Alkane Alkyl groups are represented by the R
... cis-alkene cis-Alkenes are 1,2-disubstituted functions with the two R, X or other groups on the same side of the C=C function. Due to the non-rotation of the C=C bond, cis and trans isomers occur. ...
... cis-alkene cis-Alkenes are 1,2-disubstituted functions with the two R, X or other groups on the same side of the C=C function. Due to the non-rotation of the C=C bond, cis and trans isomers occur. ...
A2 Chemistry
... Lonsdale found that all of the carbon bonds were the same length 0.139nm. (between the lengths of CC and C=C). ...
... Lonsdale found that all of the carbon bonds were the same length 0.139nm. (between the lengths of CC and C=C). ...
Discussion Worksheet #10 Formation of Alcohols Skill 1: Functional
... There are ways to control regiochemistry and stereochemistry with alcohol formation ...
... There are ways to control regiochemistry and stereochemistry with alcohol formation ...
review sheet
... Which carboxylic acid is most acidic? (Which one forms the most stable anion?) Why? Which of the carboxylic acid derivatives (acid chloride, acid anhydride, ester, amide) is the most stable? Which is the most reactive? Why are acid chlorides highly reactive? What is the mechanism for nucleophilic ac ...
... Which carboxylic acid is most acidic? (Which one forms the most stable anion?) Why? Which of the carboxylic acid derivatives (acid chloride, acid anhydride, ester, amide) is the most stable? Which is the most reactive? Why are acid chlorides highly reactive? What is the mechanism for nucleophilic ac ...
LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-18
... neutral (in terms of acids and bases) even though they can act as very weak acids or bases as water does. They undergo several kinds of chemical reactions, the most important of which is oxidation. Oxidation in organic chemistry is defined as the elimination of hydrogen from or the addition of oxyge ...
... neutral (in terms of acids and bases) even though they can act as very weak acids or bases as water does. They undergo several kinds of chemical reactions, the most important of which is oxidation. Oxidation in organic chemistry is defined as the elimination of hydrogen from or the addition of oxyge ...
Organic Chemistry Assignments Topic 1: Review
... Organic Chemistry Assignments Chapter 2: Week 4 (9/12 -16) Work Due by: Thursday, September 15 Learning Goal: To be able to write the mechanisms for the reactions of alkenes and be able to predict the products of alkene reactions. Topic ...
... Organic Chemistry Assignments Chapter 2: Week 4 (9/12 -16) Work Due by: Thursday, September 15 Learning Goal: To be able to write the mechanisms for the reactions of alkenes and be able to predict the products of alkene reactions. Topic ...
Chapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones
... IUPAC names for aldehydes: • The longest chain must have an aldehyde group (COH) • No need to use a number to indicate the aldehyde group • To name an aldehyde, change the suffix -e of the parent alkane to -al. • For unsaturated aldehydes, indicate the presence of a carbon-carbon double bond by chan ...
... IUPAC names for aldehydes: • The longest chain must have an aldehyde group (COH) • No need to use a number to indicate the aldehyde group • To name an aldehyde, change the suffix -e of the parent alkane to -al. • For unsaturated aldehydes, indicate the presence of a carbon-carbon double bond by chan ...
Secondary alcohols
... Haloalkanes can be made from alcohols through inorganic esters. As an alternative to the acid-catalyzed conversions of alcohols into haloalkanes, a number of inorganic reagents can convert the alcoholic hydroxyl group into a good leaving group under milder conditions. Reaction of PBr3 with a second ...
... Haloalkanes can be made from alcohols through inorganic esters. As an alternative to the acid-catalyzed conversions of alcohols into haloalkanes, a number of inorganic reagents can convert the alcoholic hydroxyl group into a good leaving group under milder conditions. Reaction of PBr3 with a second ...
Haloalkanes
... The Environmental problems associated with CFC Because of the lack of reactivity and insolubility in water, there is no natural process for removing CFC. In fact they drift up into the stratosphere (the upper atmosphere), where they receive sufficient ultraviolet Light to cause photolysis. The chlor ...
... The Environmental problems associated with CFC Because of the lack of reactivity and insolubility in water, there is no natural process for removing CFC. In fact they drift up into the stratosphere (the upper atmosphere), where they receive sufficient ultraviolet Light to cause photolysis. The chlor ...
Bk3BP08EE
... The reaction between ethane and chlorine proceeds by a free radical chain mechanism. The chlorine radical formed attacks an ethane molecule, forming CH3CH2• radical which attacks a chlorine molecule to form chloroethane. The chloroethane formed may be attacked by another chlorine radical to form CH3 ...
... The reaction between ethane and chlorine proceeds by a free radical chain mechanism. The chlorine radical formed attacks an ethane molecule, forming CH3CH2• radical which attacks a chlorine molecule to form chloroethane. The chloroethane formed may be attacked by another chlorine radical to form CH3 ...
Single Replacement Reactions - Tri
... isn't enough oxygen to allow the fuel (usually a hydrocarbon) to react completely. • Carbon monoxide and pure carbon will be produced in addition to carbon dioxide and water in incomplete combustion. ...
... isn't enough oxygen to allow the fuel (usually a hydrocarbon) to react completely. • Carbon monoxide and pure carbon will be produced in addition to carbon dioxide and water in incomplete combustion. ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... Hyperconjugation makes substituted alkenes more stable by stabilizing p-orbitals cis alkenes are less stable than trans alkenes because of steric crowding cis cycloalkenes are more stable than trans for the small rings ...
... Hyperconjugation makes substituted alkenes more stable by stabilizing p-orbitals cis alkenes are less stable than trans alkenes because of steric crowding cis cycloalkenes are more stable than trans for the small rings ...
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds: Oxidation
... The starting material may be a ketone or an ester There are two routes that start with ketones (one is shown) ...
... The starting material may be a ketone or an ester There are two routes that start with ketones (one is shown) ...
Chapter 1-
... The starting material may be a ketone or an ester There are two routes that start with ketones (one is shown) ...
... The starting material may be a ketone or an ester There are two routes that start with ketones (one is shown) ...
alcohols - A-Level Chemistry
... Give the names and structures of all eight alcohols with the formula C5H12O. State in each case whether they are primary, secondary or tertiary alcohols. Identify the three isomers which can give two different alkenes when dehydrated and identify the possible alkene products in each case. Identify t ...
... Give the names and structures of all eight alcohols with the formula C5H12O. State in each case whether they are primary, secondary or tertiary alcohols. Identify the three isomers which can give two different alkenes when dehydrated and identify the possible alkene products in each case. Identify t ...
Chapter 4 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Lecture Outline
... There are six functional groups that are most important to the chemistry of life: hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, sulfhydryl, and phosphate groups. ...
... There are six functional groups that are most important to the chemistry of life: hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, sulfhydryl, and phosphate groups. ...
Chapter 4 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Lecture Outline
... There are six functional groups that are most important to the chemistry of life: hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, sulfhydryl, and phosphate groups. ...
... There are six functional groups that are most important to the chemistry of life: hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, sulfhydryl, and phosphate groups. ...
Chapter 4 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Lecture Outline
... There are six functional groups that are most important to the chemistry of life: hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, sulfhydryl, and phosphate groups. ...
... There are six functional groups that are most important to the chemistry of life: hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, sulfhydryl, and phosphate groups. ...
HYDROCARBONS HYDROCARBONS Types of Hydrocarbons
... 8. Certain common nomenclatures are used in the IUPAC system CH3CH2CH2CH2CHCH2CH2CH3 ...
... 8. Certain common nomenclatures are used in the IUPAC system CH3CH2CH2CH2CHCH2CH2CH3 ...
Name (Last, First):
... There are two structural isomers possible, one of which also shows cis-trans isomerism across the double bond. Give their structural formulas below ...
... There are two structural isomers possible, one of which also shows cis-trans isomerism across the double bond. Give their structural formulas below ...
Chem 400 Review Chem 350 JJ.S17
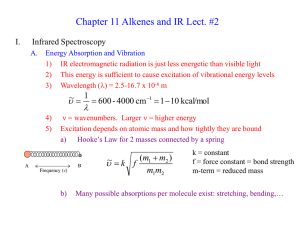
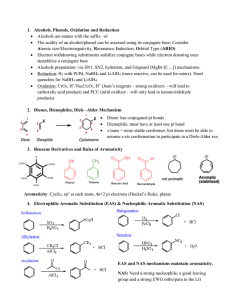
... Electron withdrawing substituents stabilize conjugate bases while electron donating ones destabilize a conjugate base Alcohols preparation: via SN1, SN2, hydration, and Grignard (MgBr-[C…]) mechanisms Reduction: H2 with Pt/Pd, NaBH4 and LiAlH4 (more reactive, can be used for esters). Need quen ...
... Electron withdrawing substituents stabilize conjugate bases while electron donating ones destabilize a conjugate base Alcohols preparation: via SN1, SN2, hydration, and Grignard (MgBr-[C…]) mechanisms Reduction: H2 with Pt/Pd, NaBH4 and LiAlH4 (more reactive, can be used for esters). Need quen ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.