* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The life of a Star (pages 468-471)
Survey
Document related concepts
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
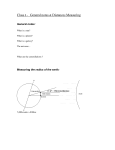
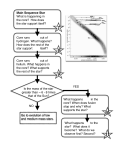
The life of a Star (pages 468-471). 1. Explain gravity. 2. Explain how a nebula turns into a cloud leading to a star(3 steps)? 3. What happens when a star runs out of the fuels needed to produce energy? 4. What is a supernova? During this stage, what happens to the core of the star? When our Sun eventually swells into a red giant star, its outer layers will grow to be about 100 times its present size swallowing up Mercury, Venus, Earth and maybe even Mars 5. What is a neutron star? 6. What is a pulsar? 7. What type of stars can eventually turn into a black hole? 8. What is a black hole? The word hole is misleading because it sounds as though there is nothing there; it actually has a huge amount of matter packed into a sphere only a few kilometers across. It is so compact that a handful of it would have a mass of 10 billion cars. 9. Describe the life of a low mass star and that of a star 10 times bigger than our sun 10. Explain the terms red giants, red supergiants and white dwarfs. 11. Explain how a star goes from Major part of life to death. Become familiar with figure 2 on page 469. The life of a Star (pages 468-471). 1. Explain gravity. 2. Explain how a nebula turns into a cloud leading to a star (3 steps)? 3. What happens when a star runs out of the fuels needed to produce energy? 4. What is a supernova? During this stage, what happens to the core of the star? When our Sun eventually swells into a red giant star, its outer layers will grow to be about 100 times its present size swallowing up Mercury, Venus, Earth and maybe even Mars 5. What is a neutron star? 6. What is a pulsar? 7. What type of stars can eventually turn into a black hole? 8. What is a black hole? The word hole is misleading because it sounds as though there is nothing there; it actually has a huge amount of matter packed into a sphere only a few kilometers across. It is so compact that a handful of it would have a mass of 10 billion cars. 9. Describe the life of a low mass star and that of a star 10 times bigger than our sun 10. Explain the terms red giants, red supergiants and white dwarfs. 11. Explain how a star goes from Major part of life to death. Become familiar with figure 2 on page 469. The life of a Star (pages 468-471). 1. Explain gravity. 2. Explain how a nebula turns into a cloud leading to a star(3 steps)? 3. What happens when a star runs out of the fuels needed to produce energy? 4. What is a supernova? During this stage, what happens to the core of the star? When our Sun eventually swells into a red giant star, its outer layers will grow to be about 100 times its present size swallowing up Mercury, Venus, Earth and maybe even Mars 5. What is a neutron star? 6. What is a pulsar? 7. What type of stars can eventually turn into a black hole? 8. What is a black hole? The word hole is misleading because it sounds as though there is nothing there; it actually has a huge amount of matter packed into a sphere only a few kilometers across. It is so compact that a handful of it would have a mass of 10 billion cars. 9. Describe the life of a low mass star and that of a star 10 times bigger than our sun 10. Explain the terms red giants, red supergiants and white dwarfs. 11. Explain how a star goes from Major part of life to death. Become familiar with figure 2 on page 469.