Chemical Reactivity and Biological Activity of Diketene
... activation, ∆Gq, is approximately constant (33). The results shown in Figure 6 support the idea of a common mechanism for the NBP alkylation reactions by DIK in different water/ dioxane media, ranging from 3:7 to 7:3 (vol). Decomposition of the NBP-DIK Adduct. Contrary to what occurs with BPL and BB ...
... activation, ∆Gq, is approximately constant (33). The results shown in Figure 6 support the idea of a common mechanism for the NBP alkylation reactions by DIK in different water/ dioxane media, ranging from 3:7 to 7:3 (vol). Decomposition of the NBP-DIK Adduct. Contrary to what occurs with BPL and BB ...
Chemistry 162 Workbook 10.6
... experience with testing environments. Once the student has completed an exam, the tutor may choose to grade the exam during a normal session while the student works on other materials ...
... experience with testing environments. Once the student has completed an exam, the tutor may choose to grade the exam during a normal session while the student works on other materials ...
Organic Chemistry
... Use of Carboxylate Anion Nucleophile to form Esters . 87 Hydrolysis of Acid Halides . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88 Reaction of Acyl Halide with Ammonia or Amine . . . 89 Esterification of Acid Halides . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90 Esterification of Acid Anhydrides . . . . . . ...
... Use of Carboxylate Anion Nucleophile to form Esters . 87 Hydrolysis of Acid Halides . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88 Reaction of Acyl Halide with Ammonia or Amine . . . 89 Esterification of Acid Halides . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90 Esterification of Acid Anhydrides . . . . . . ...
Fluorination Chemistry - Sigma
... carbinol group (CH2OH). The Aldrich catalog has innovative sources for installing the difluoromethyl group through nucleophilic addition and radical functionalization of C-H bonds. Nucleophlic difluoromethylation of carbonyls and imines using (Difluoromethyl)trimethylsilane (744050) and Difluorometh ...
... carbinol group (CH2OH). The Aldrich catalog has innovative sources for installing the difluoromethyl group through nucleophilic addition and radical functionalization of C-H bonds. Nucleophlic difluoromethylation of carbonyls and imines using (Difluoromethyl)trimethylsilane (744050) and Difluorometh ...
Substitution Reactions of Specifically Ortho
... i,R CH,CH=CHZ; Z = 0 j,R=CO,HZ=O k,R = CO,CH,; Z = 0 ...
... i,R CH,CH=CHZ; Z = 0 j,R=CO,HZ=O k,R = CO,CH,; Z = 0 ...
Alcools
... Alcohols are noticeably less volatile; their melting points are greater and they are more water soluble than the corresponding hydrocarbons having similar molecular weights. These differences are due to the OH group which renders a certain polarity to the molecule. The result is an important intermo ...
... Alcohols are noticeably less volatile; their melting points are greater and they are more water soluble than the corresponding hydrocarbons having similar molecular weights. These differences are due to the OH group which renders a certain polarity to the molecule. The result is an important intermo ...
Slide 1
... carboxylic acids by nucleophilic acyl substitution by a methyl or 1º alcohol. Heating the acid and alcohol in the presence of a small quantity of acid catalyst (H2SO4 or HCl (g)) causes ester formation (esterification) along with dehydration. The equilibrium constant is not large (Keq ~ 1) but high ...
... carboxylic acids by nucleophilic acyl substitution by a methyl or 1º alcohol. Heating the acid and alcohol in the presence of a small quantity of acid catalyst (H2SO4 or HCl (g)) causes ester formation (esterification) along with dehydration. The equilibrium constant is not large (Keq ~ 1) but high ...
1990-Spring-Exam-2-student
... formula as C10H16. There are two possible structural formulas, A and B. Using a simple chemical reaction that we have discussed a number of times as a quantitative reaction, how can you determine the structure of the oil to be A or B? 1. What is this simple reaction, in general terms? ("For Sale": 4 ...
... formula as C10H16. There are two possible structural formulas, A and B. Using a simple chemical reaction that we have discussed a number of times as a quantitative reaction, how can you determine the structure of the oil to be A or B? 1. What is this simple reaction, in general terms? ("For Sale": 4 ...
Study materials of Chemistry for class XII
... Q12. Pure silicon is an insulator. Silicon doped with phosphorus is a semiconductor. Silicon doped with gallium is also a semiconductor what is the difference between the two semiconductors? 2M Ans. In pure silicon all electrons are involved in bonds formation. The bond formed is strong and cannot b ...
... Q12. Pure silicon is an insulator. Silicon doped with phosphorus is a semiconductor. Silicon doped with gallium is also a semiconductor what is the difference between the two semiconductors? 2M Ans. In pure silicon all electrons are involved in bonds formation. The bond formed is strong and cannot b ...
Lithium Bromide Original Commentary
... as a source of bromide in nucleophilic substitution and addition reactions. Interconversion of halides2 and transformation of alcohols to alkyl bromides via the corresponding sulfonate3 or trifluoroacetate4 have been widely used in organic synthesis. Primary and secondary alcohols have been directly ...
... as a source of bromide in nucleophilic substitution and addition reactions. Interconversion of halides2 and transformation of alcohols to alkyl bromides via the corresponding sulfonate3 or trifluoroacetate4 have been widely used in organic synthesis. Primary and secondary alcohols have been directly ...
... with a cyclic bis-amino carbene ligand. A. Herrmann had earlier synthesized ruthenium complexes with two such carbene ligands, but the catalytic activity of such compounds was modest. In Grubbs` catalysts containing only one such ligand the dissociation rate of the remaining phosphine is increased, ...
guess paper class xii
... .27 Answer the following: (i) K2Cr2O7 is orange in colour but turns yellow in an alkaline medium, why? (j) Draw the structure of dichromate and chromate ion. (k) Silver halides dissolve in thiosulphate ions. Write chemical reaction and the structure of silver complex formed in the reaction. (l) With ...
... .27 Answer the following: (i) K2Cr2O7 is orange in colour but turns yellow in an alkaline medium, why? (j) Draw the structure of dichromate and chromate ion. (k) Silver halides dissolve in thiosulphate ions. Write chemical reaction and the structure of silver complex formed in the reaction. (l) With ...
File
... Although they share the same functional group with alcohols, where the –OH group is attached to an aliphatic carbon, the chemistry of phenols is very different from that of alcohols. ...
... Although they share the same functional group with alcohols, where the –OH group is attached to an aliphatic carbon, the chemistry of phenols is very different from that of alcohols. ...
Amide bond formation and peptide coupling
... SOCl2 4,5 oxalyl chloride (COCl)2 5,6,7 phosphorus trichloride PCl3,8 phosphorus oxychloride POCl39 and phosphorus pentachloride PCl510 are commonly used to generate acyl chlorides from their corresponding acids. Phoshonium pentachloride is generally used for aromatic acids, which contains electron- ...
... SOCl2 4,5 oxalyl chloride (COCl)2 5,6,7 phosphorus trichloride PCl3,8 phosphorus oxychloride POCl39 and phosphorus pentachloride PCl510 are commonly used to generate acyl chlorides from their corresponding acids. Phoshonium pentachloride is generally used for aromatic acids, which contains electron- ...
Glycosyl amines
... Many glycosyl amines occur in Nature and play important roles in living matter. The most important are glycosyl amines derived from D-ribose or 2-deoxy-D-ribose and purine or pyrimidine beses (nucleosides), isolated from the hydrolyzates of nucleic acids. Another important group of glycosyl amines m ...
... Many glycosyl amines occur in Nature and play important roles in living matter. The most important are glycosyl amines derived from D-ribose or 2-deoxy-D-ribose and purine or pyrimidine beses (nucleosides), isolated from the hydrolyzates of nucleic acids. Another important group of glycosyl amines m ...
Organic Chemistry
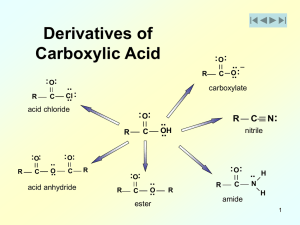
... Organic nitriles (R-C≡N) are usually considered together with R-C(=O)-Z compounds in organic chemistry textbooks. This is because nitriles (R-C≡N) are readily hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids (R-C(=O)-OH) via intermediate amides (R-C(=O)-NH2) (Figure 15.13). Figure 15.13 ...
... Organic nitriles (R-C≡N) are usually considered together with R-C(=O)-Z compounds in organic chemistry textbooks. This is because nitriles (R-C≡N) are readily hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids (R-C(=O)-OH) via intermediate amides (R-C(=O)-NH2) (Figure 15.13). Figure 15.13 ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... Takacs and co-worker have reported the stereoselective synthesis of bicyclic ring in presence of Fecatalyst using enediene carbocyclization. This tool was shown to be useful for synthesis of several heterobicyclic ring compounds, e.g. tetrahydropyran, indolizidine and quinolizidine which was effecti ...
... Takacs and co-worker have reported the stereoselective synthesis of bicyclic ring in presence of Fecatalyst using enediene carbocyclization. This tool was shown to be useful for synthesis of several heterobicyclic ring compounds, e.g. tetrahydropyran, indolizidine and quinolizidine which was effecti ...
Derivatization Reagents - Sigma
... Pentafluorobenzylbromide is convenient for making esters and ethers, and has been used in trace analyses. This strong lachrymator should be used in a hood. Hexacyclooctadecane and pentafluorobenzylbromide are used to prepare pentafluorobenzyldilute with 50mL 2-propanol. 1mL of this reagent will deri ...
... Pentafluorobenzylbromide is convenient for making esters and ethers, and has been used in trace analyses. This strong lachrymator should be used in a hood. Hexacyclooctadecane and pentafluorobenzylbromide are used to prepare pentafluorobenzyldilute with 50mL 2-propanol. 1mL of this reagent will deri ...
Synthetic Applications of Zinc Borohydride
... Chiral amino alcohols are useful in, among others, asymmetric synthesis,22 peptide and pharmaceutical chemistry,23 and the synthesis of insecticidal compounds.24 Earlier preparative methods used reduction of esters of amino acids by sodium in ethanol.25 Subsequently, LiAlH426 and NaBH427 were used f ...
... Chiral amino alcohols are useful in, among others, asymmetric synthesis,22 peptide and pharmaceutical chemistry,23 and the synthesis of insecticidal compounds.24 Earlier preparative methods used reduction of esters of amino acids by sodium in ethanol.25 Subsequently, LiAlH426 and NaBH427 were used f ...
iNTRODUCTiON TO ORGANiC COMPOUNDS
... systems and which are thought to be involved in the depletion of ozone in the upper atmosphere. This class of organic compounds is known as the halogenated hydrocarbons. In addition to their use in refrigerants they are used as solvents, aerosol sprays, antiseptics, dry cleaning fluids, insecticides ...
... systems and which are thought to be involved in the depletion of ozone in the upper atmosphere. This class of organic compounds is known as the halogenated hydrocarbons. In addition to their use in refrigerants they are used as solvents, aerosol sprays, antiseptics, dry cleaning fluids, insecticides ...
Derivatization reactions for the determination of amines by gas
... Phosphoamide formation Dimethylthiophosphinicchloride Dimethylthiophosphorylchloride Diethylthiophosphoryl chloride ...
... Phosphoamide formation Dimethylthiophosphinicchloride Dimethylthiophosphorylchloride Diethylthiophosphoryl chloride ...
Ch. 10 Notes with Answers
... 5. The formation of Grignard Reagents is completely general for all R-Halides: • 3º, 2º, and 1º alkyl halides all work well • Aryl and Vinyl halides as well as alkyl halides work well • RCl, RBr, and RI all work well • For class, we will normally use bromides, due to synthetic accessibility 6. View ...
... 5. The formation of Grignard Reagents is completely general for all R-Halides: • 3º, 2º, and 1º alkyl halides all work well • Aryl and Vinyl halides as well as alkyl halides work well • RCl, RBr, and RI all work well • For class, we will normally use bromides, due to synthetic accessibility 6. View ...
BSA + TMCS + TMSI - Sigma
... with single bonds) are separated by these phases. More polar phases, SPB-1701 and SP-2250, separate carbon-hydrogen analytes that also contain Br, Cl, F, N, O, P, or S atoms or groups. A highly polar cyanopropylphenylsiloxane phase, SP-2330, is useful for separating fatty acid methyl esters or aroma ...
... with single bonds) are separated by these phases. More polar phases, SPB-1701 and SP-2250, separate carbon-hydrogen analytes that also contain Br, Cl, F, N, O, P, or S atoms or groups. A highly polar cyanopropylphenylsiloxane phase, SP-2330, is useful for separating fatty acid methyl esters or aroma ...
74 CHAPTER-IV "LEAD (IV) ACETATE OXIDATIONS"
... With short chain alcohols eg, 1-propanol where 4-C cyclization didnot occur, complicated reactions were observed in benzene giving large number of products. ...
... With short chain alcohols eg, 1-propanol where 4-C cyclization didnot occur, complicated reactions were observed in benzene giving large number of products. ...
Haloalkane

The haloalkanes (also known, as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and commercial names. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes which contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone layer depleter. For more information, see Halomethane. Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula ″RX″ where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I).Haloalkanes have been known for centuries. Chloroethane was produced synthetically in the 15th century. The systematic synthesis of such compounds developed in the 19th century in step with the development of organic chemistry and the understanding of the structure of alkanes. Methods were developed for the selective formation of C-halogen bonds. Especially versatile methods included the addition of halogens to alkenes, hydrohalogenation of alkenes, and the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides. These methods are so reliable and so easily implemented that haloalkanes became cheaply available for use in industrial chemistry because the halide could be further replaced by other functional groups.While most haloalkanes are human-produced, non-artificial-source haloalkanes do occur on Earth, mostly through enzyme-mediated synthesis by bacteria, fungi, and especially sea macroalgae (seaweeds). More than 1600 halogenated organics have been identified, with bromoalkanes being the most common haloalkanes. Brominated organics in biology range from biologically produced methyl bromide to non-alkane aromatics and unsaturates (indoles, terpenes, acetogenins, and phenols). Halogenated alkanes in land plants are more rare, but do occur, as for example the fluoroacetate produced as a toxin by at least 40 species of known plants. Specific dehalogenase enzymes in bacteria which remove halogens from haloalkanes, are also known.