Types of Stars
... • The change in position of an object with respect to a distant background is called parallax. • As Earth moves in its orbit, astronomers are able to observe stars from two different positions. • Astronomers measure the parallax of nearby stars to ...
... • The change in position of an object with respect to a distant background is called parallax. • As Earth moves in its orbit, astronomers are able to observe stars from two different positions. • Astronomers measure the parallax of nearby stars to ...
Slide 1 - Physics @ IUPUI
... rotations (seconds) • Only seem to last 10,000 years or so • Hard to observe flare up only very randomly ...
... rotations (seconds) • Only seem to last 10,000 years or so • Hard to observe flare up only very randomly ...
The Life of a Star
... reaches 1.0 x 106°C, helium fusion begins in the core (secondary fusion). Once all fusion reactions stop, the star throws its outer layers into space, forming a planetary nebula – This leaves behind the hot dense core of the red giant. – The remaining core is called a white dwarf. Over time, the whi ...
... reaches 1.0 x 106°C, helium fusion begins in the core (secondary fusion). Once all fusion reactions stop, the star throws its outer layers into space, forming a planetary nebula – This leaves behind the hot dense core of the red giant. – The remaining core is called a white dwarf. Over time, the whi ...
Nuclear Interactions in Supernovae .
... an enormous amount of energy is released from all the hydrogen being fused in a short amount of time. • This causes an explosion on the surface of the dwarf, which doesn’t affect the star, but increases its brightness by 50,000 to 100,000 times that of the sun. ...
... an enormous amount of energy is released from all the hydrogen being fused in a short amount of time. • This causes an explosion on the surface of the dwarf, which doesn’t affect the star, but increases its brightness by 50,000 to 100,000 times that of the sun. ...
Stellar Luminosity
... In 1843, the massive star Eta Carinae flared remarkably, increasing in magnitude to m = −1 (becoming the 2nd-brightest star in the entire sky) before fading away again to 8th mag. How much did its luminosity change then? A ...
... In 1843, the massive star Eta Carinae flared remarkably, increasing in magnitude to m = −1 (becoming the 2nd-brightest star in the entire sky) before fading away again to 8th mag. How much did its luminosity change then? A ...
The Daily Telegraph – London… 14th February 2008… New Solar
... The smaller planet is roughly twice as far from its star as the larger one, just as Saturn is about twice as far from the sun as Jupiter. Planetary scientists who discovered them believe there could be rocky planets, like Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, closer to the star. Of around 250 planets so f ...
... The smaller planet is roughly twice as far from its star as the larger one, just as Saturn is about twice as far from the sun as Jupiter. Planetary scientists who discovered them believe there could be rocky planets, like Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, closer to the star. Of around 250 planets so f ...
HERE
... lifespan,burn-rate, size: Spectral class O, B stars (rare, but very interesting): Giant, hot, bright, blue stars burn up quickly and die violently. Lifetime is only 1-10 million years. Spectral class A,F,G,K stars (like the Sun): Middle of the road habits. Orange, yellow or white in color. Typic ...
... lifespan,burn-rate, size: Spectral class O, B stars (rare, but very interesting): Giant, hot, bright, blue stars burn up quickly and die violently. Lifetime is only 1-10 million years. Spectral class A,F,G,K stars (like the Sun): Middle of the road habits. Orange, yellow or white in color. Typic ...
Chapter 13 - USD Home Pages
... a white dwarf might be at several hundred million K, but this extremely high temperature contributes only a small amount of the pressure, compared to EDP. As a result, as a white dwarf cools down, the decrease in total pressure (EDP plus thermodynamic) is slight, so the white dwarf does not shrink a ...
... a white dwarf might be at several hundred million K, but this extremely high temperature contributes only a small amount of the pressure, compared to EDP. As a result, as a white dwarf cools down, the decrease in total pressure (EDP plus thermodynamic) is slight, so the white dwarf does not shrink a ...
Night Sky Checklist October–November
... M31, the Andromeda Galaxy, is one of the most distant things visible to the unaided eye and probably the most distant object visible in the murky skies of Acadiana. The Andromeda Galaxy is a spiral of well over 500 billion stars so far away that we can barely see it, at a distance of nearly 3 millio ...
... M31, the Andromeda Galaxy, is one of the most distant things visible to the unaided eye and probably the most distant object visible in the murky skies of Acadiana. The Andromeda Galaxy is a spiral of well over 500 billion stars so far away that we can barely see it, at a distance of nearly 3 millio ...
A star by any other name - Baruch Sterman
... The wobble of the earth’s axis leads to another phenomenon, besides the drift of seasons. Imagine the earth’s axis like a giant finger pointing out into the vast reaches of space. The star closest to that point in the sky (called the North Celestial Pole) will have particular significance, as it wil ...
... The wobble of the earth’s axis leads to another phenomenon, besides the drift of seasons. Imagine the earth’s axis like a giant finger pointing out into the vast reaches of space. The star closest to that point in the sky (called the North Celestial Pole) will have particular significance, as it wil ...
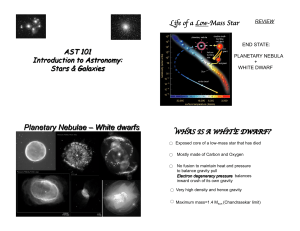
Planetary Nebulae – White dwarfs
... stages of life in a low-mass star? A. protostar, main-sequence star, red giant, planetary nebula, white dwarf B. protostar, main-sequence star, red giant, supernova, neutron star C. main-sequence star, white dwarf, red giant, planetary nebula, protostar D. protostar, main-sequence star, planetar ...
... stages of life in a low-mass star? A. protostar, main-sequence star, red giant, planetary nebula, white dwarf B. protostar, main-sequence star, red giant, supernova, neutron star C. main-sequence star, white dwarf, red giant, planetary nebula, protostar D. protostar, main-sequence star, planetar ...
Blowing Bubbles in Space: The Birth and Death of Practically
... shape of E0102 is most likely a cylinder that is viewed end-on rather than a spherical bubble. • The intriguing result implies that the massive star's explosion has produced a shape similar to what is seen in some planetary nebulae associated with lower mass stars. • SMC=190 kly away, so this field ...
... shape of E0102 is most likely a cylinder that is viewed end-on rather than a spherical bubble. • The intriguing result implies that the massive star's explosion has produced a shape similar to what is seen in some planetary nebulae associated with lower mass stars. • SMC=190 kly away, so this field ...
june 2011 - Holt Planetarium
... Zealand survey that scanned the center of the Milky Way galaxy, revealing evidence for up to 10 freefloating planets roughly the mass of Jupiter. The isolated orbs, also known as orphan planets, are difficult to spot, and had gone undetected until now. The newfound planets are located at an average ...
... Zealand survey that scanned the center of the Milky Way galaxy, revealing evidence for up to 10 freefloating planets roughly the mass of Jupiter. The isolated orbs, also known as orphan planets, are difficult to spot, and had gone undetected until now. The newfound planets are located at an average ...
june 2011 - Holt Planetarium
... Zealand survey that scanned the center of the Milky Way galaxy, revealing evidence for up to 10 freefloating planets roughly the mass of Jupiter. The isolated orbs, also known as orphan planets, are difficult to spot, and had gone undetected until now. The newfound planets are located at an average ...
... Zealand survey that scanned the center of the Milky Way galaxy, revealing evidence for up to 10 freefloating planets roughly the mass of Jupiter. The isolated orbs, also known as orphan planets, are difficult to spot, and had gone undetected until now. The newfound planets are located at an average ...
Chapter 29 Notes
... distance to stars • Constellations: Groups of stars in the same part of the sky • Clusters: groups of stars bound together by gravity • Binaries: two stars that orbit a common center of mass ...
... distance to stars • Constellations: Groups of stars in the same part of the sky • Clusters: groups of stars bound together by gravity • Binaries: two stars that orbit a common center of mass ...
Solutions
... Problem 1 (12 points): Five of the following celestial objects represent (or likely contain) a solar mass star at some point in its evolution. We associate the sixth object with an evolutionary stage of a much more massive star. Place a 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 in age order (youngest to oldest) for the fiv ...
... Problem 1 (12 points): Five of the following celestial objects represent (or likely contain) a solar mass star at some point in its evolution. We associate the sixth object with an evolutionary stage of a much more massive star. Place a 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 in age order (youngest to oldest) for the fiv ...
22 Stellar Remnant/HR Diagram
... Spectroscopic Parallax? We can now get the temperature (within a few 10’s of a degree) Find a MS star at that Temp Find the Luminosity/absolute magnitude Gives a distance! ...
... Spectroscopic Parallax? We can now get the temperature (within a few 10’s of a degree) Find a MS star at that Temp Find the Luminosity/absolute magnitude Gives a distance! ...
astronomy practice Answers - hhs-snc1d
... 23) We age the Earth at about 4billion years based on: a) Cepheid variables b) triangulation c) retrograde motion d) radiometric dating e) Doppler shift 24) We believe the planets were all created from a swirling disk of dust at about the same time ...
... 23) We age the Earth at about 4billion years based on: a) Cepheid variables b) triangulation c) retrograde motion d) radiometric dating e) Doppler shift 24) We believe the planets were all created from a swirling disk of dust at about the same time ...
binary stars - El Camino College
... fainter orange star, but still about 100 times brighter than our full Moon. The 2nd star would easily be visible in the day time and you could easily read by its light at night. From this fictional planet, tiny Proxima would be a deep red star four times fainter than the stars in the Big Dipper! Thr ...
... fainter orange star, but still about 100 times brighter than our full Moon. The 2nd star would easily be visible in the day time and you could easily read by its light at night. From this fictional planet, tiny Proxima would be a deep red star four times fainter than the stars in the Big Dipper! Thr ...
PPT - Mr.E Science
... Star Life Cycle Nebula – a huge gas cloud made up mainly of Hydrogen that collapse down on itself and compresses the gas down into a Protostar Star is “born” when the protostar has contracting tight enough for Hydrogen to fuse into Helium, this releases the light and energy we normally associate wi ...
... Star Life Cycle Nebula – a huge gas cloud made up mainly of Hydrogen that collapse down on itself and compresses the gas down into a Protostar Star is “born” when the protostar has contracting tight enough for Hydrogen to fuse into Helium, this releases the light and energy we normally associate wi ...
Stellar evolution
... - Whole star pulsates more and more violently. - Eventually, shells thrown off star altogether! 0.1 - 0.2 MSun ejected. - Shells appear as a nebula around star, called "Planetary Nebula" (awful, historical name, nothing to do with planets. ...
... - Whole star pulsates more and more violently. - Eventually, shells thrown off star altogether! 0.1 - 0.2 MSun ejected. - Shells appear as a nebula around star, called "Planetary Nebula" (awful, historical name, nothing to do with planets. ...
Astronomy Unit Test – Chapter 21
... hemisphere: days are longer than nights and Southern hemisphere days are shorter than nights ...
... hemisphere: days are longer than nights and Southern hemisphere days are shorter than nights ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.