Asymmetry and Stereoisomers
... • the carbon atom with reference to valence number, bond strength, stability of carbon bonds with other elements and the formation of isomers to explain carbon compound diversity, including identification of chiral centres in optical isomers of simple organic compounds and distinction between cis- a ...
... • the carbon atom with reference to valence number, bond strength, stability of carbon bonds with other elements and the formation of isomers to explain carbon compound diversity, including identification of chiral centres in optical isomers of simple organic compounds and distinction between cis- a ...
Worksheets for this unit
... break down these large molecules to useable size is called ___________________. There are two types called ______________ and _________________________. 7. The opposite to cracking is called ____________________________ ...
... break down these large molecules to useable size is called ___________________. There are two types called ______________ and _________________________. 7. The opposite to cracking is called ____________________________ ...
aminepp - Knockhardy
... produce a 2° amine. This too is a nucleophile and can react further producing a 3° amine and, eventually an ionic quarternary ammonium salt. C2H5NH2 + C2H5Br ...
... produce a 2° amine. This too is a nucleophile and can react further producing a 3° amine and, eventually an ionic quarternary ammonium salt. C2H5NH2 + C2H5Br ...
Benzene, amines, amino acids and polymers File
... STRUCTURE OF BENZENE Primary analysis revealed benzene had... an ...
... STRUCTURE OF BENZENE Primary analysis revealed benzene had... an ...
No Slide Title
... produce a 2° amine. This too is a nucleophile and can react further producing a 3° amine and, eventually an ionic quarternary ammonium salt. C2H5NH2 + C2H5Br ...
... produce a 2° amine. This too is a nucleophile and can react further producing a 3° amine and, eventually an ionic quarternary ammonium salt. C2H5NH2 + C2H5Br ...
Chapter 19: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... Nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions of esters (Table 19.4). Esters are less reactive toward nucleophilic acyl substitution than acid chlorides or acid anhydrides. 1. Aminolysis (Ch.19.11): Esters react with ammonia, 1° and 2° amines to give amides ...
... Nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions of esters (Table 19.4). Esters are less reactive toward nucleophilic acyl substitution than acid chlorides or acid anhydrides. 1. Aminolysis (Ch.19.11): Esters react with ammonia, 1° and 2° amines to give amides ...
Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
... conjugated enone as it is formed, especially if reaction conditions are pushed, eg high temperature. Mixed or "crossed" Aldol Reactions — If two different carbonyl compounds are allowed to react in an aldol reaction four products usually result; each carbonyl compound forms an enolate and each enola ...
... conjugated enone as it is formed, especially if reaction conditions are pushed, eg high temperature. Mixed or "crossed" Aldol Reactions — If two different carbonyl compounds are allowed to react in an aldol reaction four products usually result; each carbonyl compound forms an enolate and each enola ...
102 Lab 7 Esters Fall05
... bioactive. Isoamyl acetate, which smells like bananas, is also an alarm pheromone released by honey bees when they sting an intruder. The pheromone attracts other bees and incites them to attack the intruder. For these reasons, fragrances are more often made from essential oils (phenols, aldehydes, ...
... bioactive. Isoamyl acetate, which smells like bananas, is also an alarm pheromone released by honey bees when they sting an intruder. The pheromone attracts other bees and incites them to attack the intruder. For these reasons, fragrances are more often made from essential oils (phenols, aldehydes, ...
Experimen tt: Dehydration of an Alcohol
... mixture by touching the side of the flask. Have a beaker of ice water ready in case the reaction mixture becomes too hot to touch. After you have added all of the acid, swirl the flask again to be certain that the contents are thoroughly mixed. The receiver should be a 25mL round bottom flask. Heat ...
... mixture by touching the side of the flask. Have a beaker of ice water ready in case the reaction mixture becomes too hot to touch. After you have added all of the acid, swirl the flask again to be certain that the contents are thoroughly mixed. The receiver should be a 25mL round bottom flask. Heat ...
A Straightforward Route to Enantiopure Pyrrolizidines and
... special comments regarding preparative applicability of such esters. It is noteworthy that the experiment described is, to the best of our knowledge, the first example for preparation of an alkyl trichloromethanesulfonate on this route starting from an alcohol. In addition to this initial aim, the u ...
... special comments regarding preparative applicability of such esters. It is noteworthy that the experiment described is, to the best of our knowledge, the first example for preparation of an alkyl trichloromethanesulfonate on this route starting from an alcohol. In addition to this initial aim, the u ...
Introduction to Chemical Reactions
... Sodium chloride is the product of the reaction 2 Mg + O2 → 2 MgO Magnesium atoms and oxygen gas molecules combine to form a single new product Magnesium oxide is the product of the reaction In a moment, we will also see that this reaction can also be classified as a combustion reaction ...
... Sodium chloride is the product of the reaction 2 Mg + O2 → 2 MgO Magnesium atoms and oxygen gas molecules combine to form a single new product Magnesium oxide is the product of the reaction In a moment, we will also see that this reaction can also be classified as a combustion reaction ...
Edexcel Chemistry for A2
... [d) part (v) and e) come after section f).] f) describe and carry out, where appropriate, the preparation of a compound, e.g. cholesteryl benzoate (a liquid crystal) and methyl 3-nitrobenzoate, requiring some of the following techniques: (i) refluxing (ii) purification by washing, e.g. with water an ...
... [d) part (v) and e) come after section f).] f) describe and carry out, where appropriate, the preparation of a compound, e.g. cholesteryl benzoate (a liquid crystal) and methyl 3-nitrobenzoate, requiring some of the following techniques: (i) refluxing (ii) purification by washing, e.g. with water an ...
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 12 – Alcohols
... o Sodium borohydride, NaBH4, does not affect double and triple bonds between carbons, but does reduce the C=O of aldehydes and ketones. It is not strong enough to affect carboxylic acids or esters. It is the most common reagent for converting aldehydes and ketones to alcohols. o Lithium aluminum hyd ...
... o Sodium borohydride, NaBH4, does not affect double and triple bonds between carbons, but does reduce the C=O of aldehydes and ketones. It is not strong enough to affect carboxylic acids or esters. It is the most common reagent for converting aldehydes and ketones to alcohols. o Lithium aluminum hyd ...
Organic_2_7ed_07th_module_carboxylic_acids 370KB May 03
... (ArOH) or a carboxylic acid (RCO2H). This is reaction solubility, not like-dissolves-like solubility; the alkaline test solution reacts with acidic compounds to give ionic, water-soluble products. You must run the water solubility test first for this test to be useful; 5% NaOH is 95% water, and comp ...
... (ArOH) or a carboxylic acid (RCO2H). This is reaction solubility, not like-dissolves-like solubility; the alkaline test solution reacts with acidic compounds to give ionic, water-soluble products. You must run the water solubility test first for this test to be useful; 5% NaOH is 95% water, and comp ...
Hydrogen Bonding • Aldehydes and ketones don`t hydrogen bond
... hydrogen bond with themselves or each other Boiling Points of Different Functional Groups Aldehydes’ and ketones’ polarity gives them higher boiling points than alkanes and alkenes. However, their inability to hydrogen bond makes their boiling points lower than alcohols. ...
... hydrogen bond with themselves or each other Boiling Points of Different Functional Groups Aldehydes’ and ketones’ polarity gives them higher boiling points than alkanes and alkenes. However, their inability to hydrogen bond makes their boiling points lower than alcohols. ...
Ch 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... Ch 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Subst’n Acid Derivatives and their Names - Acid Halides have a Cl or Br instead of OH. Replace “ic acid” with “yl halide”, such as propionyl chloride (a common name) and propanoyl bromide (a systematic name). Replace “carboxylic acid” with “carbonyl hali ...
... Ch 21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Subst’n Acid Derivatives and their Names - Acid Halides have a Cl or Br instead of OH. Replace “ic acid” with “yl halide”, such as propionyl chloride (a common name) and propanoyl bromide (a systematic name). Replace “carboxylic acid” with “carbonyl hali ...
Lecture12
... a preferred ligand to Pd ratio for the stable complex. The true active species will have a lower coordination number due to the need for an open site for oxidative addition to occur. ...
... a preferred ligand to Pd ratio for the stable complex. The true active species will have a lower coordination number due to the need for an open site for oxidative addition to occur. ...
C - Ms Critchley`s Lab
... distillation, which can be used as fuels or for processing into petrochemicals • Alkanes and cycloalkanes are saturated hydrocarbons which have only single bonds between carbon atoms. Unsaturated carbon atoms have at least one carboncarbon double bond. • There is a tetrahedral shape around each carb ...
... distillation, which can be used as fuels or for processing into petrochemicals • Alkanes and cycloalkanes are saturated hydrocarbons which have only single bonds between carbon atoms. Unsaturated carbon atoms have at least one carboncarbon double bond. • There is a tetrahedral shape around each carb ...
Chapter 16 Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides
... name the groups attached to oxygen in alphabetical order as separate words; "ether" is ...
... name the groups attached to oxygen in alphabetical order as separate words; "ether" is ...
Unit 6 web
... • Contain atoms other than C and H • To understand their properties, they are grouped according to the nature of these atoms and how they are bonded • Classified according to reactivity and function, hence “functional groups” ...
... • Contain atoms other than C and H • To understand their properties, they are grouped according to the nature of these atoms and how they are bonded • Classified according to reactivity and function, hence “functional groups” ...
Extra Organic Notes and Activities
... Chemistry based on carbon and carbon compounds Originally, all organic compounds came from plants or animals (hence the name organic chemistry - chemistry from living sources). However, a great number of these can now be synthesized in the laboratory. The important thing to remember about organic ch ...
... Chemistry based on carbon and carbon compounds Originally, all organic compounds came from plants or animals (hence the name organic chemistry - chemistry from living sources). However, a great number of these can now be synthesized in the laboratory. The important thing to remember about organic ch ...
File
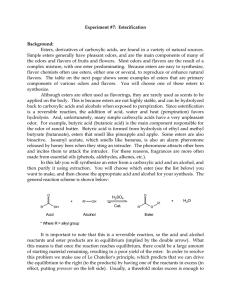
... o Know the required conditions for each Substitution reaction: the functional groups switch places o We only looked at the substitution of alcohols and alkyl halides o Alkanes and aromatics can also undergo substitution, but require energy or a catalyst Esterification reaction: reaction between an a ...
... o Know the required conditions for each Substitution reaction: the functional groups switch places o We only looked at the substitution of alcohols and alkyl halides o Alkanes and aromatics can also undergo substitution, but require energy or a catalyst Esterification reaction: reaction between an a ...
Study Guide for Exam 2-‐ Aldehydes and Ketones
... writing) at solving the synthesis on your own. During review sessions, any student that asks about the syntheses will be asked to go to the board to present what they have worked out so far. ...
... writing) at solving the synthesis on your own. During review sessions, any student that asks about the syntheses will be asked to go to the board to present what they have worked out so far. ...
Sp09 Survival Organic Chem
... single, double and triple bonds, bond lengths and angles, resonance, and bond dissociation energies. Your textbook will play an important role as a reference tool in this laboratory. Chapters and sections which will be important to refer to include; Chapter 15, sections 15.1 - 15.4 Chapter 9, sectio ...
... single, double and triple bonds, bond lengths and angles, resonance, and bond dissociation energies. Your textbook will play an important role as a reference tool in this laboratory. Chapters and sections which will be important to refer to include; Chapter 15, sections 15.1 - 15.4 Chapter 9, sectio ...
Haloalkane

The haloalkanes (also known, as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes which contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula ″RX″ where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).Haloalkanes have been known for centuries. Chloroethane was produced synthetically in the 15th century. The systematic synthesis of such compounds developed in the 19th century in step with the development of organic chemistry and the understanding of the structure of alkanes. Methods were developed for the selective formation of C-halogen bonds. Especially versatile methods included the addition of halogens to alkenes, hydrohalogenation of alkenes, and the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides. These methods are so reliable and so easily implemented that haloalkanes became cheaply available for use in industrial chemistry because the halide could be further replaced by other functional groups.While most haloalkanes are human-produced, non-artificial-source haloalkanes do occur on Earth, mostly through enzyme-mediated synthesis by bacteria, fungi, and especially sea macroalgae (seaweeds). More than 1600 halogenated organics have been identified, with bromoalkanes being the most common haloalkanes. Brominated organics in biology range from biologically produced methyl bromide to non-alkane aromatics and unsaturates (indoles, terpenes, acetogenins, and phenols). Halogenated alkanes in land plants are more rare, but do occur, as for example the fluoroacetate produced as a toxin by at least 40 species of known plants. Specific dehalogenase enzymes in bacteria which remove halogens from haloalkanes, are also known.