Sample Exam #2 Answer Key
... bonding properties while thiols are incapable of hydrogen bonding. Consequently, alcohols have comparatively higher melting points, boiling points and densities than thiols. Finally, alcohols are much more water soluble than thiols due to their greater polarity and hydrogen bonding. 2) Compare the m ...
... bonding properties while thiols are incapable of hydrogen bonding. Consequently, alcohols have comparatively higher melting points, boiling points and densities than thiols. Finally, alcohols are much more water soluble than thiols due to their greater polarity and hydrogen bonding. 2) Compare the m ...
NAME Chem 204 Spring, 1990 Final Exam FINAL EXAM: Chaps. 1
... alkyl chloride, there is NO one reaction that will convert a chiral alcohol into its alkyl chloride with "retained" configuration. Thus, it is necessary to use several reaction steps, each of 100% inversion or 100% retention of configuration, in order to convert (X) into (XI). Outlines below a serie ...
... alkyl chloride, there is NO one reaction that will convert a chiral alcohol into its alkyl chloride with "retained" configuration. Thus, it is necessary to use several reaction steps, each of 100% inversion or 100% retention of configuration, in order to convert (X) into (XI). Outlines below a serie ...
aa-2005-38-71-negishi - University of Windsor
... The Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling has proved to be of wide scope with respect to metal countercations.1 In many less demanding cases, all or most of the ten or more metals that have been used as countercations may work satisfactorily. In other more demanding cases, however, critical differences among ...
... The Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling has proved to be of wide scope with respect to metal countercations.1 In many less demanding cases, all or most of the ten or more metals that have been used as countercations may work satisfactorily. In other more demanding cases, however, critical differences among ...
Ch. 6 - Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry
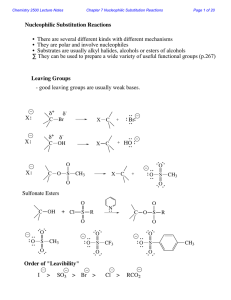
... Different reactivity than alkyl halides, and do not undergo SN or E reactions ...
... Different reactivity than alkyl halides, and do not undergo SN or E reactions ...
Get PDF - Wiley Online Library
... outgrowth in primary cultured rat cortical neurons at concentrations as low as 10 nm. Given the important regulatory role of neurotrophins in the central nervous system, jiadifenolide represents a valuable small-molecule lead for the potential therapeutic treatment of neurodegenerative conditions su ...
... outgrowth in primary cultured rat cortical neurons at concentrations as low as 10 nm. Given the important regulatory role of neurotrophins in the central nervous system, jiadifenolide represents a valuable small-molecule lead for the potential therapeutic treatment of neurodegenerative conditions su ...
Synthetic Organic Chemistry - Name
... The present book entitled “Synthetic Organic Chemistry” has been designed so as to cover the unit-wise syllabus of MScCH-07 course for M.Sc. Chemistry (Final) students of Vardhman Mahaveer Open University, Kota. The basic principles and theory have been explained in simple, concise and lucid manner. ...
... The present book entitled “Synthetic Organic Chemistry” has been designed so as to cover the unit-wise syllabus of MScCH-07 course for M.Sc. Chemistry (Final) students of Vardhman Mahaveer Open University, Kota. The basic principles and theory have been explained in simple, concise and lucid manner. ...
Chapter 19 - U of L Class Index
... This is a great way to make 3° alcohols in which two of the alkyl substituents are the same (both derived from the Grignard reagent). The mechanism for this process is completely analogous to that of hydride reaction above. Just replace "H - " with "Et-" and you have it. ...
... This is a great way to make 3° alcohols in which two of the alkyl substituents are the same (both derived from the Grignard reagent). The mechanism for this process is completely analogous to that of hydride reaction above. Just replace "H - " with "Et-" and you have it. ...
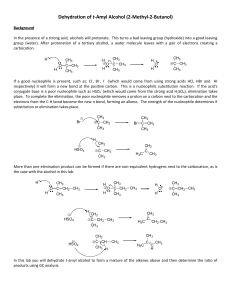
Dehydration of t-Amyl Alcohol (2-Methyl-2
... In the presence of a strong acid, alcohols will protonate. This turns a bad leaving group (hydroxide) into a good leaving group (water). After protonation of a tertiary alcohol, a water molecule leaves with a pair of electrons creating a carbocation. H+ ...
... In the presence of a strong acid, alcohols will protonate. This turns a bad leaving group (hydroxide) into a good leaving group (water). After protonation of a tertiary alcohol, a water molecule leaves with a pair of electrons creating a carbocation. H+ ...
Chapter 16-18 - Bakersfield College
... – Take the largest group bonded to nitrogen as the parent amine. – Name the smaller group(s) bonded to nitrogen, and show their locations on nitrogen by using the prefix “N”. ...
... – Take the largest group bonded to nitrogen as the parent amine. – Name the smaller group(s) bonded to nitrogen, and show their locations on nitrogen by using the prefix “N”. ...
homogeneous catalysis
... Written mainly from a pedagogical point of view, this book is not comprehensive but selective. The material presented was selected on the basis of two criteria. We have tried to include most of the homogeneous catalytic reactions with proven industrial applications and well-established mechanisms. T ...
... Written mainly from a pedagogical point of view, this book is not comprehensive but selective. The material presented was selected on the basis of two criteria. We have tried to include most of the homogeneous catalytic reactions with proven industrial applications and well-established mechanisms. T ...
- University at Albany
... does the acidity. Therefore, acetylenic protons are relatively acidic, with a pKa of ~ 25. Acetylenic protons are more acidic than vinyl (pKa = 44) or alkane (pka = 50) protons. Strong bases such as -NH (but not alkoxide and hydroxide ions) can ...
... does the acidity. Therefore, acetylenic protons are relatively acidic, with a pKa of ~ 25. Acetylenic protons are more acidic than vinyl (pKa = 44) or alkane (pka = 50) protons. Strong bases such as -NH (but not alkoxide and hydroxide ions) can ...
Synthetic Strategies for the Construction of Enantiomeric
... Our first approach to the synthesis of azabicyclo[3.3.0]octane 3 employed Trost's palladium-catalyzed [3+2] annulation9 utilizing 2-trimethylsilylmethyl-2-propen-1-yl acetate. Several attempts to access a bicyclic system via direct annulation of an existing olefin-containing ring were not successful ...
... Our first approach to the synthesis of azabicyclo[3.3.0]octane 3 employed Trost's palladium-catalyzed [3+2] annulation9 utilizing 2-trimethylsilylmethyl-2-propen-1-yl acetate. Several attempts to access a bicyclic system via direct annulation of an existing olefin-containing ring were not successful ...
Document
... • With cyclic ketones, numbering always begins at the carbonyl carbon, but the “1” is usually omitted from the name. The ring is then numbered clockwise or counterclockwise to give the first substituent the lower number. ...
... • With cyclic ketones, numbering always begins at the carbonyl carbon, but the “1” is usually omitted from the name. The ring is then numbered clockwise or counterclockwise to give the first substituent the lower number. ...
History of Organic Chemistry
... A student is told to draw the structural diagram of the compound with formula C4H10 . Confused, the student tells the naive chemistry-challenged person that the task is impossible. a) Why can=t the student show the structure of C4H10? (2) b) Rephrase the question by changing one word so that the que ...
... A student is told to draw the structural diagram of the compound with formula C4H10 . Confused, the student tells the naive chemistry-challenged person that the task is impossible. a) Why can=t the student show the structure of C4H10? (2) b) Rephrase the question by changing one word so that the que ...
BIORANSFORMATION
... • Strongly bound to plasma proteins. • This property also stops them from getting eliminated. • They have to be converted to simpler hydrophilic compounds so that they are eliminated and their action is terminated. ...
... • Strongly bound to plasma proteins. • This property also stops them from getting eliminated. • They have to be converted to simpler hydrophilic compounds so that they are eliminated and their action is terminated. ...
Modern Organic Chemistry
... IUPAC Names The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) is responsible for chemistry names. Before learning the IUPAC rules for naming alkanes, the names and structures of eight alkyl groups must be learned. These alkyl groups are historical names accepted by the IUPAC and integra ...
... IUPAC Names The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) is responsible for chemistry names. Before learning the IUPAC rules for naming alkanes, the names and structures of eight alkyl groups must be learned. These alkyl groups are historical names accepted by the IUPAC and integra ...
Amidations of Rosin with Isocyanates
... abietic acid with phenyl isocyanate. Amidation of rosin with phenyl isocyanate Table 3 shows the results of amidation of rosin with phenyl isocyanate in toluene. Based on the comparison of the data in Table 3 with those in Tables 1 and 2, it is found that the amidation of rosin with phenyl isocyanat ...
... abietic acid with phenyl isocyanate. Amidation of rosin with phenyl isocyanate Table 3 shows the results of amidation of rosin with phenyl isocyanate in toluene. Based on the comparison of the data in Table 3 with those in Tables 1 and 2, it is found that the amidation of rosin with phenyl isocyanat ...
File
... The alcohol molecules form hydrogen bonds with one another, resulting in a higher boiling point. They also form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, causing 1- butanol to be more soluble than diethyl ether. (Although diethyl ether is polar, 1- butanol has greater polarity). ...
... The alcohol molecules form hydrogen bonds with one another, resulting in a higher boiling point. They also form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, causing 1- butanol to be more soluble than diethyl ether. (Although diethyl ether is polar, 1- butanol has greater polarity). ...
KENYATTA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF OPEN LEARNING SCH
... Ketones are not.easily easily oxidised. Oxidation involves breaking the carbon-carbon bonds. They are resistant to mild oxidation with Cr(VI) reagents and acetone can even be used as a solvent for oxidation with such reagents. KMnO4 oxidises ketones and is not a useful reagent for the preparation of ...
... Ketones are not.easily easily oxidised. Oxidation involves breaking the carbon-carbon bonds. They are resistant to mild oxidation with Cr(VI) reagents and acetone can even be used as a solvent for oxidation with such reagents. KMnO4 oxidises ketones and is not a useful reagent for the preparation of ...
Thermodynamics and kinetics of the hydrolysis of atmospherically
... ensure solution homogeneity, an aliquot of the reaction mixture was loaded into an NMR tube and NMR spectral collection was started. The reaction time was recorded as the ending time of each 30 s NMR data collection period. Depending on the rate of reaction for the various species, the solutions wer ...
... ensure solution homogeneity, an aliquot of the reaction mixture was loaded into an NMR tube and NMR spectral collection was started. The reaction time was recorded as the ending time of each 30 s NMR data collection period. Depending on the rate of reaction for the various species, the solutions wer ...
Anionic rearrangement of 2-benzyloxypyridine derivatives and a synthetic approach to aldingenin B
... could not have achieved what I have today. From him, I learned not only new ideas and information, but also how to properly conduct research. The way he teaches is not by giving a simple answer, but by guiding us to the right path and making us find the answer. Gradually, I learned to do research mo ...
... could not have achieved what I have today. From him, I learned not only new ideas and information, but also how to properly conduct research. The way he teaches is not by giving a simple answer, but by guiding us to the right path and making us find the answer. Gradually, I learned to do research mo ...
Haloalkane

The haloalkanes (also known, as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes which contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula ″RX″ where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).Haloalkanes have been known for centuries. Chloroethane was produced synthetically in the 15th century. The systematic synthesis of such compounds developed in the 19th century in step with the development of organic chemistry and the understanding of the structure of alkanes. Methods were developed for the selective formation of C-halogen bonds. Especially versatile methods included the addition of halogens to alkenes, hydrohalogenation of alkenes, and the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides. These methods are so reliable and so easily implemented that haloalkanes became cheaply available for use in industrial chemistry because the halide could be further replaced by other functional groups.While most haloalkanes are human-produced, non-artificial-source haloalkanes do occur on Earth, mostly through enzyme-mediated synthesis by bacteria, fungi, and especially sea macroalgae (seaweeds). More than 1600 halogenated organics have been identified, with bromoalkanes being the most common haloalkanes. Brominated organics in biology range from biologically produced methyl bromide to non-alkane aromatics and unsaturates (indoles, terpenes, acetogenins, and phenols). Halogenated alkanes in land plants are more rare, but do occur, as for example the fluoroacetate produced as a toxin by at least 40 species of known plants. Specific dehalogenase enzymes in bacteria which remove halogens from haloalkanes, are also known.