Chapter 3 – Carbon Compounds
... other electrons from other elements. This allows it to make lots of combinations. • ORGANIC COMPOUNDS are made primarily from carbon atoms. They are found in things that were once living or are now living. – Fossil fuels are organic compounds – they are decayed trees, algaes in ponds, swamp plants ...
... other electrons from other elements. This allows it to make lots of combinations. • ORGANIC COMPOUNDS are made primarily from carbon atoms. They are found in things that were once living or are now living. – Fossil fuels are organic compounds – they are decayed trees, algaes in ponds, swamp plants ...
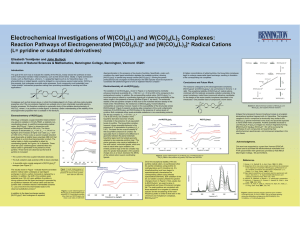
Electrochemical Investigations of W(CO) (L) and W(CO) (L) Complexes:
... moeity, such as Re(CO)3(LL), where LL = a polypyridyl ligand such as 2,2’-bipyridine (bpy), 1,10phenanthroline or related ligands, would be bridged to a non-emissive second metal center, W(CO)5 in this example, that undergoes reversible redox processes. Such compounds could potentially have “redox-t ...
... moeity, such as Re(CO)3(LL), where LL = a polypyridyl ligand such as 2,2’-bipyridine (bpy), 1,10phenanthroline or related ligands, would be bridged to a non-emissive second metal center, W(CO)5 in this example, that undergoes reversible redox processes. Such compounds could potentially have “redox-t ...
presentation - WordPress.com
... an extra electron is added to an atom. For the bond formation electron gain enthalpy of an element should be high. ...
... an extra electron is added to an atom. For the bond formation electron gain enthalpy of an element should be high. ...
Lipids practice problems
... 3) In the formation of a triglyceride, what functional groups chemically combine and what functional group is formed? 4) How does the presence of a double bond in a fatty acid (or a molecule containing a fatty acyl chain) affect its physical properties. 5) Arrange the following fatty acids in order ...
... 3) In the formation of a triglyceride, what functional groups chemically combine and what functional group is formed? 4) How does the presence of a double bond in a fatty acid (or a molecule containing a fatty acyl chain) affect its physical properties. 5) Arrange the following fatty acids in order ...
MIDTERM EXAM – JANUARY, 2003
... 73. Describe how ionization energy changes as you move across the periodic table. 74. Describe how electronegativity changes as you move across the periodic table. 75. The transition metals occupy the ______________ block of the periodic table 76. The alkali metals and alkaline earth metals occupy t ...
... 73. Describe how ionization energy changes as you move across the periodic table. 74. Describe how electronegativity changes as you move across the periodic table. 75. The transition metals occupy the ______________ block of the periodic table 76. The alkali metals and alkaline earth metals occupy t ...
Ionic Bonding - Effingham County Schools
... •The Octet Rule is the basis for the predictions about the charges on ions. •Ionic compounds are formed as a result of the formation of (+) and (-) ions. ...
... •The Octet Rule is the basis for the predictions about the charges on ions. •Ionic compounds are formed as a result of the formation of (+) and (-) ions. ...
I. Introduction to NMR spectroscopy
... What elements are commonly found in organic molecules? Which are suitable for NMR? element: ...
... What elements are commonly found in organic molecules? Which are suitable for NMR? element: ...
In the preparation of the esters given in this experiment
... 15. Caffeine is soluble in ethyl acetate. Do you think that the purity of your product could be checked by TLC using ethyl acetate as an elution solvent? Explain. 16. List several advantages and disadvantages of steam distillation as a method of purification. 17. Explain why the distillate collected ...
... 15. Caffeine is soluble in ethyl acetate. Do you think that the purity of your product could be checked by TLC using ethyl acetate as an elution solvent? Explain. 16. List several advantages and disadvantages of steam distillation as a method of purification. 17. Explain why the distillate collected ...
S3 Summary - Glow Blogs
... IONS are formed. The oppositely charged ions attract each other strongly. This attraction is an IONIC BOND. In an ionic compound the ions arrange themselves in a regular pattern. ...
... IONS are formed. The oppositely charged ions attract each other strongly. This attraction is an IONIC BOND. In an ionic compound the ions arrange themselves in a regular pattern. ...
The Ties That Bind
... or covalent: The bond in CsCl; the bond in H2S; and the NN bond in H2NNH2. ...
... or covalent: The bond in CsCl; the bond in H2S; and the NN bond in H2NNH2. ...
Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
... chemical compound that can take place in a chemical reaction. • Has the same chemical properties of that element or compound. • Some molecules consist of two atoms of the same element. • Ex. O2 • Other molecules consists of two or more atoms. • Ex. (H2O) ...
... chemical compound that can take place in a chemical reaction. • Has the same chemical properties of that element or compound. • Some molecules consist of two atoms of the same element. • Ex. O2 • Other molecules consists of two or more atoms. • Ex. (H2O) ...
Chapter 2 - Families of Carbon Compounds
... alcohol has the functional group known as a hydroxyl group, −OH, that attaches to an sp3 -hybridized ...
... alcohol has the functional group known as a hydroxyl group, −OH, that attaches to an sp3 -hybridized ...
CHEM 203 Important Topics for Review – See Chapters 1
... Presence of two independent π-bonds in acetylene leftover p-type atomic orbitals (in the plane of the paper) ...
... Presence of two independent π-bonds in acetylene leftover p-type atomic orbitals (in the plane of the paper) ...
Interactive comment on “Observations of oxidation products
... Taking a closer look, I do see quite a number of questions: Several other previous experiments have found that ozone can lead to the formation of oxidated organic artifact compounds (in particular long-chain n-aldehydes) in Teflon sampling materials/tubing. Do the observed OXx profiles possibly corr ...
... Taking a closer look, I do see quite a number of questions: Several other previous experiments have found that ozone can lead to the formation of oxidated organic artifact compounds (in particular long-chain n-aldehydes) in Teflon sampling materials/tubing. Do the observed OXx profiles possibly corr ...
論 文 の 内 容 の 要 旨 論文題目 Synthesis and Property of Low
... reaction of boryllithium with borane-THF complex afforded the first boryl-substituted borohydride, lithium boryltrihydroborate in 19% isolated yield (Scheme 1). This compound was fully characterized by NMR spectroscopy, elemental analysis, and X-ray crystallographic study. The result of NMR study in ...
... reaction of boryllithium with borane-THF complex afforded the first boryl-substituted borohydride, lithium boryltrihydroborate in 19% isolated yield (Scheme 1). This compound was fully characterized by NMR spectroscopy, elemental analysis, and X-ray crystallographic study. The result of NMR study in ...
Nomenclature
... • Some compounds contain H2O in their structure. These compounds are called hydrates. • This is different from (aq) because the H2O is part of the molecule (not just surrounding it). • The H2O can usually be removed if heated. • A dot separates water: e.g. CuSO4•5H2O is ...
... • Some compounds contain H2O in their structure. These compounds are called hydrates. • This is different from (aq) because the H2O is part of the molecule (not just surrounding it). • The H2O can usually be removed if heated. • A dot separates water: e.g. CuSO4•5H2O is ...
Ionic Bonding - petersonORHS
... obtain a full set of eight (8) valence electrons. • Valence- refers to the outer electrons in an atom. These are the electrons on the outer shell, which is the highest energy level. ...
... obtain a full set of eight (8) valence electrons. • Valence- refers to the outer electrons in an atom. These are the electrons on the outer shell, which is the highest energy level. ...
Chapter 2: The Chemical Context of Life
... ● Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties: – Structural isomers have different covalent arrangements of their atoms – Geometric isomers have the same covalent arrangements but differ in spatial arrangements – Enantiomers are isomers that are mirr ...
... ● Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties: – Structural isomers have different covalent arrangements of their atoms – Geometric isomers have the same covalent arrangements but differ in spatial arrangements – Enantiomers are isomers that are mirr ...
ch15 by dr Dina
... Ortho-Para Direction and Reactivity of Alkylbenzenes Alkyl groups activate aromatic rings by inductively stabilizing the transition state leading to the arenium ion Alkyl groups are ortho-para directors because they inductively stabilize one of the resonance forms of the arenium ion in ortho an ...
... Ortho-Para Direction and Reactivity of Alkylbenzenes Alkyl groups activate aromatic rings by inductively stabilizing the transition state leading to the arenium ion Alkyl groups are ortho-para directors because they inductively stabilize one of the resonance forms of the arenium ion in ortho an ...
NOTES: CH 2-4
... ● Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties: – Structural isomers have different covalent arrangements of their atoms – Geometric isomers have the same covalent arrangements but differ in spatial arrangements – Enantiomers are isomers that are mirr ...
... ● Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties: – Structural isomers have different covalent arrangements of their atoms – Geometric isomers have the same covalent arrangements but differ in spatial arrangements – Enantiomers are isomers that are mirr ...
Chapter 4 Carbon
... four covalent bonds with a variety of atoms • This tetravalence makes large, complex molecules possible • In molecules with multiple carbons, each carbon bonded to four other atoms has a tetrahedral shape • However, when two carbon atoms are joined by a double bond, the atoms joined to the carbons a ...
... four covalent bonds with a variety of atoms • This tetravalence makes large, complex molecules possible • In molecules with multiple carbons, each carbon bonded to four other atoms has a tetrahedral shape • However, when two carbon atoms are joined by a double bond, the atoms joined to the carbons a ...
AP Biology - cloudfront.net
... In structural isomers, the atoms and functional groups are joined together in different ways, as in the example of propyl alcohol above. This group includes chain isomerism whereby hydrocarbon chains have variable amounts of branching; position isomerism which deals with the position of a functional ...
... In structural isomers, the atoms and functional groups are joined together in different ways, as in the example of propyl alcohol above. This group includes chain isomerism whereby hydrocarbon chains have variable amounts of branching; position isomerism which deals with the position of a functional ...
Organic and Biological Molecules
... There is a separate class of cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbons called aromatic hydrocarbons. These compounds have a planar ring structure and a delocalized π system. The extended pi bonding provides exceptional stability to these molecules. Unlike other hydrocarbons, they do not burn well or cleanly. ...
... There is a separate class of cyclic unsaturated hydrocarbons called aromatic hydrocarbons. These compounds have a planar ring structure and a delocalized π system. The extended pi bonding provides exceptional stability to these molecules. Unlike other hydrocarbons, they do not burn well or cleanly. ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.