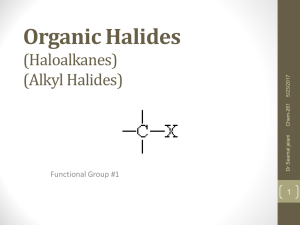The Grignard Reagent
... • It is very important that the reaction apparatus, reagents, and solvents must all be kept dry. You will be using glassware from your organic lab kits for this experiment. It is a good idea to dry your glassware in the oven before starting the reaction. Also make sure to keep the reagent bottles ca ...
... • It is very important that the reaction apparatus, reagents, and solvents must all be kept dry. You will be using glassware from your organic lab kits for this experiment. It is a good idea to dry your glassware in the oven before starting the reaction. Also make sure to keep the reagent bottles ca ...
Ground State and Bonding State Electronic Configurations
... Molecular Orbital Theory of Bonding Like valence-bond (VB) theory, molecular orbital (MO) theory recognizes that electrons cannot be localized on a single atom when that atom is part of a molecule. One major difference between the two methods is that MO theory calculates the molecular orbitals that ...
... Molecular Orbital Theory of Bonding Like valence-bond (VB) theory, molecular orbital (MO) theory recognizes that electrons cannot be localized on a single atom when that atom is part of a molecule. One major difference between the two methods is that MO theory calculates the molecular orbitals that ...
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
... produce alcohols. • The reducing agent of choice is LiAlH4 - lithium aluminium hydride • Able to transfer a hydride ion to the partially positive carbon atom of the carbonyl group • Musty be carried out in anhydrous conditions (in ...
... produce alcohols. • The reducing agent of choice is LiAlH4 - lithium aluminium hydride • Able to transfer a hydride ion to the partially positive carbon atom of the carbonyl group • Musty be carried out in anhydrous conditions (in ...
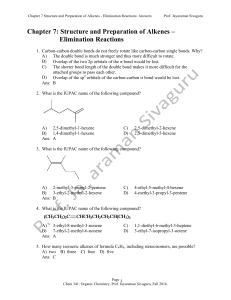
Ch 7 - Practice problem (Answers)
... Chapter 7 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes - Elimination Reactions: Answers ...
... Chapter 7 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes - Elimination Reactions: Answers ...
Organic Chemistry - Napa Valley College
... compounds are made out of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen with the occasional addition of nitrogen, chlorine, bromine, phosphorus and sulfur. Even though organic compounds only use eight of the more than one hundred elements found on the Periodic Table, the multitude of compounds made and the manner in ...
... compounds are made out of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen with the occasional addition of nitrogen, chlorine, bromine, phosphorus and sulfur. Even though organic compounds only use eight of the more than one hundred elements found on the Periodic Table, the multitude of compounds made and the manner in ...
Compounds Containing A Single Bond To A
... 15 mL causes blindness, and 100 mL causes death. 2-Propanol [(CH3)2CHOH] is the major component of rubbing alcohol. When rubbed on the skin it evaporates readily, producing a pleasant cooling sensation. Because it has weak antibacterial properties, 2-propanol is used to clean skin before minor sur ...
... 15 mL causes blindness, and 100 mL causes death. 2-Propanol [(CH3)2CHOH] is the major component of rubbing alcohol. When rubbed on the skin it evaporates readily, producing a pleasant cooling sensation. Because it has weak antibacterial properties, 2-propanol is used to clean skin before minor sur ...
Formal Charge
... the formal charge, if any, borne by the atom. Bonds to atoms with equal electronegativity (i.e., bonds to another atom of the same element) need not be considered. Only F is more electronegative than O so NO is always –2 unless an F-O bond is present. In commonly encountered organic compounds, only ...
... the formal charge, if any, borne by the atom. Bonds to atoms with equal electronegativity (i.e., bonds to another atom of the same element) need not be considered. Only F is more electronegative than O so NO is always –2 unless an F-O bond is present. In commonly encountered organic compounds, only ...
You Light Up My Life
... Peptide bond ◦ Type of covalent bond ◦ Links amino group of one amino acid with carboxyl group of next ◦ Forms through condensation reaction ...
... Peptide bond ◦ Type of covalent bond ◦ Links amino group of one amino acid with carboxyl group of next ◦ Forms through condensation reaction ...
Camp 1
... Molecule? • Cyclization of sugars takes place due to interaction between functional groups on distant carbons, C1 to C5, to make a cyclic hemiacetal ...
... Molecule? • Cyclization of sugars takes place due to interaction between functional groups on distant carbons, C1 to C5, to make a cyclic hemiacetal ...
Completed Notes for Organic Chemistry
... relative to one another differ. • One type of stereoisomerism is know as geometric isomerism. Geometric Isomerism in Alkenes • The most common structural feature which gives rise to geometric isomers in carbon compounds is the carbon/carbon double bond. • For the molecule 1,2 - dichloroethene, CRCH= ...
... relative to one another differ. • One type of stereoisomerism is know as geometric isomerism. Geometric Isomerism in Alkenes • The most common structural feature which gives rise to geometric isomers in carbon compounds is the carbon/carbon double bond. • For the molecule 1,2 - dichloroethene, CRCH= ...
Organic Chemistry : Ch. 19
... Hydrocarbons with only single bonds are termed “saturated” hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons with a double or triple bond are called “unsaturated” hydrocarbons. ...
... Hydrocarbons with only single bonds are termed “saturated” hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons with a double or triple bond are called “unsaturated” hydrocarbons. ...
chemistry 1000
... Halogens are not considered “principal functional groups” so halogens are treated in the same way as carbon chains branching off the main chain. They are described in the “substituents” section at the beginning of the name. Substituents take last priority when numbering the main chain, so substituti ...
... Halogens are not considered “principal functional groups” so halogens are treated in the same way as carbon chains branching off the main chain. They are described in the “substituents” section at the beginning of the name. Substituents take last priority when numbering the main chain, so substituti ...
Dehydrating Cyclohexanol
... The results of the Br2 test was that the unknown product changed color which meant that the cyclohexene was truly formed. The results of the (NH4)2Ce(NO3)6 was that the unknown product did turned a little bit red which means there was still some cyclohexanol remained in the product after distillatio ...
... The results of the Br2 test was that the unknown product changed color which meant that the cyclohexene was truly formed. The results of the (NH4)2Ce(NO3)6 was that the unknown product did turned a little bit red which means there was still some cyclohexanol remained in the product after distillatio ...
Variant 1 - Egypt IG Student Room
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
Lesson 3 Mechanisms of Organic Reactions
... general formula R-X, where X is an electron-withdrawing group. Nucleophiles are often, though not always, negatively charged. The most widely known nucleophiles are a hydroxide ion, alkoxide ions (RO-), thiolate ions (RS-), halide ions, a hydride ion (H-), carbanions (particles with negatively charg ...
... general formula R-X, where X is an electron-withdrawing group. Nucleophiles are often, though not always, negatively charged. The most widely known nucleophiles are a hydroxide ion, alkoxide ions (RO-), thiolate ions (RS-), halide ions, a hydride ion (H-), carbanions (particles with negatively charg ...
PowerPoint **
... α-Elimination: Generation of Carbene Defination: A carbene is a divalent carbon species link to two adjacent groups by covalent bonds, possessing two nonbonded electrons and six valence electrons. Preparation of carbenes a. ...
... α-Elimination: Generation of Carbene Defination: A carbene is a divalent carbon species link to two adjacent groups by covalent bonds, possessing two nonbonded electrons and six valence electrons. Preparation of carbenes a. ...
Organic Halides (Haloalkanes) (Alkyl Halides)
... • PCB’s (polychlorinated biphenyls) – electrical transformers ...
... • PCB’s (polychlorinated biphenyls) – electrical transformers ...
Chapter 18 Reactions of aromatics
... carbocations are too hard to form) • Will not work with rings containing an amino group substituent or a strongly electron-withdrawing group ...
... carbocations are too hard to form) • Will not work with rings containing an amino group substituent or a strongly electron-withdrawing group ...
Carbon Bond - Rutgers Chemistry
... industrial and synthetic organic chemical processes. Our initial finding of C-H oxidative addition reactions in low-valent iridium (I) complexes was followed by a more recent discovery and exploration of C-H activation processes at Ir (III) centers. This paper reviews recent studies of the Ir (III) ...
... industrial and synthetic organic chemical processes. Our initial finding of C-H oxidative addition reactions in low-valent iridium (I) complexes was followed by a more recent discovery and exploration of C-H activation processes at Ir (III) centers. This paper reviews recent studies of the Ir (III) ...
04 DetailLectOut 2012
... The Swedish chemist Jons Jacob Berzelius was the first to make a distinction between organic compounds that seemed to arise in only living organisms and inorganic compounds that were found in the nonliving world. ...
... The Swedish chemist Jons Jacob Berzelius was the first to make a distinction between organic compounds that seemed to arise in only living organisms and inorganic compounds that were found in the nonliving world. ...
chapter 4 carbon and the molecular diversity of life
... skeleton but also on the chemical groups attached to that skeleton. If we start with hydrocarbons as the simplest organic molecules, characteristic chemical groups can replace one or more of the hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon skeleton of a hydrocarbon. These chemical groups may be involved in c ...
... skeleton but also on the chemical groups attached to that skeleton. If we start with hydrocarbons as the simplest organic molecules, characteristic chemical groups can replace one or more of the hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon skeleton of a hydrocarbon. These chemical groups may be involved in c ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... primary (1˚) amine (15.1) an amine with the general formula RNH2. quaternary ammonium salt (15.1) an amine salt with the general formula R4N+ A– (in which R– can be an alkyl or aryl group or a hydrogen atom and A– can be any anion. secondary (2˚) amine (15.1) an amine with the general formula R2-NH. ...
... primary (1˚) amine (15.1) an amine with the general formula RNH2. quaternary ammonium salt (15.1) an amine salt with the general formula R4N+ A– (in which R– can be an alkyl or aryl group or a hydrogen atom and A– can be any anion. secondary (2˚) amine (15.1) an amine with the general formula R2-NH. ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.