without affecting any carbonyl functions in the same molecule. By using a platinum catalyst and inc ...
Chapter 12: Oxidations In order to discuss the oxidation
... oxidation state. Alkenes that are bound geminally to heteroatoms are also at the carboxylic acid oxidation state. ...
... oxidation state. Alkenes that are bound geminally to heteroatoms are also at the carboxylic acid oxidation state. ...
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
... Addition of amines with an atom containing a lone pair of electrons on the adjacent atom occurs very readily, giving useful, stable imines For example, hydroxylamine forms oximes and 2,4dinitrophenylhydrazine readily forms 2,4dinitrophenylhydrazones ...
... Addition of amines with an atom containing a lone pair of electrons on the adjacent atom occurs very readily, giving useful, stable imines For example, hydroxylamine forms oximes and 2,4dinitrophenylhydrazine readily forms 2,4dinitrophenylhydrazones ...
lecture 3 - aldehydes and ketones
... Dipole/Dipole Interactions The electronegativity number (E.N.) of carbon is 2.5. The E.N. of oxygen is 3.5. As a result of unequal sharing, the carbonyl bond is polar covalent and the oxygen acquires a partial negative charge. Dipole/dipole interactions aren’t as strong as hydrogen bonds, but they ...
... Dipole/Dipole Interactions The electronegativity number (E.N.) of carbon is 2.5. The E.N. of oxygen is 3.5. As a result of unequal sharing, the carbonyl bond is polar covalent and the oxygen acquires a partial negative charge. Dipole/dipole interactions aren’t as strong as hydrogen bonds, but they ...
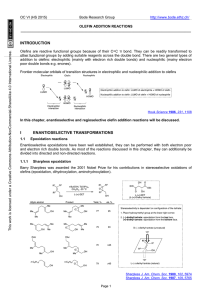
Lecture 1: Key Concepts in Stereoselective Synthesis
... OLEFIN ADDITION REACTIONS ______________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... OLEFIN ADDITION REACTIONS ______________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.