Enantioselective Organocatalytic Aminomethylation of Aldehydes: A
... reactants. The Mannich reaction products, R-substituted β-amino aldehydes, were immediately reduced to the corresponding β-substituted γ-amino alcohols to avoid epimerization. Initial studies involving pentanal revealed modest enantioselectivity when the reaction was carried out with 20 mol % cataly ...
... reactants. The Mannich reaction products, R-substituted β-amino aldehydes, were immediately reduced to the corresponding β-substituted γ-amino alcohols to avoid epimerization. Initial studies involving pentanal revealed modest enantioselectivity when the reaction was carried out with 20 mol % cataly ...
IUPAC System of Nomenclature
... 3-bromo-2-methylpentane Naming Alcohols The parent chain of the alcohol must be the longest that includes the carbon holding the OH group. Give the -OH group the lower location number on the chain regardless of where alkyl substituents occur. Name the alkane attached to the OH group and replace the ...
... 3-bromo-2-methylpentane Naming Alcohols The parent chain of the alcohol must be the longest that includes the carbon holding the OH group. Give the -OH group the lower location number on the chain regardless of where alkyl substituents occur. Name the alkane attached to the OH group and replace the ...
Chapter 4 Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
... Other ways to convert alcohols to alky halides (1) Thionyl Chloride: We can treat alcohols with boiling thionyl chloride (SOCl2) to convert the alcohol to an alkyl chloride. This method is considerably milder than using concentrated hydrochloric acid and is useful when the molecule contains sensitiv ...
... Other ways to convert alcohols to alky halides (1) Thionyl Chloride: We can treat alcohols with boiling thionyl chloride (SOCl2) to convert the alcohol to an alkyl chloride. This method is considerably milder than using concentrated hydrochloric acid and is useful when the molecule contains sensitiv ...
Organic Chemistry - UCR Chemistry
... deprotonation. The three "chromate" species, or the three "dichromate" species, are simply differently protonated froms of CrO4-2 or Cr2O7-2, respectively Unwanted Oxidation of Aldehydes. Cr(VI) reagents are powerful oxidizing agents useful for oxidizing 2° alcohols to ketones (Figure 17.005) becaus ...
... deprotonation. The three "chromate" species, or the three "dichromate" species, are simply differently protonated froms of CrO4-2 or Cr2O7-2, respectively Unwanted Oxidation of Aldehydes. Cr(VI) reagents are powerful oxidizing agents useful for oxidizing 2° alcohols to ketones (Figure 17.005) becaus ...
Ketones and Aldehydes
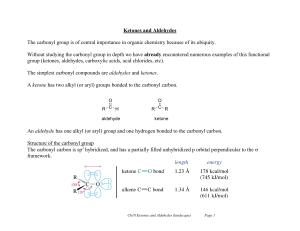
... Ketones and Aldehydes The carbonyl group is of central importance in organic chemistry because of its ubiquity. Without studying the carbonyl group in depth we have already encountered numerous examples of this functional group (ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, acid chlorides, etc). The simples ...
... Ketones and Aldehydes The carbonyl group is of central importance in organic chemistry because of its ubiquity. Without studying the carbonyl group in depth we have already encountered numerous examples of this functional group (ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, acid chlorides, etc). The simples ...
II. Nomenclature Rules For Alkenes 1. The parent name will be the
... double bond are assigned a priority based on atomic number. Higher atomic number atoms are assigned a higher priority. In organic chemistry we are mostly concerned with the halogens, oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen and occasionally sulfur or phosphorous. It would seem like nothing could be lower than a h ...
... double bond are assigned a priority based on atomic number. Higher atomic number atoms are assigned a higher priority. In organic chemistry we are mostly concerned with the halogens, oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen and occasionally sulfur or phosphorous. It would seem like nothing could be lower than a h ...
Development of Multi-Component Reactions using Catalytically Generated Allyl Metal Reagents
... to homoallylic alcohols is an important C-C bond forming reaction. Several attractive properties of allylboronates account for their popularity as synthetic intermediates in organic synthesis.8-62 Their high diastereoselectivity in the coupling reactions with aldehydes is predictable and often super ...
... to homoallylic alcohols is an important C-C bond forming reaction. Several attractive properties of allylboronates account for their popularity as synthetic intermediates in organic synthesis.8-62 Their high diastereoselectivity in the coupling reactions with aldehydes is predictable and often super ...
Stereoselective synthesis: chiral auxiliaries
... • Chiral auxiliary - allows enantioselective synthesis via diastereoselective reaction • Add chiral unit to substrate to control stereoselective reaction • Can act as a built in resolving agent (if reaction not diastereoselective) • Problems - need point of attachment ....................adds additi ...
... • Chiral auxiliary - allows enantioselective synthesis via diastereoselective reaction • Add chiral unit to substrate to control stereoselective reaction • Can act as a built in resolving agent (if reaction not diastereoselective) • Problems - need point of attachment ....................adds additi ...
CHEM 121 Chapter 14. Name: Date: ______ 1. The simplest alcohol
... B) rubbing alcohol is pure methyl alcohol C) absolute alcohol is pure methanol D) absolute ethanol has all water removed from it 5. In which of the following pairs of alcohols do both members of the pair contain two or more hydroxyl groups? A) s-butanol and ethylene glycol B) propylene glycol and gl ...
... B) rubbing alcohol is pure methyl alcohol C) absolute alcohol is pure methanol D) absolute ethanol has all water removed from it 5. In which of the following pairs of alcohols do both members of the pair contain two or more hydroxyl groups? A) s-butanol and ethylene glycol B) propylene glycol and gl ...
Cerium(IV) Ammonium Nitrate as a Catalyst in
... representative examples of these transformations are summarized in Table 1, and it should be remarked that some of them (e.g., those in entries 2 and 3) were not possible in the presence of stoichiometric amounts of CAN, as they led to fragmentation products. Another development in this area was the ...
... representative examples of these transformations are summarized in Table 1, and it should be remarked that some of them (e.g., those in entries 2 and 3) were not possible in the presence of stoichiometric amounts of CAN, as they led to fragmentation products. Another development in this area was the ...
The Acid Hydrolysis Mechanism of Acetals Catalyzed
... Although electrocyclic reactions received much early attention in studies of supramolecular reactivity, due to the ability of the cavities of synthetic hosts cavities to preorganize substrates in reactive conformations or to increase the effective concentrations of the reactants in the cavity of the ...
... Although electrocyclic reactions received much early attention in studies of supramolecular reactivity, due to the ability of the cavities of synthetic hosts cavities to preorganize substrates in reactive conformations or to increase the effective concentrations of the reactants in the cavity of the ...
Chemical Properties of Monocyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons(5)
... • The common feature of all activating groups is that they donate electrons to the ring, thereby stabilizing the carbocation intermediate from electrophilic addition and causing it to form faster. • The common feature of all deactivating groups is that they withdraw electrons from the ring, thereby ...
... • The common feature of all activating groups is that they donate electrons to the ring, thereby stabilizing the carbocation intermediate from electrophilic addition and causing it to form faster. • The common feature of all deactivating groups is that they withdraw electrons from the ring, thereby ...
50 chemistry questions for class xii
... Ans→(a) All positions are cis,There is no trans position. (b) They give different types of ions SO4-2 and Cl- ions respectively. Write IUPAC names of (a) CH3-NH-CH(CH3)2 (b) m-BrC6H4NH2 . Ans→(a) N-methyl propan-2-amine (b) 3-bromo benzenamine ...
... Ans→(a) All positions are cis,There is no trans position. (b) They give different types of ions SO4-2 and Cl- ions respectively. Write IUPAC names of (a) CH3-NH-CH(CH3)2 (b) m-BrC6H4NH2 . Ans→(a) N-methyl propan-2-amine (b) 3-bromo benzenamine ...
CHAPTER 15
... (1) Aldehydes and ketones readily undergo oxidation to carboxylic acids. (2) Propanone and dimethyl ketone are two names for the same compound. (3) The “silver mirror test” distinguishes between aldehydes and ketones. a) All three statements are true. b) Two of the three statements are true. c) Only ...
... (1) Aldehydes and ketones readily undergo oxidation to carboxylic acids. (2) Propanone and dimethyl ketone are two names for the same compound. (3) The “silver mirror test” distinguishes between aldehydes and ketones. a) All three statements are true. b) Two of the three statements are true. c) Only ...
Handout 3
... • Some free radical reaction mechanisms, Halogenation of alkanes, NBS alllylic substitution, • Free radical addition to alkenes (HBr / Peroxide addition), Radical polymerization of alkenes • Addition Reactions of Alkenes; Hydrohalogenation, Halogenation, Halohydrin Formation , Alcohols from, Syn add ...
... • Some free radical reaction mechanisms, Halogenation of alkanes, NBS alllylic substitution, • Free radical addition to alkenes (HBr / Peroxide addition), Radical polymerization of alkenes • Addition Reactions of Alkenes; Hydrohalogenation, Halogenation, Halohydrin Formation , Alcohols from, Syn add ...
Chemistry 30 - SharpSchool
... ________________________________________ will allow polar compounds to ________________________________, since it is also polar ...
... ________________________________________ will allow polar compounds to ________________________________, since it is also polar ...
Alkenes
... reaction yields the more highly substituted alkene as the major product. The more stable alkene product predominates. ...
... reaction yields the more highly substituted alkene as the major product. The more stable alkene product predominates. ...
MOLECULAR REPRESENTATIONS AND INFRARED
... C=O: 1630-1780 cm-1, strong absorption If you need to use other frequencies to identify other functional groups (and sometimes you will), a table of IR frequencies will be provided. ...
... C=O: 1630-1780 cm-1, strong absorption If you need to use other frequencies to identify other functional groups (and sometimes you will), a table of IR frequencies will be provided. ...
Latest Publication (still not complete)
... cyclization processes, concentrating on the synthesis of three- to seven-membered ring containing products. However, in addition to this, the structure and bonding of carbene complexes is also discussed. In particular, an analysis of information gained through computational analysis is provided. Suc ...
... cyclization processes, concentrating on the synthesis of three- to seven-membered ring containing products. However, in addition to this, the structure and bonding of carbene complexes is also discussed. In particular, an analysis of information gained through computational analysis is provided. Suc ...
Year 2 Chemistry Contents Guide
... Identifying the names of carboxylic acids Animated graph comparing the boiling points of carboxylic acids with alcohols, aldehydes and alkanes of similar Mr. Virtual experiment illustrating the preparation of carboxylic acids • Preparation of carboxylic acids by the oxidation of primary alcohols, an ...
... Identifying the names of carboxylic acids Animated graph comparing the boiling points of carboxylic acids with alcohols, aldehydes and alkanes of similar Mr. Virtual experiment illustrating the preparation of carboxylic acids • Preparation of carboxylic acids by the oxidation of primary alcohols, an ...
Catalytic asymmetric carbonyl addition reactions catalysed by group
... Catalytic asymmetric carbonyl addition reactions catalysed by group 10 metals The addition of a nucleophilic species to the carbonyl group is one of the most important methodology for carbon-carbon bond construction and various solutions have been offered to achieve an asymmetric version. ...
... Catalytic asymmetric carbonyl addition reactions catalysed by group 10 metals The addition of a nucleophilic species to the carbonyl group is one of the most important methodology for carbon-carbon bond construction and various solutions have been offered to achieve an asymmetric version. ...
CHEM 494 Lecture 8 - UIC Department of Chemistry
... • C-O bond breaks at the same time the nucleophile (Br) forms the C-X bond • RDS is nucleophilic attack; bimolecular, therefore Ingold notation = SN2 • fewer steps does not mean faster reaction University of Illinois at Chicago ...
... • C-O bond breaks at the same time the nucleophile (Br) forms the C-X bond • RDS is nucleophilic attack; bimolecular, therefore Ingold notation = SN2 • fewer steps does not mean faster reaction University of Illinois at Chicago ...
Unit 13: Organic Chemistry
... Objective: What are Alkenes, and how do they function in chemistry? Alkene Family: 1. The alkene family, also known as the olefin family, differ from their related alkanes by having one carbon to carbon double bond (C=C) somewhere along the longest chain. 2. Ethane (C2H4) and propene (C3H6) are the ...
... Objective: What are Alkenes, and how do they function in chemistry? Alkene Family: 1. The alkene family, also known as the olefin family, differ from their related alkanes by having one carbon to carbon double bond (C=C) somewhere along the longest chain. 2. Ethane (C2H4) and propene (C3H6) are the ...
Unit 13: Organic Chemistry
... Objective: What are Alkenes, and how do they function in chemistry? Alkene Family: 1. The alkene family, also known as the olefin family, differ from their related alkanes by having one carbon to carbon double bond (C=C) somewhere along the longest chain. 2. Ethane (C2H4) and propene (C3H6) are the ...
... Objective: What are Alkenes, and how do they function in chemistry? Alkene Family: 1. The alkene family, also known as the olefin family, differ from their related alkanes by having one carbon to carbon double bond (C=C) somewhere along the longest chain. 2. Ethane (C2H4) and propene (C3H6) are the ...
Haloalkane

The haloalkanes (also known, as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes which contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula ″RX″ where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).Haloalkanes have been known for centuries. Chloroethane was produced synthetically in the 15th century. The systematic synthesis of such compounds developed in the 19th century in step with the development of organic chemistry and the understanding of the structure of alkanes. Methods were developed for the selective formation of C-halogen bonds. Especially versatile methods included the addition of halogens to alkenes, hydrohalogenation of alkenes, and the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides. These methods are so reliable and so easily implemented that haloalkanes became cheaply available for use in industrial chemistry because the halide could be further replaced by other functional groups.While most haloalkanes are human-produced, non-artificial-source haloalkanes do occur on Earth, mostly through enzyme-mediated synthesis by bacteria, fungi, and especially sea macroalgae (seaweeds). More than 1600 halogenated organics have been identified, with bromoalkanes being the most common haloalkanes. Brominated organics in biology range from biologically produced methyl bromide to non-alkane aromatics and unsaturates (indoles, terpenes, acetogenins, and phenols). Halogenated alkanes in land plants are more rare, but do occur, as for example the fluoroacetate produced as a toxin by at least 40 species of known plants. Specific dehalogenase enzymes in bacteria which remove halogens from haloalkanes, are also known.