Chapter 20 The Universe
... Distance that light travels in 1 yr. ~10 billion km Sirius (Dog star) only 9 light years away Proxima Centauri (closest) 4.25 light yrs Other than sun Galaxy- large grouping of stars -our solar system is part of Milky Way Galaxy - what we see as the Milky Way is only the edge (spiral galaxy) ...
... Distance that light travels in 1 yr. ~10 billion km Sirius (Dog star) only 9 light years away Proxima Centauri (closest) 4.25 light yrs Other than sun Galaxy- large grouping of stars -our solar system is part of Milky Way Galaxy - what we see as the Milky Way is only the edge (spiral galaxy) ...
Constellations - Sierra Star Gazers
... Just rising over the northeastern horizon is the constellation Perseus. Between Perseus and Cassiopeia is found one the most interesting objects to be seen through a small to medium aperture scope. The best thing is that it so easy to locate. NGC 869 & 884, popularly known as the Double Cluster, are ...
... Just rising over the northeastern horizon is the constellation Perseus. Between Perseus and Cassiopeia is found one the most interesting objects to be seen through a small to medium aperture scope. The best thing is that it so easy to locate. NGC 869 & 884, popularly known as the Double Cluster, are ...
Document
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are ...
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are ...
Milky Way
... • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are denoted by a roman numeral (V, III, I,…). ...
... • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are denoted by a roman numeral (V, III, I,…). ...
Earth Science – Quiz 2
... C) one-half those on Earth; main gases are methane and nitrogen D) 1.5 times those on Earth; main gases are methane and nitrogen 21. Which one of the following statements is believed to be true of comets? A) They have highly elliptical orbits around the Sun. B) They are composed mostly of dense rock ...
... C) one-half those on Earth; main gases are methane and nitrogen D) 1.5 times those on Earth; main gases are methane and nitrogen 21. Which one of the following statements is believed to be true of comets? A) They have highly elliptical orbits around the Sun. B) They are composed mostly of dense rock ...
Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) Diagram Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram March 16 −
... How to read H-R Diagram Spectrum of black body: Hotter=>bluer Energy generation in the sun X ...
... How to read H-R Diagram Spectrum of black body: Hotter=>bluer Energy generation in the sun X ...
a geolocation. Obtain the information related to certain star.
... An amateur astronomer is searching for a star in the field. She forgot her star charts or they don't have the exact information she is looking for.... ...
... An amateur astronomer is searching for a star in the field. She forgot her star charts or they don't have the exact information she is looking for.... ...
Binary Stars - Mid-Pacific Institute
... Alpha Centauri A & B They orbit each other with a period of 80 years ...
... Alpha Centauri A & B They orbit each other with a period of 80 years ...
chapter 28 pages 747-752
... • 2. Rotation causes formation of protostar • 3. Once it is hot enough for H to fuse into He, main sequence stage occurs • This is the longest stage of a stars life. • 4. In medium sized stars, once all H has been fused into He, He then starts to fuse into C during the Red Giant stage ...
... • 2. Rotation causes formation of protostar • 3. Once it is hot enough for H to fuse into He, main sequence stage occurs • This is the longest stage of a stars life. • 4. In medium sized stars, once all H has been fused into He, He then starts to fuse into C during the Red Giant stage ...
Lesson 10 Red Shift
... energy). Although the electromagnetic spectrum comprises wavelengths from ultra high energy (and dangerous) gamma rays to ultra low energy radio waves, the only part that we can see is the very limited "visual spectrum." In the visual spectrum, wavelength corresponds to colour. In other words, viole ...
... energy). Although the electromagnetic spectrum comprises wavelengths from ultra high energy (and dangerous) gamma rays to ultra low energy radio waves, the only part that we can see is the very limited "visual spectrum." In the visual spectrum, wavelength corresponds to colour. In other words, viole ...
Assessment Star Characteristics and Life Cycle
... 1. Below is a Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram that scientists use to compare stars based on their properties. ...
... 1. Below is a Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram that scientists use to compare stars based on their properties. ...
Teacher Sheet 1. What variables does the HR Diagram compare
... 14. Describe stars A, B, C, and D in terms of their brightness and temperature. Star A is red and therefore, cool. Its luminosity is 1/1000 of that of the sun; therefore, it is dim. Star B is a hot, blue star and very luminous. Both A and B are on the Main Sequence. Star C is also a hot, blue star. ...
... 14. Describe stars A, B, C, and D in terms of their brightness and temperature. Star A is red and therefore, cool. Its luminosity is 1/1000 of that of the sun; therefore, it is dim. Star B is a hot, blue star and very luminous. Both A and B are on the Main Sequence. Star C is also a hot, blue star. ...
The Life Cycle of a Star
... the star has ignited, it becomes a main sequence star. Main Sequence stars fuse hydrogen to form helium, releasing enormous amounts of energy. It takes about 10 billion years to consume all the hydrogen in a Main Sequence star. ...
... the star has ignited, it becomes a main sequence star. Main Sequence stars fuse hydrogen to form helium, releasing enormous amounts of energy. It takes about 10 billion years to consume all the hydrogen in a Main Sequence star. ...
Chapter #10 Question #27: (c) Four individual protons. During
... The final result is an iron core which is released to the interstellar space during a high mass star supernova. A massive star supernova that blew up before the formation of the solar system would have released iron into the surrounding space which was used up by our solar system during its formatio ...
... The final result is an iron core which is released to the interstellar space during a high mass star supernova. A massive star supernova that blew up before the formation of the solar system would have released iron into the surrounding space which was used up by our solar system during its formatio ...
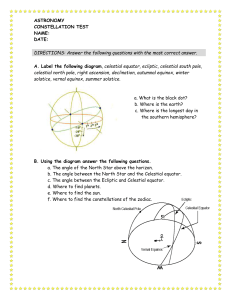
ASTRONOMY
... E. Fill in the blank. 1. There are about __________ stars you can see at night. 2. Latitudes on earth are like ____________ in space. 3. There are about ________ constellations. 4. The north-star has a magnitude of _____________. 5. The point directly overhead is called the ______________. 6. Polar ...
... E. Fill in the blank. 1. There are about __________ stars you can see at night. 2. Latitudes on earth are like ____________ in space. 3. There are about ________ constellations. 4. The north-star has a magnitude of _____________. 5. The point directly overhead is called the ______________. 6. Polar ...
DOC
... neutron star and white dwarf). 13. I can recall why the length of a star’s life depends on its mass. 14. I can recall that parallax and the inverse square law are used to determine distance of stars and galaxies. 15. I can recall when the best times to take parallax data are. 16. I can descr ...
... neutron star and white dwarf). 13. I can recall why the length of a star’s life depends on its mass. 14. I can recall that parallax and the inverse square law are used to determine distance of stars and galaxies. 15. I can recall when the best times to take parallax data are. 16. I can descr ...
Astronomy 12: Introduction to Astronomy
... c. A type of solar flares that occurs on the surface of sun-type stars. d. A flash of white light that occurs when a star collapses into a white dwarf. 6. What is a planetary nebula? a. The destroyed remains of a planetary solar system when a sun-type star expands into a red giant. b. The ejected en ...
... c. A type of solar flares that occurs on the surface of sun-type stars. d. A flash of white light that occurs when a star collapses into a white dwarf. 6. What is a planetary nebula? a. The destroyed remains of a planetary solar system when a sun-type star expands into a red giant. b. The ejected en ...
class17
... How would the apparent brightness of Alpha Centauri change if it were three times farther away? ...
... How would the apparent brightness of Alpha Centauri change if it were three times farther away? ...
Stars - Science
... are red. Medium temperature stars are orange and yellow. The hottest stars are blue. ...
... are red. Medium temperature stars are orange and yellow. The hottest stars are blue. ...
powerpoint version
... The binary system Cygnus X-1 appears to contain a black hole which is sucking material in from its blue supergiant companion star. Figs. Z17.36 & K15-21 or 15-23 ...
... The binary system Cygnus X-1 appears to contain a black hole which is sucking material in from its blue supergiant companion star. Figs. Z17.36 & K15-21 or 15-23 ...
Stellar Brightness Apparent magnitude
... What if we could line up all the stars the same distance away to do a fair test for their brightness? This is what astronomers do with the Absolute Magnitude scale They ‘pretend’ to line up the stars exactly 10 parsecs (32.6 l.y.)away and figure out how bright each start would look ...
... What if we could line up all the stars the same distance away to do a fair test for their brightness? This is what astronomers do with the Absolute Magnitude scale They ‘pretend’ to line up the stars exactly 10 parsecs (32.6 l.y.)away and figure out how bright each start would look ...
Document
... determining the distance of stars. The change in position of an object with respect to a distant background is called parallax. As Earth moves in its orbit, astronomers are able to observe stars from two different positions. Astronomers measure the parallax of nearby stars to determine their distanc ...
... determining the distance of stars. The change in position of an object with respect to a distant background is called parallax. As Earth moves in its orbit, astronomers are able to observe stars from two different positions. Astronomers measure the parallax of nearby stars to determine their distanc ...
3 - MrFuglestad
... succession of fusion from Hydrogen to Iron. Stars that end up with mass less than 1.5 times our Sun’s mass White Dwarf – Earth sized star that is stable with no nuclear reactions and is made of helium or carbon depending on the mass. Less massive than our Sun = Helium. There can be other elements pr ...
... succession of fusion from Hydrogen to Iron. Stars that end up with mass less than 1.5 times our Sun’s mass White Dwarf – Earth sized star that is stable with no nuclear reactions and is made of helium or carbon depending on the mass. Less massive than our Sun = Helium. There can be other elements pr ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.