parallax in arc seconds
... and much smaller than our Sun. It is roughly the size of Earth. It is a white dwarf star. Any star smaller than our Sun is called a dwarf. ...
... and much smaller than our Sun. It is roughly the size of Earth. It is a white dwarf star. Any star smaller than our Sun is called a dwarf. ...
Only Thirty Questions To Go (150,000 points) 1.) If the distance
... 12.) The Earth is closest to the Sun when… A – it is at perihelion. B – it going the fastest. C – when it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere. D – All of the above. 13.) The Hubble Space Telescope in orbit is in… B – free-fall. 14.) Most people spend little time looking at the stars because… A – ai ...
... 12.) The Earth is closest to the Sun when… A – it is at perihelion. B – it going the fastest. C – when it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere. D – All of the above. 13.) The Hubble Space Telescope in orbit is in… B – free-fall. 14.) Most people spend little time looking at the stars because… A – ai ...
PHYS 2410 General Astronomy Homework 5
... I. the latitude at which sunspots are visible at a given time. II. the number of sunspots that are visible at a given time. III. the rotation rate of the sun's equator at a given time. ...
... I. the latitude at which sunspots are visible at a given time. II. the number of sunspots that are visible at a given time. III. the rotation rate of the sun's equator at a given time. ...
Midterm Exam - 2 Set B Solution
... • Write your name, SB ID number and Lab section (A/B) on each blue book you use. • Solve any four of the five problems and start a new problem solution on a new page • You can use one A4 size formula sheet and use any non programmable calculator. Constants: c = 3 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10−34 J s, e ...
... • Write your name, SB ID number and Lab section (A/B) on each blue book you use. • Solve any four of the five problems and start a new problem solution on a new page • You can use one A4 size formula sheet and use any non programmable calculator. Constants: c = 3 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10−34 J s, e ...
Lives of Stars - Madison County Schools
... outshine the entire galaxy (300,000,000,000 stars) it was in. Supernovae can be seen from Earth. There are historic records of some stars that were so bright that they could be seen during the day for weeks at a time. ...
... outshine the entire galaxy (300,000,000,000 stars) it was in. Supernovae can be seen from Earth. There are historic records of some stars that were so bright that they could be seen during the day for weeks at a time. ...
Astro 1 & 100 Levine Homework Stars Name:____________________________
... Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Dimmest Or, all have the same apparent brightness ______________ 3. Rank these stars in order of distance from the Sun, from closest to farthest (Hint: you only need to know m — M to figure this out!) ...
... Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Dimmest Or, all have the same apparent brightness ______________ 3. Rank these stars in order of distance from the Sun, from closest to farthest (Hint: you only need to know m — M to figure this out!) ...
PPT Format - HubbleSOURCE
... a system of two objects in space (usually stars), which are so close that their gravitational interaction causes them to orbit around their common center of mass. ...
... a system of two objects in space (usually stars), which are so close that their gravitational interaction causes them to orbit around their common center of mass. ...
What is a T Tauri star?
... photons, close to star (also seen in solar chromosphere) • Used to model accretion – Asymmetric shape – Doppler broadening >100 km/s (supersonic) ...
... photons, close to star (also seen in solar chromosphere) • Used to model accretion – Asymmetric shape – Doppler broadening >100 km/s (supersonic) ...
GIZMO H-RDiagramSE
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
... Gizmo Warm-up In the early 1900s, astronomers were able to identify many star characteristics such as color, size, temperature, and luminosity—or how bright a star is. However, astronomers did not yet understand exactly how these characteristics were related. Using the H-R Diagram Gizmo™, you will d ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 •
... • Composite spectrum binary: Two stellar spectra • Eclipsing binary: Information from “light curves” • Astrometric binary: Watch a “single” star wobble • Spectrographic binary: Doppler shifted spectrum ...
... • Composite spectrum binary: Two stellar spectra • Eclipsing binary: Information from “light curves” • Astrometric binary: Watch a “single” star wobble • Spectrographic binary: Doppler shifted spectrum ...
HOMEWORK #1
... Just as brightness is related to apparent magnitude, luminosity is related to a term called “absolute magnitude.” Astronomers refer to a star’s “absolute magnitude (M)” as the apparent magnitude it would have at an arbitrary standardized distance of 10 parsecs (i.e., 32.6 light-years). #2. Combine ...
... Just as brightness is related to apparent magnitude, luminosity is related to a term called “absolute magnitude.” Astronomers refer to a star’s “absolute magnitude (M)” as the apparent magnitude it would have at an arbitrary standardized distance of 10 parsecs (i.e., 32.6 light-years). #2. Combine ...
Word
... Just as brightness is related to apparent magnitude, luminosity is related to a term called “absolute magnitude.” Astronomers refer to a star’s “absolute magnitude (M)” as the apparent magnitude it would have at an arbitrary standardized distance of 10 parsecs (i.e., 32.6 light-years). #2. Combine ...
... Just as brightness is related to apparent magnitude, luminosity is related to a term called “absolute magnitude.” Astronomers refer to a star’s “absolute magnitude (M)” as the apparent magnitude it would have at an arbitrary standardized distance of 10 parsecs (i.e., 32.6 light-years). #2. Combine ...
Stellar Evolution - Hays High Indians
... concentrated in the central regions of the galaxy. The X-ray source could be another example of a veiled black hole associated with a Type 2 Quasar. This discovery adds to a CXO 0312 Fiore P3 (CXOUJ031238.9growing body of evidence that our 765134): A possible Type 2 quasar veiled black hole.(Credit: ...
... concentrated in the central regions of the galaxy. The X-ray source could be another example of a veiled black hole associated with a Type 2 Quasar. This discovery adds to a CXO 0312 Fiore P3 (CXOUJ031238.9growing body of evidence that our 765134): A possible Type 2 quasar veiled black hole.(Credit: ...
North Star pulses brightly with constant change
... Polaris is only the 49th-brightest star visible from Earth. But two things make Polaris special. One is that the spin axis of Earth happens to be pointing toward it, which is why we call it the "North Star." The other is that Polaris is the closest Cepheid variable. I've written before about these s ...
... Polaris is only the 49th-brightest star visible from Earth. But two things make Polaris special. One is that the spin axis of Earth happens to be pointing toward it, which is why we call it the "North Star." The other is that Polaris is the closest Cepheid variable. I've written before about these s ...
Classifying Stars - Concord Academy Boyne
... of years. These small stars die quietly, and in their place, a small white dwarf is left behind. ...
... of years. These small stars die quietly, and in their place, a small white dwarf is left behind. ...
Activity 10: Lifecycle Of A Star
... 7. If the leftover core was above a certain mass, it will continue to collapse in on itself and form a ___________ area called a singularity or __________ __________. Its gravity is so powerful that nothing within its range can escape it - not even ___________! ...
... 7. If the leftover core was above a certain mass, it will continue to collapse in on itself and form a ___________ area called a singularity or __________ __________. Its gravity is so powerful that nothing within its range can escape it - not even ___________! ...
chapter-30-pp
... the surface of a star or in the vicinity of a black hole. A cosmological red shift only begins to affect the light from galaxies at great distances from the earth. This happens due to the expansion of the universe. The expansion causes more distant objects to move ...
... the surface of a star or in the vicinity of a black hole. A cosmological red shift only begins to affect the light from galaxies at great distances from the earth. This happens due to the expansion of the universe. The expansion causes more distant objects to move ...
The HR Diagram Interpreted (PowerPoint version)
... Notice that we do not measure these sizes directly: essentially all the stars appear as unresolved points of light. But knowing their intrinsic luminosities (how much total energy they emit) and their surface temperatures tells us their sizes right away! (The study of eclipsing binary stars allows u ...
... Notice that we do not measure these sizes directly: essentially all the stars appear as unresolved points of light. But knowing their intrinsic luminosities (how much total energy they emit) and their surface temperatures tells us their sizes right away! (The study of eclipsing binary stars allows u ...
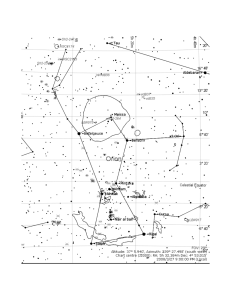
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.