Stars and Light
... out) gravity will force the sun to collapse, which will increase the temperature so He can fuse (to form carbon). • When it does this, the outer layers “explode” and it becomes a Red Giant star. ...
... out) gravity will force the sun to collapse, which will increase the temperature so He can fuse (to form carbon). • When it does this, the outer layers “explode” and it becomes a Red Giant star. ...
02-02Stars_Part_One
... size, temperature, and distance. -1 is bright, 6 is dim •Absolute magnitude: Apparent magnitude at a distance of 10 parsecs. Factor of only size and temperature ...
... size, temperature, and distance. -1 is bright, 6 is dim •Absolute magnitude: Apparent magnitude at a distance of 10 parsecs. Factor of only size and temperature ...
The Sun and Other Stars - Tuslaw Local School District
... 2 or more stars called star systems • Binary stars - star systems w/ 2 stars • Triple stars - 3 stars ...
... 2 or more stars called star systems • Binary stars - star systems w/ 2 stars • Triple stars - 3 stars ...
"Stars" Power Point notes
... • 90% of stars fall on a diagonal, curved line, called the main sequence. • The remaining stars fall into one of three other groups. - Red giants - Supergiants - White dwarfs ...
... • 90% of stars fall on a diagonal, curved line, called the main sequence. • The remaining stars fall into one of three other groups. - Red giants - Supergiants - White dwarfs ...
The Future Sun • Homework 5 is due Wed, 24 March at 6:30am
... If stars A-D replaced the sun, would people be able to live in Michigan? a. b. c. d. e. ...
... If stars A-D replaced the sun, would people be able to live in Michigan? a. b. c. d. e. ...
Astronomy - AG Web Services
... ASTRONOMY 1. Define astronomy and name two important astronomers. 2. Explain the major differences between the following: planets, moons, stars, comets, asteroids, meteoroids, solar systems, and galaxies. 3. Find one interesting fact about each planet in our solar system. Draw a chart or make a disp ...
... ASTRONOMY 1. Define astronomy and name two important astronomers. 2. Explain the major differences between the following: planets, moons, stars, comets, asteroids, meteoroids, solar systems, and galaxies. 3. Find one interesting fact about each planet in our solar system. Draw a chart or make a disp ...
Star Life Cycle – Web Activity
... 3. How long ago was our sun born in a nebula? Protostar 4. Click on the animation that shows how a star forms from a nebula. Describe why the core of a forming star is hot. ...
... 3. How long ago was our sun born in a nebula? Protostar 4. Click on the animation that shows how a star forms from a nebula. Describe why the core of a forming star is hot. ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... Task #4: Types of Stars Continue to read on to the section “Types of Stars” on the same webpage http://www.seasky.org/cosmic/sky7a01.html and answer the following questions: 1. What does the main ...
... Task #4: Types of Stars Continue to read on to the section “Types of Stars” on the same webpage http://www.seasky.org/cosmic/sky7a01.html and answer the following questions: 1. What does the main ...
Stellar evolution, II
... The faster the nuclear reactions run, the more luminosity the star has. This explains why more massive stars have greater luminosity, and why more massive stars use up their core hydrogen at a much faster rate. ...
... The faster the nuclear reactions run, the more luminosity the star has. This explains why more massive stars have greater luminosity, and why more massive stars use up their core hydrogen at a much faster rate. ...
Astronomy 120
... Look around you. Of the items you see, what would not there if supernovas didn’t occur? ...
... Look around you. Of the items you see, what would not there if supernovas didn’t occur? ...
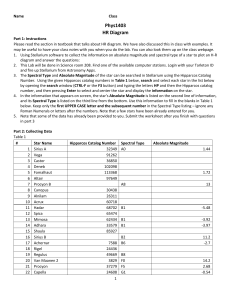
H-R Diagram - Faculty Website Listing
... 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on absolute magnitude and spectral type of a star to plot an H-R diagram and answer the questions: 2. This Lab will be done in Science room 208. Find one of the available computer stations. Login with your Tarleton ID and fire up Stellarium fro ...
... 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on absolute magnitude and spectral type of a star to plot an H-R diagram and answer the questions: 2. This Lab will be done in Science room 208. Find one of the available computer stations. Login with your Tarleton ID and fire up Stellarium fro ...
Exoplanets Rising: Understanding Doppler Shift
... Exo means outside of and Planet means Wanderer ...
... Exo means outside of and Planet means Wanderer ...
24exoplanets5s
... Recently many planets around other stars have been found The planets are detected by measuring the motions they induce in the central star The period and velocity of the motions allows the determination of the mass and orbit of the planet New missions in the next 20 years will allow for the dete ...
... Recently many planets around other stars have been found The planets are detected by measuring the motions they induce in the central star The period and velocity of the motions allows the determination of the mass and orbit of the planet New missions in the next 20 years will allow for the dete ...
The hierarchical structure of the Universe (go from little to large)
... D 50% inside the Galaxy, 50% outside. E nowhere close to the Galaxy, which is much farther away from us than the individual stars in the sky are. ...
... D 50% inside the Galaxy, 50% outside. E nowhere close to the Galaxy, which is much farther away from us than the individual stars in the sky are. ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... Sheetthat not even – An object so massive and dense light can escape its gravity – The end result from a supernova of a star that has a mass greater than 3x the sun ...
... Sheetthat not even – An object so massive and dense light can escape its gravity – The end result from a supernova of a star that has a mass greater than 3x the sun ...
Astronomy 242: Review Questions #1 Distributed: February 10
... 12. You observe a sample of Cepheid variable stars in a nearby galaxy. Plotting the average apparent K-band magnitude of each one against the period of pulsation yields Fig. 3. The straight line, a least-squares fit to the data, has the equation mK = 16.40 − 3.53 log(P/day). (a) Does it seem reasona ...
... 12. You observe a sample of Cepheid variable stars in a nearby galaxy. Plotting the average apparent K-band magnitude of each one against the period of pulsation yields Fig. 3. The straight line, a least-squares fit to the data, has the equation mK = 16.40 − 3.53 log(P/day). (a) Does it seem reasona ...
Physics@Brock - Brock University
... • Describe luminosity classes and how they are determined. • Explain how the masses of stars are estimated, and apply Newton’s version of Kepler’s third law to determine such masses. • Describe the layout of the Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram, and infer a star’s size and evolutionary state based ...
... • Describe luminosity classes and how they are determined. • Explain how the masses of stars are estimated, and apply Newton’s version of Kepler’s third law to determine such masses. • Describe the layout of the Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram, and infer a star’s size and evolutionary state based ...
Astronomy Exam review
... 41.The _____ planets are characterized by deep atmospheres, many satellites, and a solar-like elemental abundance. 42.The _____ planets are relatively slow rotators, are dense, and have few satellites. 43. The most abundant element in the solar system is _____ 44. The second most abundant element in ...
... 41.The _____ planets are characterized by deep atmospheres, many satellites, and a solar-like elemental abundance. 42.The _____ planets are relatively slow rotators, are dense, and have few satellites. 43. The most abundant element in the solar system is _____ 44. The second most abundant element in ...
iClicker Questions
... Discovering the Universe, Eighth Edition by Neil F. Comins and William J. Kaufmann III Chapter 12 12-1. Protostars are not seen in visible light telescopes because: a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust * c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are al ...
... Discovering the Universe, Eighth Edition by Neil F. Comins and William J. Kaufmann III Chapter 12 12-1. Protostars are not seen in visible light telescopes because: a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust * c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are al ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.