Chapter 4 REVIEW
... 28. Chlorine is a very reactive element that forms stable compounds with most other elements. For each of the following chlorine compounds, draw Lewis and structural diagrams, and then predict the polarity of the molecules: (a) NCl3 (c) PCl5 (b) SiCl4 (d) SCl6 ...
... 28. Chlorine is a very reactive element that forms stable compounds with most other elements. For each of the following chlorine compounds, draw Lewis and structural diagrams, and then predict the polarity of the molecules: (a) NCl3 (c) PCl5 (b) SiCl4 (d) SCl6 ...
w/s dipole moments
... molecule to have bond moments and yet be nonpolar? 2. The dipole moments of the hydrogen halides decrease from HF to HI. Explain this trend. 3. Sketch the bond moments for the following molecules, and predict whether the molecule is polar (has a net dipole moment) or nonpolar: a. AlCl3 d. H2O g. PCl ...
... molecule to have bond moments and yet be nonpolar? 2. The dipole moments of the hydrogen halides decrease from HF to HI. Explain this trend. 3. Sketch the bond moments for the following molecules, and predict whether the molecule is polar (has a net dipole moment) or nonpolar: a. AlCl3 d. H2O g. PCl ...
Actinides (actinoids)
... - Laser ionisation separation Neutrons slowed by moderators For cooling many methods (water) ...
... - Laser ionisation separation Neutrons slowed by moderators For cooling many methods (water) ...
Investigating Chemistry - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... • When two elements from the upper right corner of the periodic table combine, we use a different system for naming these covalent compounds. • This results in discrete molecules with directional bonds. For example, H2O. • It can also result in an infinite network of covalently bonded atoms as in di ...
... • When two elements from the upper right corner of the periodic table combine, we use a different system for naming these covalent compounds. • This results in discrete molecules with directional bonds. For example, H2O. • It can also result in an infinite network of covalently bonded atoms as in di ...
Review 3rd Qtr KEY
... 13. Explain why chromium’s electron configuration is [Ar] 4s13d5 instead of the expected configuration of [Ar] 4s23d4 Filled & ½ filled orbital’s are more stable. 14. Complete the following question based upon Cobalt (#27) a) Give the noble gas electron configuration for this element: ______________ ...
... 13. Explain why chromium’s electron configuration is [Ar] 4s13d5 instead of the expected configuration of [Ar] 4s23d4 Filled & ½ filled orbital’s are more stable. 14. Complete the following question based upon Cobalt (#27) a) Give the noble gas electron configuration for this element: ______________ ...
Text questions - Corwin - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... 2. What was surprising about Wohler’s result of obtaining urea from ammonium cyanate? ...
... 2. What was surprising about Wohler’s result of obtaining urea from ammonium cyanate? ...
Chapt3
... 4. Types of Chemical Formulas (e.g., see Table 3.1) empirical formula shows the simplest ratio of the elements present molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms in one molecule structural formula shows how the atoms are connected e.g., for "hydrogen peroxide" the three formulas are: ...
... 4. Types of Chemical Formulas (e.g., see Table 3.1) empirical formula shows the simplest ratio of the elements present molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms in one molecule structural formula shows how the atoms are connected e.g., for "hydrogen peroxide" the three formulas are: ...
Naming Ionic Compounds
... this is harder because you must balance out the electronic charges to zero! use these rules: o write down the symbols for the elements in the order they appear in the compound name – the metal will always be first and the non metal second e.g. calcium chloride…. write down CaCl o figure out the ioni ...
... this is harder because you must balance out the electronic charges to zero! use these rules: o write down the symbols for the elements in the order they appear in the compound name – the metal will always be first and the non metal second e.g. calcium chloride…. write down CaCl o figure out the ioni ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions C Kapler ` , , I 27 O//#W SELF
... 3. Describe zinc as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid; main group, transition or posttransition element. Describe its place in the periodic table (group and period). ...
... 3. Describe zinc as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid; main group, transition or posttransition element. Describe its place in the periodic table (group and period). ...
Molecules, Compounds, and Chemical Equations (Chapter 3)
... 4. Types of Chemical Formulas (e.g., see Table 3.1) empirical formula shows the simplest ratio of the elements present molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms in one molecule structural formula shows how the atoms are connected e.g., for "hydrogen peroxide" the three formulas are: ...
... 4. Types of Chemical Formulas (e.g., see Table 3.1) empirical formula shows the simplest ratio of the elements present molecular formula shows the actual number of atoms in one molecule structural formula shows how the atoms are connected e.g., for "hydrogen peroxide" the three formulas are: ...
Document
... a Bunsen burner. Using any combination of these substances and common lab equipment, suggest a procedure below which will produce at least one new compound. Write a reaction to show how the new compound(s) form(s). Also, identify the formula for the new compound. NOTE: There are several acceptable p ...
... a Bunsen burner. Using any combination of these substances and common lab equipment, suggest a procedure below which will produce at least one new compound. Write a reaction to show how the new compound(s) form(s). Also, identify the formula for the new compound. NOTE: There are several acceptable p ...
Chapter 2 Reading Guide
... This chapter covers the basics that you may have learned in your chemistry class. Whether your teacher goes over this chapter, or assigns it for you do review on your own, the questions that follow should help you focus on the most important points. Concept 2.1 Matter consists of chemical elements i ...
... This chapter covers the basics that you may have learned in your chemistry class. Whether your teacher goes over this chapter, or assigns it for you do review on your own, the questions that follow should help you focus on the most important points. Concept 2.1 Matter consists of chemical elements i ...
Organic Chem WS - mvhs
... the parent structure. In the example, the longest chain contains seven carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent hydrocarbon structure is heptane. 2. Number the carbons in the main chain in sequence. To do this, start at the end that will give the groups attached to the chain the smallest numbers. 3. Add ...
... the parent structure. In the example, the longest chain contains seven carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent hydrocarbon structure is heptane. 2. Number the carbons in the main chain in sequence. To do this, start at the end that will give the groups attached to the chain the smallest numbers. 3. Add ...
Identifying Organic Compounds
... following: 1. All organic compounds contain carbon. Most inorganic compounds do not contain carbon. Carbon Dioxide is an exception. 2. In carbohydrate molecules, the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is 2:1; that is for every 2 molecules of hydrogen (H) there is 1 molecule of oxygen (O). 3. In lipids (fat ...
... following: 1. All organic compounds contain carbon. Most inorganic compounds do not contain carbon. Carbon Dioxide is an exception. 2. In carbohydrate molecules, the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is 2:1; that is for every 2 molecules of hydrogen (H) there is 1 molecule of oxygen (O). 3. In lipids (fat ...
SBI4U1.1Chemistry of Life
... Aldehydes if the carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon skeleton ...
... Aldehydes if the carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon skeleton ...
Electophilic Aromatic Substituion
... Evidence for Benzyne as an Intermediate • Bromobenzene with 14C only at C1 gives substitution product with label scrambled between C1 and C2 • Reaction proceeds through a symmetrical intermediate in which C1 and C2 are equivalent— must be benzyne ...
... Evidence for Benzyne as an Intermediate • Bromobenzene with 14C only at C1 gives substitution product with label scrambled between C1 and C2 • Reaction proceeds through a symmetrical intermediate in which C1 and C2 are equivalent— must be benzyne ...
CHEM 122: Introduction to Organic Chemistry Chapter 1: Organic
... artificial tanning lotions) d) ...
... artificial tanning lotions) d) ...
Chemical Equation
... Predicting Formulas of Ionic Compounds (cont.2) • When using subscripts for polyatomic ions, the ion is placed in parentheses, and the subscript is placed on the outside to indicate “x” ion units. – The subscript applies to all the elements in the ...
... Predicting Formulas of Ionic Compounds (cont.2) • When using subscripts for polyatomic ions, the ion is placed in parentheses, and the subscript is placed on the outside to indicate “x” ion units. – The subscript applies to all the elements in the ...
Group IV Elements
... because they can be just melted out of their minerals Ge was discovered after its existance has been predicted. It is purified from coal and zinc ore concentrates ...
... because they can be just melted out of their minerals Ge was discovered after its existance has been predicted. It is purified from coal and zinc ore concentrates ...
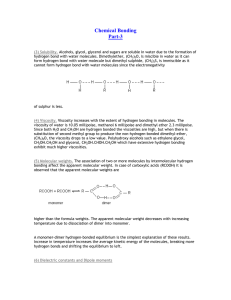
Chemical Bonding
... molecule is associated with four other water molecules in tetrahedral pattern. Ice has an open structure with large empty space due to existence of hydrogen-bonds. When ice melts a number of hydrogen bonds are broken and the space between water molecules decreases and the density of water increases, ...
... molecule is associated with four other water molecules in tetrahedral pattern. Ice has an open structure with large empty space due to existence of hydrogen-bonds. When ice melts a number of hydrogen bonds are broken and the space between water molecules decreases and the density of water increases, ...
.
... trace amount of cholestanone and base gives 90% cholestanol and 10% of its stereoisomer known as epicholestanol. However, similar equilibration of coprostanol (in the presence of coprostanone) gives 10% coprostanol and 90% epicoprostanol. (To explain such observation, you must draw the boat form con ...
... trace amount of cholestanone and base gives 90% cholestanol and 10% of its stereoisomer known as epicholestanol. However, similar equilibration of coprostanol (in the presence of coprostanone) gives 10% coprostanol and 90% epicoprostanol. (To explain such observation, you must draw the boat form con ...
Solubility of Alcohols
... By definition, an Alcohol is an organic compound containing a –OH grouping. Each of the above are referred to as n-Alcohols, or Normal Alcohols, as the –OH group occurs at the end of the carbon chain. ...
... By definition, an Alcohol is an organic compound containing a –OH grouping. Each of the above are referred to as n-Alcohols, or Normal Alcohols, as the –OH group occurs at the end of the carbon chain. ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.