What do you know about light?
... • The atomic number of an element provides information about its atomic structure. • For example, the atomic number of fluorine is 9, indicating that there must be 9 protons in the nucleus. ...
... • The atomic number of an element provides information about its atomic structure. • For example, the atomic number of fluorine is 9, indicating that there must be 9 protons in the nucleus. ...
the atomic theory
... Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element are identical. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element; the atoms of different elements can be distinguished from one another by their respective relative weights. Atoms of one element c ...
... Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms. All atoms of a given element are identical. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element; the atoms of different elements can be distinguished from one another by their respective relative weights. Atoms of one element c ...
Chemistry Unit Study Guide Key
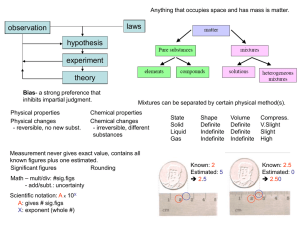
... 5) examples of physical changes – Breaking glass; melting ice; Cutting; Boiling 6) difference between physical and chemical changes – In a physical change, nothing new is formed. In a chemical change, a new substance is formed. 7) what it means if elements are in the same family/group – They have si ...
... 5) examples of physical changes – Breaking glass; melting ice; Cutting; Boiling 6) difference between physical and chemical changes – In a physical change, nothing new is formed. In a chemical change, a new substance is formed. 7) what it means if elements are in the same family/group – They have si ...
Slide 1 - Effingham County Schools
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... react with other forms of matter. For example, some substances are flammable. If they are heated with oxygen, they will react and burst into flames. The ability of a substance to combine with oxygen is an example of chemical property. ...
... react with other forms of matter. For example, some substances are flammable. If they are heated with oxygen, they will react and burst into flames. The ability of a substance to combine with oxygen is an example of chemical property. ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... react with other forms of matter. For example, some substances are flammable. If they are heated with oxygen, they will react and burst into flames. The ability of a substance to combine with oxygen is an example of chemical property. ...
... react with other forms of matter. For example, some substances are flammable. If they are heated with oxygen, they will react and burst into flames. The ability of a substance to combine with oxygen is an example of chemical property. ...
The Atom Power point - Effingham County Schools
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
Chapter 4 4.1 Defining the Atom • Early Models of the Atom atom
... one element are different from those of any other element 3) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. 4) Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated from each other, joined, or rearranged in a different c ...
... one element are different from those of any other element 3) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. 4) Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated from each other, joined, or rearranged in a different c ...
a) air c) milk f) beer
... one kind of atom. 3. A compound is a type of matter composed of two or more elements chemically combined in fixed ...
... one kind of atom. 3. A compound is a type of matter composed of two or more elements chemically combined in fixed ...
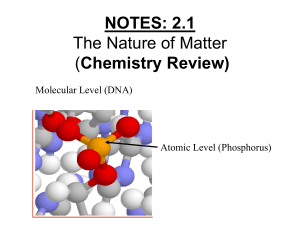
NOTES: 2.1 - Intro to Chemistry
... • In a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms are formed or broken, causing substances to combine and recombine as different molecules; • All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism are referred to as that organism’s METABOLISM. ...
... • In a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms are formed or broken, causing substances to combine and recombine as different molecules; • All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism are referred to as that organism’s METABOLISM. ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Reactions and Physical Changes
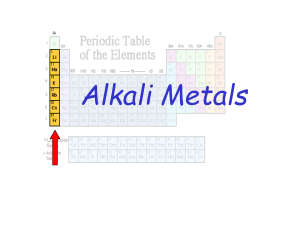
... • Mass number: total protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus • Atomic mass: the average mass of a sample of atoms of that element found in nature • Periodic table: chart that arranges elements by atomic number into rows and columns according to similarities in their properties ...
... • Mass number: total protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus • Atomic mass: the average mass of a sample of atoms of that element found in nature • Periodic table: chart that arranges elements by atomic number into rows and columns according to similarities in their properties ...
File
... b. How do you know? _____________________________________________________________________ c. Identify the solute: _____________________________________________________________________ d. Identify the solvent: ____________________________________________________________________ 1. List the 4 signs of ...
... b. How do you know? _____________________________________________________________________ c. Identify the solute: _____________________________________________________________________ d. Identify the solvent: ____________________________________________________________________ 1. List the 4 signs of ...
Chemical Bonding
... • A water molecule is polar because there is an uneven distribution of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. • Cohesion is attraction between molecules of the same substance. • Adhesion is an attraction between molecules of different substances. ...
... • A water molecule is polar because there is an uneven distribution of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. • Cohesion is attraction between molecules of the same substance. • Adhesion is an attraction between molecules of different substances. ...
Chapter 3 Discovering the atom and subatomic particles (History of
... Proust proposed the Law of Definite Proportions Henry Cavendish isolated hydrogen and Lavoisier named it meaning “water former”. Lavoisier also realized that water is not an element, but a compound. Joseph Proust found that hydrogen and oxygen always react in a particular mass ratio and proposed th ...
... Proust proposed the Law of Definite Proportions Henry Cavendish isolated hydrogen and Lavoisier named it meaning “water former”. Lavoisier also realized that water is not an element, but a compound. Joseph Proust found that hydrogen and oxygen always react in a particular mass ratio and proposed th ...
Chapter 3 Discovering the atom and subatomic particles (History of
... Proust proposed the Law of Definite Proportions Henry Cavendish isolated hydrogen and Lavoisier named it meaning “water former”. Lavoisier also realized that water is not an element, but a compound. Joseph Proust found that hydrogen and oxygen always react in a particular mass ratio and proposed th ...
... Proust proposed the Law of Definite Proportions Henry Cavendish isolated hydrogen and Lavoisier named it meaning “water former”. Lavoisier also realized that water is not an element, but a compound. Joseph Proust found that hydrogen and oxygen always react in a particular mass ratio and proposed th ...
JJ Thompson Webquest
... type of atom, therefore rejecting Newton's theory of chemical affinities. Dalton inferred proportions of elements in compounds by taking ratios of the weights of reactants, setting the atomic weight of hydrogen to be identically one. He proposed that chemical elements combine in integral ratios. Des ...
... type of atom, therefore rejecting Newton's theory of chemical affinities. Dalton inferred proportions of elements in compounds by taking ratios of the weights of reactants, setting the atomic weight of hydrogen to be identically one. He proposed that chemical elements combine in integral ratios. Des ...
atoms, molecules, and matter (2)
... All earthly objects are a mixture of: 1. EARTH (bottom – center of universe) 2. WATER (water covers earth) 3. AIR (air over water) 4. FIRE (highest – at top) 5. Ether = QUINTESSENCE (Latin) – substance whose natural motion is that most symmetrical and eternal of all conceivable motion = endless circ ...
... All earthly objects are a mixture of: 1. EARTH (bottom – center of universe) 2. WATER (water covers earth) 3. AIR (air over water) 4. FIRE (highest – at top) 5. Ether = QUINTESSENCE (Latin) – substance whose natural motion is that most symmetrical and eternal of all conceivable motion = endless circ ...
Minerals * Chemistry Review
... the atom its atomic mass • All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons ...
... the atom its atomic mass • All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons ...
Earth`s Chemistry
... Some atoms don’t have the same number of neutrons Each additional neutron increases the mass number. Isotopes = atoms of the same element that differ from each other by mass number. ...
... Some atoms don’t have the same number of neutrons Each additional neutron increases the mass number. Isotopes = atoms of the same element that differ from each other by mass number. ...
Chemical Bonds
... compounds An atom is chemically stable when it has a complete outer energy level ...
... compounds An atom is chemically stable when it has a complete outer energy level ...