CARBONYL COMPOUNDS ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
... The most common oxidation reaction of carbonyl compounds is the oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids. A variety of oxidizing agents can be used, including CrO3, Na2Cr2O7, K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4. Aldehydes are also oxidized selectively in the presence of other functional groups using silver(I) oxide ...
... The most common oxidation reaction of carbonyl compounds is the oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids. A variety of oxidizing agents can be used, including CrO3, Na2Cr2O7, K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4. Aldehydes are also oxidized selectively in the presence of other functional groups using silver(I) oxide ...
CaCl2.2H2O assisted oxidation of alcohols with (NH4)2Cr2O7
... dichromate in the presence of CaCl2.2H2O (Table I, Scheme I). The reaction is simply performed by stirring a mixture of alcohol, (NH4)2Cr2O7 and CaCl2.2H2O in an oil-bath (60°C) for the appropriate time (Table I). Alcohols were oxidized efficiently and the corresponding carbonyl compounds were isola ...
... dichromate in the presence of CaCl2.2H2O (Table I, Scheme I). The reaction is simply performed by stirring a mixture of alcohol, (NH4)2Cr2O7 and CaCl2.2H2O in an oil-bath (60°C) for the appropriate time (Table I). Alcohols were oxidized efficiently and the corresponding carbonyl compounds were isola ...
Esterification Worksheet
... • Describe the esterification of alcohols with carboxylic acids. • Produce a sample of a pure Phenyl Benzoate ester using a range of advanced chemical techniques. • Explain the process of re-crystallisation. Numeracy starter: Resolution of measuring Cylinder A= ________ ...
... • Describe the esterification of alcohols with carboxylic acids. • Produce a sample of a pure Phenyl Benzoate ester using a range of advanced chemical techniques. • Explain the process of re-crystallisation. Numeracy starter: Resolution of measuring Cylinder A= ________ ...
quiz 2 -- chemistry
... __ 17. Nitrogen gas, which makes up about 79% of the air you breathe, is composed of two molecules of nitrogen (atomic number 7) joined together in what type of bond? a. hydrogen c. ionic e. hydrophobic b. triple covalent d. double covalent f. single covalent __ 18. Which of the following best depic ...
... __ 17. Nitrogen gas, which makes up about 79% of the air you breathe, is composed of two molecules of nitrogen (atomic number 7) joined together in what type of bond? a. hydrogen c. ionic e. hydrophobic b. triple covalent d. double covalent f. single covalent __ 18. Which of the following best depic ...
Kazzie`s Guide to Orgo 2
... like…look it up, it is good to get used to using anything they might throw at you. Draw the amino acid Gly at physiologic pH (~6.5), what is this form of a molecule called? ...
... like…look it up, it is good to get used to using anything they might throw at you. Draw the amino acid Gly at physiologic pH (~6.5), what is this form of a molecule called? ...
Suggested Problems for Chapter 1
... 7. (12 pts.) An unknown compound A (molecular formula C7H14O) was treated with NaBH4 in CH3OH to form compound B (molecular formula C7H16O). Compound A has a strong absorption in its IR spectrum at 1716 cm-1. Compound B has strong absorption in its IR spectrum at 3200-3600 cm-1. The 1H NMR spectra ...
... 7. (12 pts.) An unknown compound A (molecular formula C7H14O) was treated with NaBH4 in CH3OH to form compound B (molecular formula C7H16O). Compound A has a strong absorption in its IR spectrum at 1716 cm-1. Compound B has strong absorption in its IR spectrum at 3200-3600 cm-1. The 1H NMR spectra ...
Principles of Organic and Biochemistry
... They are very large molecules They are made of specialized molecules called amino acids ...
... They are very large molecules They are made of specialized molecules called amino acids ...
infrared spectroscopy (ir) - Dr rer. nat. Rubin Gulaboski
... Carbonyl compounds are those that contain the C=O functional group. In aldehydes, this group is at the end of a carbon chain, whereas in ketones it’s in the middle of the chain. As a result, the carbon in the C=O bond of aldehydes is also bonded to another carbon and a hydrogen, whereas the same car ...
... Carbonyl compounds are those that contain the C=O functional group. In aldehydes, this group is at the end of a carbon chain, whereas in ketones it’s in the middle of the chain. As a result, the carbon in the C=O bond of aldehydes is also bonded to another carbon and a hydrogen, whereas the same car ...
INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY (IR)
... Carbonyl compounds are those that contain the C=O functional group. In aldehydes, this group is at the end of a carbon chain, whereas in ketones it’s in the middle of the chain. As a result, the carbon in the C=O bond of aldehydes is also bonded to another carbon and a hydrogen, whereas the same car ...
... Carbonyl compounds are those that contain the C=O functional group. In aldehydes, this group is at the end of a carbon chain, whereas in ketones it’s in the middle of the chain. As a result, the carbon in the C=O bond of aldehydes is also bonded to another carbon and a hydrogen, whereas the same car ...
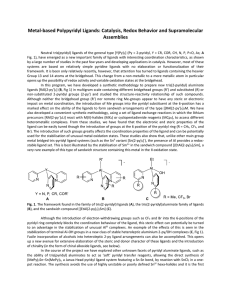
final1-final_report
... Neutral tris(pyridyl) ligands of the general type [Y(Py) 3] (Py = 2-pyridyl, Y = CR, COR, CH, N, P, P=O, As; A Fig. 1), have emerged as a new important family of ligands with interesting coordination characteristics, as shown by a large number of studies in the past few years and developing applicat ...
... Neutral tris(pyridyl) ligands of the general type [Y(Py) 3] (Py = 2-pyridyl, Y = CR, COR, CH, N, P, P=O, As; A Fig. 1), have emerged as a new important family of ligands with interesting coordination characteristics, as shown by a large number of studies in the past few years and developing applicat ...
Chapter 16. Biological Reagents
... any organic reactions that use the carbon dioxide lost from acetoacetic acid (or malonic acid) use in a coupled synthetic step? 16.5 Show the analogous mechanism between decarboxylation of a β-ketoacid and the thiamin decarboxylation of pyruvate. 16.6 Another biological reagent is vitamin B6 which d ...
... any organic reactions that use the carbon dioxide lost from acetoacetic acid (or malonic acid) use in a coupled synthetic step? 16.5 Show the analogous mechanism between decarboxylation of a β-ketoacid and the thiamin decarboxylation of pyruvate. 16.6 Another biological reagent is vitamin B6 which d ...
Introduction to Organic Synthesis 2011
... Some organometallic compounds such as organocobalts and organomercury compounds have very weak carbon-metal bonds that undergo homolysis very easily to give carbon cantered radicals: ...
... Some organometallic compounds such as organocobalts and organomercury compounds have very weak carbon-metal bonds that undergo homolysis very easily to give carbon cantered radicals: ...
Synthesis of Aliphatic Nitro Compounds1i2 A simple new
... 35'/3 mm.; n'," 1.4088)were isolated. I n addition, there was obtained 43.4 g. of material boiling in between the nitrite ester and the nitro compound (36"/3 mm. to 58"/2 mm.); n y 1.4117-1.4781. Since 40.6 g. out of the 43.4 g. had ng above 1.4721 i t is clear that this material is largely unreacte ...
... 35'/3 mm.; n'," 1.4088)were isolated. I n addition, there was obtained 43.4 g. of material boiling in between the nitrite ester and the nitro compound (36"/3 mm. to 58"/2 mm.); n y 1.4117-1.4781. Since 40.6 g. out of the 43.4 g. had ng above 1.4721 i t is clear that this material is largely unreacte ...
ORGANIC NOMENCLATURE
... configuration (zusammen, German for together) and if they are on opposite sides the configuration is E (entgegen, German for opposite). A was once called cis and B trans and this form of nomenclature is still used occasionally for simple compounds. C is a different structural isomer; A and B are the ...
... configuration (zusammen, German for together) and if they are on opposite sides the configuration is E (entgegen, German for opposite). A was once called cis and B trans and this form of nomenclature is still used occasionally for simple compounds. C is a different structural isomer; A and B are the ...
CHEM 202_ Part 2
... Carbonyl group is stabilized by adjacent alkyl groups (e-donor), so ketone is more stable than aldehyde. Steric effect also play a role in the relative reactivities of aldehydes and ketones. ...
... Carbonyl group is stabilized by adjacent alkyl groups (e-donor), so ketone is more stable than aldehyde. Steric effect also play a role in the relative reactivities of aldehydes and ketones. ...
polar covalent bonds.
... sp2 Hybrids create trigonal structures. Hybridization of a 2s and two 2p orbitals results in three new hybrid orbitals that point to the corners of an equilateral triangle. The remaining p orbital points up and down, perpendicular to each of the three hybrid orbitals. Bond angles in molecules using ...
... sp2 Hybrids create trigonal structures. Hybridization of a 2s and two 2p orbitals results in three new hybrid orbitals that point to the corners of an equilateral triangle. The remaining p orbital points up and down, perpendicular to each of the three hybrid orbitals. Bond angles in molecules using ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... NAMING ALDEHYDES • ALDEHYDES ARE NAMED BY REPLACING THE FINAL “E” OF THE NAME OF THE ALKANE WITH THE SAME NUMBER OF CARBONS TO “AL”. • BECAUSE IN ALDEHYDES THE CARBONYL GROUP IS ALWAYS ATTACHED TO THE FIRST CARBON, THERE IS NO NEED TO PLACE A 1 IN FRONT OF THE NAME. • IF THERE ARE SUBSTITUENTS PRES ...
... NAMING ALDEHYDES • ALDEHYDES ARE NAMED BY REPLACING THE FINAL “E” OF THE NAME OF THE ALKANE WITH THE SAME NUMBER OF CARBONS TO “AL”. • BECAUSE IN ALDEHYDES THE CARBONYL GROUP IS ALWAYS ATTACHED TO THE FIRST CARBON, THERE IS NO NEED TO PLACE A 1 IN FRONT OF THE NAME. • IF THERE ARE SUBSTITUENTS PRES ...
04_Lecture_Presentation
... Concept 4.1: Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds • Organic chemistry is the study of compounds that contain carbon • Organic compounds range from simple molecules to colossal ones • Most organic compounds contain hydrogen atoms in addition to carbon atoms ...
... Concept 4.1: Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds • Organic chemistry is the study of compounds that contain carbon • Organic compounds range from simple molecules to colossal ones • Most organic compounds contain hydrogen atoms in addition to carbon atoms ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.