The HR Diagram Interpreted: Properties of Stars
... Notice that we do not measure these sizes directly: essentially all the stars appear as unresolved points of light. But knowing their intrinsic luminosities (how much total energy they emit) and their surface temperatures tells us their sizes right away! (The study of eclipsing binary stars allows u ...
... Notice that we do not measure these sizes directly: essentially all the stars appear as unresolved points of light. But knowing their intrinsic luminosities (how much total energy they emit) and their surface temperatures tells us their sizes right away! (The study of eclipsing binary stars allows u ...
$doc.title
... of the Earth. What is the effect of increasing the cloud cover on the equilibrium temperature of our planet? ...
... of the Earth. What is the effect of increasing the cloud cover on the equilibrium temperature of our planet? ...
Making H-R Diagrams - PLC-METS
... Making an H-R Diagram BACKGOUND INFORMATION: Stars in the sky are not created equal and are composed of different materials, different temperatures, different brightness, different sizes, and different distances from Earth. A star’s mass dictates how bright it will be, how long it will live, its tem ...
... Making an H-R Diagram BACKGOUND INFORMATION: Stars in the sky are not created equal and are composed of different materials, different temperatures, different brightness, different sizes, and different distances from Earth. A star’s mass dictates how bright it will be, how long it will live, its tem ...
Branches of Earth Science
... White ______________ (size of Earth) Medium Size (the sun) *MOST ______________ * ______________ (10-1000 x’s the sun) o Largest ______________ Giant (1000 x the diameter of the sun) o Belelgeus o Rigel o Antares Composition (______________ Makeup) o Most stars have the ______________ general ...
... White ______________ (size of Earth) Medium Size (the sun) *MOST ______________ * ______________ (10-1000 x’s the sun) o Largest ______________ Giant (1000 x the diameter of the sun) o Belelgeus o Rigel o Antares Composition (______________ Makeup) o Most stars have the ______________ general ...
Chapter20
... Black Holes at Galactic Centers? Recent results by astronomers using the Hubble Space Telescope now indicate that most - and possibly even all - large galaxies may harbor a black hole. In all the galaxies studied, star speeds continue to increase closer the very center. This indicates a center mill ...
... Black Holes at Galactic Centers? Recent results by astronomers using the Hubble Space Telescope now indicate that most - and possibly even all - large galaxies may harbor a black hole. In all the galaxies studied, star speeds continue to increase closer the very center. This indicates a center mill ...
That is an irrelevant question, Ms Gajda, there was no
... That cooler star could be bigger than the hotter star therefore it would appear brighter from Earth. The cooler star could also be closer than the hotter star. 16. Out of which material do stars begin to form? Hydrogen/gas and dust found in nebulae 17. What are the nuclear reactions that take place ...
... That cooler star could be bigger than the hotter star therefore it would appear brighter from Earth. The cooler star could also be closer than the hotter star. 16. Out of which material do stars begin to form? Hydrogen/gas and dust found in nebulae 17. What are the nuclear reactions that take place ...
Stars - HMXEarthScience
... 1. Large clouds of dust and gas are pulled together by gravity (these clouds are called nebulae) 2. Gases in the nebula contract due to gravity, resulting in the formation of a protostar. 3. Pressure and temperature increase until the gases “ignite” and nuclear fusion begins 4. Once the star has ful ...
... 1. Large clouds of dust and gas are pulled together by gravity (these clouds are called nebulae) 2. Gases in the nebula contract due to gravity, resulting in the formation of a protostar. 3. Pressure and temperature increase until the gases “ignite” and nuclear fusion begins 4. Once the star has ful ...
OUSNMAY06 - The George Abell Observatory
... the borders of Canes Venatici and Ursa Major. NGC4395 (11.0) sg. Bright core with a low surface brightness circular halo. NGC4449 (10.5) ir. Appears almost rectangular making it an unusual object to view. NGC4485 (12.5) ir and NGC4490 (10.1) sg. Interacting pair of galaxies. NGC4631 (9.7) sg and NG4 ...
... the borders of Canes Venatici and Ursa Major. NGC4395 (11.0) sg. Bright core with a low surface brightness circular halo. NGC4449 (10.5) ir. Appears almost rectangular making it an unusual object to view. NGC4485 (12.5) ir and NGC4490 (10.1) sg. Interacting pair of galaxies. NGC4631 (9.7) sg and NG4 ...
LIGO Star Chart
... super giant and that if our sun were to be replaced by Betelgeuse the surface of the star’s atmosphere would extend almost to the orbit of Jupiter! Betelgeuse is a very old star that is a prime candidate for self-destruction in a supernova explosion. If we were to begin seeing the explosion today, i ...
... super giant and that if our sun were to be replaced by Betelgeuse the surface of the star’s atmosphere would extend almost to the orbit of Jupiter! Betelgeuse is a very old star that is a prime candidate for self-destruction in a supernova explosion. If we were to begin seeing the explosion today, i ...
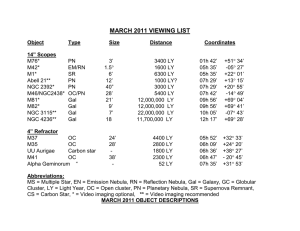
March
... M82 is an irregular galaxy of 8th magnitude in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh-MAY-jer). Also known as the Cigar Galaxy for it’s elongated shape, M82 is also about 12 million Light Years distant. The close encounter with M81 described above distorted the shape of this irregular galaxy, creatin ...
... M82 is an irregular galaxy of 8th magnitude in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh-MAY-jer). Also known as the Cigar Galaxy for it’s elongated shape, M82 is also about 12 million Light Years distant. The close encounter with M81 described above distorted the shape of this irregular galaxy, creatin ...
Practice questions for Stars File
... 1. Describe the difference in the stages of the life cycle for a large and massive star compared to an average star 2. Describe the fuel use changes from birth to death for a black hole 3. Describe the fuel use changes from birth to death for a neutron star 4. Explain how the energy changes are invo ...
... 1. Describe the difference in the stages of the life cycle for a large and massive star compared to an average star 2. Describe the fuel use changes from birth to death for a black hole 3. Describe the fuel use changes from birth to death for a neutron star 4. Explain how the energy changes are invo ...
The life of a Star (pages 468-471)
... 2. Explain how a nebula turns into a cloud leading to a star (3 steps)? 3. What happens when a star runs out of the fuels needed to produce energy? 4. What is a supernova? During this stage, what happens to the core of the star? When our Sun eventually swells into a red giant star, its outer layer ...
... 2. Explain how a nebula turns into a cloud leading to a star (3 steps)? 3. What happens when a star runs out of the fuels needed to produce energy? 4. What is a supernova? During this stage, what happens to the core of the star? When our Sun eventually swells into a red giant star, its outer layer ...
Review Questions for Chp 2
... 77. In summer in Doylestown what kind of rays from the sun are we receiving? ...
... 77. In summer in Doylestown what kind of rays from the sun are we receiving? ...
At the Heart of the Matter: The Blue White Dwarf in M 57. Paul Temple
... molecular or atomic carbon in any part of the spectrum. These stars are cool enough so that H atoms can join together into molecules, and so the signature of molecular H may also be observed. DZ Stars exhibiting only metal lines from species such as Ca and Fe. No H or He present. ...
... molecular or atomic carbon in any part of the spectrum. These stars are cool enough so that H atoms can join together into molecules, and so the signature of molecular H may also be observed. DZ Stars exhibiting only metal lines from species such as Ca and Fe. No H or He present. ...
Stars
... size, temperature, and distance from the observer. The hotter the star, the brighter its color. Blue and white stars are the brightest and hottest stars. Red stars are the dimmest and coolest. ...
... size, temperature, and distance from the observer. The hotter the star, the brighter its color. Blue and white stars are the brightest and hottest stars. Red stars are the dimmest and coolest. ...
Stars
... • They look small because they are a long way away, but in fact many are bigger and brighter than our Sun. • The heat of the star is made in the center by nuclear fusion reactions. • There are lots of different colours and sizes of stars. ...
... • They look small because they are a long way away, but in fact many are bigger and brighter than our Sun. • The heat of the star is made in the center by nuclear fusion reactions. • There are lots of different colours and sizes of stars. ...
PPT - University of Delaware
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
Theoretical Modeling of Massive Stars Mr. Russell University of Delaware
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
Document
... d. iron is the most tightly bound of all nuclei. e. massive stars supernova before they create an iron core. 23. Synchrotron radiation is produced by a. objects with temperature below 10,000 K. b. high-velocity electrons moving through a magnetic field. c. cold hydrogen atoms in space. d. the collap ...
... d. iron is the most tightly bound of all nuclei. e. massive stars supernova before they create an iron core. 23. Synchrotron radiation is produced by a. objects with temperature below 10,000 K. b. high-velocity electrons moving through a magnetic field. c. cold hydrogen atoms in space. d. the collap ...
Astronomy Review - Cockeysville Middle
... because it travels so quickly, all light takes time to go any distance. Light travels at 3 x 108 m/s. To the right, are some light travel times. Even when I look at you, I see what was! The further away we look, the further back in time we see. ...
... because it travels so quickly, all light takes time to go any distance. Light travels at 3 x 108 m/s. To the right, are some light travel times. Even when I look at you, I see what was! The further away we look, the further back in time we see. ...
How many stars are visible to the naked eye in the night sky?
... A light-year is a measure of... ...
... A light-year is a measure of... ...
Size Color and Temperature
... Some stars are much larger than the Sun. Giant and supergiant stars range from ten to hundreds of times larger. A supergiant called Betelgeuse (BEET-uhl-JOOZ) is more than 600 times greater in diameter than the Sun. If Betelgeuse replaced the Sun, it would fill space in our solar system well beyond ...
... Some stars are much larger than the Sun. Giant and supergiant stars range from ten to hundreds of times larger. A supergiant called Betelgeuse (BEET-uhl-JOOZ) is more than 600 times greater in diameter than the Sun. If Betelgeuse replaced the Sun, it would fill space in our solar system well beyond ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.