Main Sequence Star
... • 4 hydrogen fuse to make helium plus energy • Occurs in the core • Must be 10 mil ...
... • 4 hydrogen fuse to make helium plus energy • Occurs in the core • Must be 10 mil ...
Astronomy 120
... Be careful about units! Please CIRCLE or put a box around your final answer if it is numerical. 1. Zeilik Study Exercise 13.1 In the winter sky, you see the following stars: Capella (yellowish), Betelgeuse (reddish), and Sirius (bluish). List these stars in order of increasing surface temperature. E ...
... Be careful about units! Please CIRCLE or put a box around your final answer if it is numerical. 1. Zeilik Study Exercise 13.1 In the winter sky, you see the following stars: Capella (yellowish), Betelgeuse (reddish), and Sirius (bluish). List these stars in order of increasing surface temperature. E ...
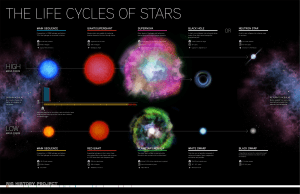
Life Cycles of Stars
... The outer layers of gas are ejected while the star's core contracts into a white dwarf. ...
... The outer layers of gas are ejected while the star's core contracts into a white dwarf. ...
chapter10
... The Deaths of Massive Stars: Supernovae Final stages of fusion in high-mass stars (> 8 Msun), leading to the formation of an iron core, happen extremely rapidly: Si burning lasts only for ~ 1 day. Iron core ultimately collapses, triggering an explosion that destroys the star: ...
... The Deaths of Massive Stars: Supernovae Final stages of fusion in high-mass stars (> 8 Msun), leading to the formation of an iron core, happen extremely rapidly: Si burning lasts only for ~ 1 day. Iron core ultimately collapses, triggering an explosion that destroys the star: ...
The Life of a Star
... Low-Mass and High-Mass If a star, like our sun, does not have much mass in it, it is called a low-mass star. For low-mass stars, when the helium becomes carbon, the center of the star shrinks even more, and the outer layers are pushed far away. The core of a lowmass star becomes a white dwarf, which ...
... Low-Mass and High-Mass If a star, like our sun, does not have much mass in it, it is called a low-mass star. For low-mass stars, when the helium becomes carbon, the center of the star shrinks even more, and the outer layers are pushed far away. The core of a lowmass star becomes a white dwarf, which ...
SOLUTIONS ASTROPHYSICS – OPTION D 2015-17
... b) State and explain the change in the luminosity of the Sun that occurs between positions S and I. ...
... b) State and explain the change in the luminosity of the Sun that occurs between positions S and I. ...
Chapter 28 – Stars and Galaxies
... If a Cepheid is located in another galaxy, astronomers can find the distance to these galaxies by comparing absolute and apparent magnitudes Other stars change in brightness because they revolve around another star. This is known as a ‘binary star system.’ ...
... If a Cepheid is located in another galaxy, astronomers can find the distance to these galaxies by comparing absolute and apparent magnitudes Other stars change in brightness because they revolve around another star. This is known as a ‘binary star system.’ ...
WebQuest-The-Life-Cycle-of-Stars-1
... Go to the website http://map.gsfc.nasa.gov/universe/rel_stars.html. Read the short section on “Where are stars born” and see pictures of the protostars of M16: The Eagle Nebula and other nebulae on this page. Continue by reading up on Main Sequence Stars and find out how our sun compares in mass to ...
... Go to the website http://map.gsfc.nasa.gov/universe/rel_stars.html. Read the short section on “Where are stars born” and see pictures of the protostars of M16: The Eagle Nebula and other nebulae on this page. Continue by reading up on Main Sequence Stars and find out how our sun compares in mass to ...
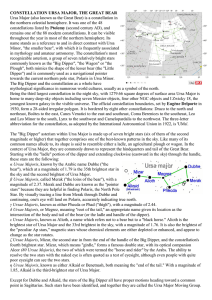
CONSTELLATION URSA MAJOR, THE GREAT
... constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, "the smaller bear", with which it is frequently a ...
... constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, "the smaller bear", with which it is frequently a ...
Chapter 28 – Stars and Galaxies
... 2. Stellar mass is expressed as multiples of the sun’s mass Betelgeuse’s mass – 20 solar masses F. Temperature and Color 1. Blue stars are hot 2. Red stars are cool G. Luminosity 1. The actual brightness of the star is luminosity 2. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star w ...
... 2. Stellar mass is expressed as multiples of the sun’s mass Betelgeuse’s mass – 20 solar masses F. Temperature and Color 1. Blue stars are hot 2. Red stars are cool G. Luminosity 1. The actual brightness of the star is luminosity 2. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star w ...
Stars with mass less than 0.5 solar masses
... slowly till they swich off completely, in black dwarf. If a white dwarf is part of a bynar system, for example with a red giant, the first one can steal some of the red giant’s mass and prime the fusion of hydrogen in the external layers. This cause a a big explosion which can be seen from the Earth ...
... slowly till they swich off completely, in black dwarf. If a white dwarf is part of a bynar system, for example with a red giant, the first one can steal some of the red giant’s mass and prime the fusion of hydrogen in the external layers. This cause a a big explosion which can be seen from the Earth ...
Planisphere Exercise
... Note the location of the North Star at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. It is located just beneath the brass fastener that holds the star wheel to the frame of the planisphere. As the night progresses, which way do the stars appear to move around the North Star (which is hidden under the ...
... Note the location of the North Star at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. It is located just beneath the brass fastener that holds the star wheel to the frame of the planisphere. As the night progresses, which way do the stars appear to move around the North Star (which is hidden under the ...
COM 2014 January
... The Perseus Cluster (Abell 426) is a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Perseus. It has a recession speed of 5,366 km/s and a diameter of 863′. It is one of the most massive objects in the universe, containing thousands of galaxies immersed in a vast cloud of multimillion degree gas. Image: ...
... The Perseus Cluster (Abell 426) is a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Perseus. It has a recession speed of 5,366 km/s and a diameter of 863′. It is one of the most massive objects in the universe, containing thousands of galaxies immersed in a vast cloud of multimillion degree gas. Image: ...
Astronomy of the Northern Sky—
... The Cat’s Eye Nebulae, NGC 6543, in Draco is among the brightest anywhere, magnitude 8.1 (17:59 +66º 38’). On the way from β to γ Ursa Majoris (and slightly outside this line which makes the bottom of the Big Dipper’s Bowl), near the point of a thin north-pointing triangle, is the Owl Nebula, M97, a ...
... The Cat’s Eye Nebulae, NGC 6543, in Draco is among the brightest anywhere, magnitude 8.1 (17:59 +66º 38’). On the way from β to γ Ursa Majoris (and slightly outside this line which makes the bottom of the Big Dipper’s Bowl), near the point of a thin north-pointing triangle, is the Owl Nebula, M97, a ...
Stars - Independence High School
... • Seasonal- Orbit equator and can only be seen during certain times of the year ...
... • Seasonal- Orbit equator and can only be seen during certain times of the year ...
Unit 2-1 Life Cycle of the Sun
... The purpose of this activity is to have you observe the changes in the temperature, absolute magnitude, and other observable characteristics of two different types of stars as they go through their life cycles. The absolute magnitude is a measure of how bright a star would appear if it was approxima ...
... The purpose of this activity is to have you observe the changes in the temperature, absolute magnitude, and other observable characteristics of two different types of stars as they go through their life cycles. The absolute magnitude is a measure of how bright a star would appear if it was approxima ...
QUIZ 1 - AY5-S13 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . YOUR NAME
... T The two gases would show different emission-line spectra F Both would show continuous spectra, with the helium-gas spectrum peaking at a shorter wavelength 6. What color would a yellow banana slug appear if illuminated with white light? Yellow ...
... T The two gases would show different emission-line spectra F Both would show continuous spectra, with the helium-gas spectrum peaking at a shorter wavelength 6. What color would a yellow banana slug appear if illuminated with white light? Yellow ...
Chapter 3: the Sun
... how much will the Sun fade during a transit of the Earth? How about during a transit of Jupiter? ...
... how much will the Sun fade during a transit of the Earth? How about during a transit of Jupiter? ...
2014 State Test
... B8. Which is more luminous: a 3000K star with a radius of 50 R, or a 7500K star with a radius of just 3.5 R? A. The large, cool star C. Both are equally luminous B. The small, hot star D. More information is needed B9. In a binary star system, one star may transfer mass to the other. What is the n ...
... B8. Which is more luminous: a 3000K star with a radius of 50 R, or a 7500K star with a radius of just 3.5 R? A. The large, cool star C. Both are equally luminous B. The small, hot star D. More information is needed B9. In a binary star system, one star may transfer mass to the other. What is the n ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.