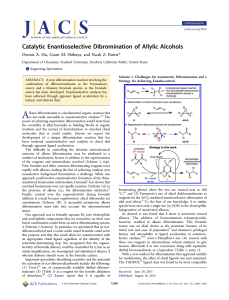
Hydroxyl-Directed Stereoselective Diboration of Alkenes
... occur selectively with monosubstituted, trans-1,2-disubstituted, and trisubstituted alkenes, the minimally biased prochiral πfaces of cis-1,2-disubstituted and 1,1-disubstituted alkenes render selective reactions of these substrate classes much more difficult to engineer. As one strategy to address th ...
... occur selectively with monosubstituted, trans-1,2-disubstituted, and trisubstituted alkenes, the minimally biased prochiral πfaces of cis-1,2-disubstituted and 1,1-disubstituted alkenes render selective reactions of these substrate classes much more difficult to engineer. As one strategy to address th ...
PREPARATION OF ORGANOLITHIUM COMPOUNDS - GCG-42
... COMPOUNDS The organometallic compounds can be prepared by following methods:By Halogen Metal Exchange From Terminal Alkynes By Trans Metalation/ Metal-Metal Exchange By Directed Metalation/ Ortho Metalation ...
... COMPOUNDS The organometallic compounds can be prepared by following methods:By Halogen Metal Exchange From Terminal Alkynes By Trans Metalation/ Metal-Metal Exchange By Directed Metalation/ Ortho Metalation ...
Cellulose und heterogene Katalyse – Eine
... on lignocellulose require liquid-phase processes in polar solvents at rather low temperatures. One of the major challenges concerning catalyst and process development is the fact, that cellulose is hardly soluble in any conventional solvent. Ionic liquids, especially based on alkyl imidazolium, diss ...
... on lignocellulose require liquid-phase processes in polar solvents at rather low temperatures. One of the major challenges concerning catalyst and process development is the fact, that cellulose is hardly soluble in any conventional solvent. Ionic liquids, especially based on alkyl imidazolium, diss ...
CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS
... combining atoms, a triple bond is formed. In a triple bond each element shares three electrons. A triple bond is denoted by triple dash ( ≡ ) e.g. N 2 , C 2 H 2 . Formation of N2 molecule Nitrogen has the atomic number 7. It has five electrons in its outermost shell. In order to attain an octet each ...
... combining atoms, a triple bond is formed. In a triple bond each element shares three electrons. A triple bond is denoted by triple dash ( ≡ ) e.g. N 2 , C 2 H 2 . Formation of N2 molecule Nitrogen has the atomic number 7. It has five electrons in its outermost shell. In order to attain an octet each ...
Reactions of Carbonyl compounds
... 2,4-DINITROPHENYLHYDRAZINE C6H3(NO2)2NHNH2 The following structural isomers have similar boiling points because of similar van der Waals forces and dipole-dipole interactions. They would be impossible to identify with any precision using boiling point determination. ...
... 2,4-DINITROPHENYLHYDRAZINE C6H3(NO2)2NHNH2 The following structural isomers have similar boiling points because of similar van der Waals forces and dipole-dipole interactions. They would be impossible to identify with any precision using boiling point determination. ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nitriles
... with an alkyl halide. This reaction is of very limited scope (it only works with primary alkyl halides, but it does work particularly well with allylic and benzylic compounds), but it has some real synthetic potential, as will be discussed later. O O O ...
... with an alkyl halide. This reaction is of very limited scope (it only works with primary alkyl halides, but it does work particularly well with allylic and benzylic compounds), but it has some real synthetic potential, as will be discussed later. O O O ...
Carboxylic acids Acyl chlorides Amides Esters
... Using this way, you will clearly see the effect on the shape of the molecule. ...
... Using this way, you will clearly see the effect on the shape of the molecule. ...
Group 13 and 14 Group 14: Carbon
... • extremely hard, inert materials, v. high melting • Industrial uses, particularly SiC – Made by high temperature reduction of Si or B oxides in the presence of graphite ...
... • extremely hard, inert materials, v. high melting • Industrial uses, particularly SiC – Made by high temperature reduction of Si or B oxides in the presence of graphite ...
Unit 7 Carbohydrates
... monosaccharide units, which may be either in straight or branched chains (e.g., cellulose, glycogen, starch). ...
... monosaccharide units, which may be either in straight or branched chains (e.g., cellulose, glycogen, starch). ...
CHM102 - National Open University of Nigeria
... Sp3 hybrid orbital has two lobes of unequal size separated from each other by a node. This situation is similar to a p orbital but with the difference that here one lobe is very small and the other is very large. In other words, in sp3 hybrid orbitals, the electron density is concentrated in one dir ...
... Sp3 hybrid orbital has two lobes of unequal size separated from each other by a node. This situation is similar to a p orbital but with the difference that here one lobe is very small and the other is very large. In other words, in sp3 hybrid orbitals, the electron density is concentrated in one dir ...
1 SECONDARY SCHOOL IMPROVEMENT PROGRAMME (SSIP
... Condensed structural formula – This notation shows the way in which atoms are bonded together in the molecule but it does not show all the bonds e.g. CH 3CH2CH2 CH2CH3 Hydrocarbon – organic compounds that consist of only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Homologous series – a series of organic compounds th ...
... Condensed structural formula – This notation shows the way in which atoms are bonded together in the molecule but it does not show all the bonds e.g. CH 3CH2CH2 CH2CH3 Hydrocarbon – organic compounds that consist of only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Homologous series – a series of organic compounds th ...
Final Review 2006
... ____ 76. What principle states that atoms tend to form compounds so that each atom can have eight electrons in its outermost energy level? a. rule of eights c. configuration rule b. Avogadro principle d. octet rule ____ 77. Multiple covalent bonds may occur in atoms that contain carbon, nitrogen, or ...
... ____ 76. What principle states that atoms tend to form compounds so that each atom can have eight electrons in its outermost energy level? a. rule of eights c. configuration rule b. Avogadro principle d. octet rule ____ 77. Multiple covalent bonds may occur in atoms that contain carbon, nitrogen, or ...
Alcohols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones
... –OH and an –OR bound to the same carbon. NOTE: An oxygen in a ring structure is considered part of an –OR group. ...
... –OH and an –OR bound to the same carbon. NOTE: An oxygen in a ring structure is considered part of an –OR group. ...
Unit 19 Chemistry Honors
... Chemistry Honors Special Topics*: Organic Unit 18, Chapter 20 Mrs. Frost 2012 www.hinsdale86.org/staff/kfrost Objectives: 1. Name and write formulas for organic compounds such as alkanes, alkenes, alkynes and molecules containing basic organic functional groups. 2. Draw organic structures. 3. Draw a ...
... Chemistry Honors Special Topics*: Organic Unit 18, Chapter 20 Mrs. Frost 2012 www.hinsdale86.org/staff/kfrost Objectives: 1. Name and write formulas for organic compounds such as alkanes, alkenes, alkynes and molecules containing basic organic functional groups. 2. Draw organic structures. 3. Draw a ...
chemistry 30 / unit c chemical changes of organic compounds
... K.2 Identify and describe significant organic compounds in daily life: demonstrating generalized knowledge of their origins and applications(eg. methane,methanol,ethane,ethanol,ethanioic acid,propane,benzene,octane glucose, polyethylene . K.3 Name and draw structural, condensed structural and line d ...
... K.2 Identify and describe significant organic compounds in daily life: demonstrating generalized knowledge of their origins and applications(eg. methane,methanol,ethane,ethanol,ethanioic acid,propane,benzene,octane glucose, polyethylene . K.3 Name and draw structural, condensed structural and line d ...
File
... Organic Chemistry Classifying Organic Compounds (Read pages 4 and 51) Define the following terms: organic chemistry aromatic hydrocarbon functional group dipole-dipole force ether aldehyde amide ...
... Organic Chemistry Classifying Organic Compounds (Read pages 4 and 51) Define the following terms: organic chemistry aromatic hydrocarbon functional group dipole-dipole force ether aldehyde amide ...
Chpt. 22: Some Families of Organic Compounds
... • Ethanol (made by fermentation of sugar cane) mixed with petroleum products – used as a motor fuel instead of petrol. • Ethanol is a very good solvent ( solubility properties). It is widely used as a solvent for perfumes, aftershaves, ...
... • Ethanol (made by fermentation of sugar cane) mixed with petroleum products – used as a motor fuel instead of petrol. • Ethanol is a very good solvent ( solubility properties). It is widely used as a solvent for perfumes, aftershaves, ...
Amine-functionalized boehmite nanoparticle-supported
... this image, needle‐shaped BNPs were seen with a length of over 50 nm and a width of up to 10 nm. According to the BET analysis, the efficient surface area for BNPs was 326 m2 g−1. BNPs themselves have promising catalytic properties for multi‐component synthesis of highly substitut ...
... this image, needle‐shaped BNPs were seen with a length of over 50 nm and a width of up to 10 nm. According to the BET analysis, the efficient surface area for BNPs was 326 m2 g−1. BNPs themselves have promising catalytic properties for multi‐component synthesis of highly substitut ...
Ch03_ Lecture
... consisting of C-C and C-H bonds to which functional groups are attached. • Structural features of a functional group include: • Heteroatoms—atoms other than carbon or hydrogen. • Bonds most commonly occur in C-C and C-O double bonds. ...
... consisting of C-C and C-H bonds to which functional groups are attached. • Structural features of a functional group include: • Heteroatoms—atoms other than carbon or hydrogen. • Bonds most commonly occur in C-C and C-O double bonds. ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... Nucleophilic Addition of Phosphorus Ylides: Using carbon Nucleophiles 3) The Wittig Reaction The Wittig reactions is an important method for the formation of alkanes The double bond forms specially at the location of the original aldehyde or ketone Ylides are naturel molecules but have +ve a ...
... Nucleophilic Addition of Phosphorus Ylides: Using carbon Nucleophiles 3) The Wittig Reaction The Wittig reactions is an important method for the formation of alkanes The double bond forms specially at the location of the original aldehyde or ketone Ylides are naturel molecules but have +ve a ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.