Basic Agricultural Chemistry - Macmillan Education South Africa
... and shape of its container. A gas can be compressed to occupy a smaller volume, or it can expand to occupy a larger one. The particles in a gas state of matter have very high kinetic energy and will move about very rapidly. They collide against one another so strongly that they move quite far apart ...
... and shape of its container. A gas can be compressed to occupy a smaller volume, or it can expand to occupy a larger one. The particles in a gas state of matter have very high kinetic energy and will move about very rapidly. They collide against one another so strongly that they move quite far apart ...
Holt Modern Chemistry Workbook: intro - ch 5
... Basic Research The goal of basic research is to increase knowledge. In chemistry, basic research includes the study of the properties of a chemical. It also includes the study of what happens when two chemicals are mixed. Sometimes, scientists do basic r esearch simply to satisfy their curiosity ...
... Basic Research The goal of basic research is to increase knowledge. In chemistry, basic research includes the study of the properties of a chemical. It also includes the study of what happens when two chemicals are mixed. Sometimes, scientists do basic r esearch simply to satisfy their curiosity ...
Export To Word
... A. A working definition of matter is that it takes up space, has mass, and has measurable properties. Matter is comprised of atomic, subatomic, and elementary particles. B. Electrons are key to defining chemical and some physical properties, reactivity, and molecular structures. Repeating (periodic) ...
... A. A working definition of matter is that it takes up space, has mass, and has measurable properties. Matter is comprised of atomic, subatomic, and elementary particles. B. Electrons are key to defining chemical and some physical properties, reactivity, and molecular structures. Repeating (periodic) ...
chemistry
... distinguished by their ability, in the solid state, to allow heat and electricity to pass through them (they are conductors as solids, unlike the vast majority of non-metals), and their density (metals are generally much heavier than non-metals). ...
... distinguished by their ability, in the solid state, to allow heat and electricity to pass through them (they are conductors as solids, unlike the vast majority of non-metals), and their density (metals are generally much heavier than non-metals). ...
Topic 1 Review - Capital High School
... period of the periodic table, and __________ as you go from the bottom to the top of a group in the table. 35. In general, as you go across a period in the periodic table from left to right: (1) the atomic radius __________; (2) the electron affinity becomes __________ negative; and (3) the first io ...
... period of the periodic table, and __________ as you go from the bottom to the top of a group in the table. 35. In general, as you go across a period in the periodic table from left to right: (1) the atomic radius __________; (2) the electron affinity becomes __________ negative; and (3) the first io ...
IB Chemistry Review. Unit I. Topics 2
... period of the periodic table, and __________ as you go from the bottom to the top of a group in the table. 35. In general, as you go across a period in the periodic table from left to right: (1) the atomic radius __________; (2) the electron affinity becomes __________ negative; and (3) the first io ...
... period of the periodic table, and __________ as you go from the bottom to the top of a group in the table. 35. In general, as you go across a period in the periodic table from left to right: (1) the atomic radius __________; (2) the electron affinity becomes __________ negative; and (3) the first io ...
Atomic combinations: Electronegativity and ionic
... You will remember that when atoms bond, electrons are either shared or they are transferred between the atoms that are bonding. In covalent bonding, electrons are shared between the atoms. There is another type of bonding, where electrons are transferred from one atom to another. This is called ioni ...
... You will remember that when atoms bond, electrons are either shared or they are transferred between the atoms that are bonding. In covalent bonding, electrons are shared between the atoms. There is another type of bonding, where electrons are transferred from one atom to another. This is called ioni ...
Chapter 9 Atomic Absorption and Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry
... Double-Beam Instruments: In double-beam instrument the beam from the hollow cathode source is split by a mirrored chopper, one half passing through the flame and the other half around it. The two beams are then recombined by a half-silvered mirror and passed into a grating monochromator; a photomul ...
... Double-Beam Instruments: In double-beam instrument the beam from the hollow cathode source is split by a mirrored chopper, one half passing through the flame and the other half around it. The two beams are then recombined by a half-silvered mirror and passed into a grating monochromator; a photomul ...
Bonding Notes
... points or boiling points. (Remember in vapor pressures the liquid with the highest intermolecular forces of attraction had the highest boiling point!) Thus ionic solids have high melting points! -Also ionic compounds in the solids state are in the fixed geometric patterns or crystal lattice. In the ...
... points or boiling points. (Remember in vapor pressures the liquid with the highest intermolecular forces of attraction had the highest boiling point!) Thus ionic solids have high melting points! -Also ionic compounds in the solids state are in the fixed geometric patterns or crystal lattice. In the ...
Preview to Mole Activity #2 preview_to_mole_activity_21
... water molecules. But how often do we as chemists limit our reactions to one or two molecules? Usually a reaction is done on a billion, trillion scale where an unimaginable number of molecules are involved. We need to count our molecules, how can we do this? This brings us to the Mole. We will start ...
... water molecules. But how often do we as chemists limit our reactions to one or two molecules? Usually a reaction is done on a billion, trillion scale where an unimaginable number of molecules are involved. We need to count our molecules, how can we do this? This brings us to the Mole. We will start ...
Chemistry - cloudfront.net
... 24. know the charges commonly found for ions in these families: alkali metal, alkaline earth, nitrogen family, oxygen family, halogens; know the charges for silver, zinc and aluminum 25. given a metal and non-metal from one of the families listed above, be able to predict the formula of its ionic co ...
... 24. know the charges commonly found for ions in these families: alkali metal, alkaline earth, nitrogen family, oxygen family, halogens; know the charges for silver, zinc and aluminum 25. given a metal and non-metal from one of the families listed above, be able to predict the formula of its ionic co ...
Empirical and Molecular Formulas and Percentage Composition
... While this is true, it’s impossible to actually study this reaction at the atomic level in a chemistry laboratory; we cannot count out just one or two atoms or molecules of anything! We have to use another way to measure out the necessary quantities of chlorine and potassium iodide. The mole A mole ...
... While this is true, it’s impossible to actually study this reaction at the atomic level in a chemistry laboratory; we cannot count out just one or two atoms or molecules of anything! We have to use another way to measure out the necessary quantities of chlorine and potassium iodide. The mole A mole ...
File
... must conserve all atoms of all types. o 1.E.2 Conservation of atoms makes it possible to compute the masses of substances involved in physical and chemical processes. Chemical processes result in the formation of new substances, and the amount of these depends on the number and the types and masses ...
... must conserve all atoms of all types. o 1.E.2 Conservation of atoms makes it possible to compute the masses of substances involved in physical and chemical processes. Chemical processes result in the formation of new substances, and the amount of these depends on the number and the types and masses ...
Some basic concepts of chemistry
... The three basic units, i.e., units of mass, length and time are independent units and cannot be derived from any other units, hence they are called fundamental units. The three fundamental units cannot describe all the physical quantities such as temperature, intensity of luminosity, electric curren ...
... The three basic units, i.e., units of mass, length and time are independent units and cannot be derived from any other units, hence they are called fundamental units. The three fundamental units cannot describe all the physical quantities such as temperature, intensity of luminosity, electric curren ...
Year Review Booklet (optional)
... Give directions on how to make 5.00 L of 0.020 M Ca(ClO)2 using solid Ca(ClO)2 and water. Include proper units in your work and in your answers. ...
... Give directions on how to make 5.00 L of 0.020 M Ca(ClO)2 using solid Ca(ClO)2 and water. Include proper units in your work and in your answers. ...
Chemistry - Plymouth Public Schools
... their properties (composition, mass, charge, and penetrating power). MA CHM 2.6 Describe the process of radioactive decay by using nuclear equations, and explain the concept of half-life for an isotope (for example, C-14 is a powerful tool in determining the age of objects). MA CHM 2.7 Compare and c ...
... their properties (composition, mass, charge, and penetrating power). MA CHM 2.6 Describe the process of radioactive decay by using nuclear equations, and explain the concept of half-life for an isotope (for example, C-14 is a powerful tool in determining the age of objects). MA CHM 2.7 Compare and c ...
971015 Exam - NTOU-Chem
... A) N to H atoms as does NH3 B) C to O atoms as does CO2 C) H to O atoms as does H2O D) C to H atoms as does C6 H6 E) N to O atoms as does NO2 Answer: E ...
... A) N to H atoms as does NH3 B) C to O atoms as does CO2 C) H to O atoms as does H2O D) C to H atoms as does C6 H6 E) N to O atoms as does NO2 Answer: E ...
Chapter 22 - 2012 Book Archive
... Group 13 is the first group to span the dividing line between metals and nonmetals, so its chemistry is more diverse than that of groups 1 and 2, which include only metallic elements. Except for the lightest element (boron), the group 13 elements are all relatively electropositive; that is, they ten ...
... Group 13 is the first group to span the dividing line between metals and nonmetals, so its chemistry is more diverse than that of groups 1 and 2, which include only metallic elements. Except for the lightest element (boron), the group 13 elements are all relatively electropositive; that is, they ten ...
CHE 128 Autumn 2011 Specific Objectives – Exam 1 A periodic
... Convert units using conversion factors Recall the density of water (1 g/cm3) Recall that 1 mL = 1 cm3 Calculate volume given the three spatial dimensions (length, width, height) of a substance Calculate density of a substance based on its mass and volume Compare densities to determine which substanc ...
... Convert units using conversion factors Recall the density of water (1 g/cm3) Recall that 1 mL = 1 cm3 Calculate volume given the three spatial dimensions (length, width, height) of a substance Calculate density of a substance based on its mass and volume Compare densities to determine which substanc ...
1 chemistry of the nonmetals
... Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe, accounting for 90% of the atoms and 75% of the mass of the universe. But hydrogen is much less abundant on earth. Even when the enormous number of hydrogen atoms in the oceans is included, hydrogen makes up less than 1% of the mass of the planet ...
... Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe, accounting for 90% of the atoms and 75% of the mass of the universe. But hydrogen is much less abundant on earth. Even when the enormous number of hydrogen atoms in the oceans is included, hydrogen makes up less than 1% of the mass of the planet ...
Ch1small - Rutgers University
... Gas – atoms or molecules are far apart and moving very fast. Liquid – particles are more closely packed and still moving relatively fast. Solid – held tightly together, usually in definite arrangements, wiggle (vibrate) only slowly in their fixed positions. ...
... Gas – atoms or molecules are far apart and moving very fast. Liquid – particles are more closely packed and still moving relatively fast. Solid – held tightly together, usually in definite arrangements, wiggle (vibrate) only slowly in their fixed positions. ...
Lecture Notes 1 - Rutgers University
... Gas – atoms or molecules are far apart and moving very fast. Liquid – particles are more closely packed and still moving relatively fast. Solid – held tightly together, usually in definite arrangements, wiggle (vibrate) only slowly in their fixed positions. ...
... Gas – atoms or molecules are far apart and moving very fast. Liquid – particles are more closely packed and still moving relatively fast. Solid – held tightly together, usually in definite arrangements, wiggle (vibrate) only slowly in their fixed positions. ...
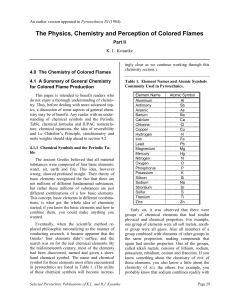
The Physics, Chemistry and Perception of Colored Flames
... not millions of different fundamental substances, but rather these millions of substances are just different combinations of a few basic elements. This concept, basic elements in different combinations, is what got the whole idea of chemistry started; if you knew the basic elements and how to combin ...
... not millions of different fundamental substances, but rather these millions of substances are just different combinations of a few basic elements. This concept, basic elements in different combinations, is what got the whole idea of chemistry started; if you knew the basic elements and how to combin ...