Science 8 Name: Unit 2 Astronomy Date: Period: LAB
... that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude. Absolute magnitude is how bright stars would appear to be if they were all the same distance away from Earth. Rather than speak of brightness of stars we often use the word “luminosity.” Luminosity of stars is ...
... that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude. Absolute magnitude is how bright stars would appear to be if they were all the same distance away from Earth. Rather than speak of brightness of stars we often use the word “luminosity.” Luminosity of stars is ...
properties of stars 2012
... So… if apparent brightness is determined (by using a light meter) and d is known (perhaps by parallax), luminosity can be determined. Apparent Magnitude: Hipparchus, in 150 B.C. classified stars by magnitude, with 1 being the brightest, and six being the dimmest. With the advent of technology, brigh ...
... So… if apparent brightness is determined (by using a light meter) and d is known (perhaps by parallax), luminosity can be determined. Apparent Magnitude: Hipparchus, in 150 B.C. classified stars by magnitude, with 1 being the brightest, and six being the dimmest. With the advent of technology, brigh ...
Stars and Galaxies
... Seeing into the Past We can’t travel into the past, but we can get a glimpse of it. Every time we look at the Moon, for example, we see it as it was a little more than a second ago. That’s because sunlight reflected from the Moon’s surface takes a little more than a second to reach Earth. We see the ...
... Seeing into the Past We can’t travel into the past, but we can get a glimpse of it. Every time we look at the Moon, for example, we see it as it was a little more than a second ago. That’s because sunlight reflected from the Moon’s surface takes a little more than a second to reach Earth. We see the ...
Study Guide for Stars and the Universe Test
... 1. What types of radiation make up the electromagnetic spectrum? 2. Define the three types of spectra. 3. How do scientists determine the elements present in a star. 4. How can scientists determine whether a star is moving toward or away from Earth? 5. How does a reflecting telescope differ from a r ...
... 1. What types of radiation make up the electromagnetic spectrum? 2. Define the three types of spectra. 3. How do scientists determine the elements present in a star. 4. How can scientists determine whether a star is moving toward or away from Earth? 5. How does a reflecting telescope differ from a r ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... Shows the relationship between a star’s surface temperature and absolute magnitude Used to study the lives of stars Most stars lie along the main sequence portion of the diagram ...
... Shows the relationship between a star’s surface temperature and absolute magnitude Used to study the lives of stars Most stars lie along the main sequence portion of the diagram ...
How Bright is that Star?
... A 1st magnitude star is 100x brighter than a “6th ” Each order of magnitude is therefore 2.15 times brighter than the one below it. Magnitude is now given in decimal form. Deneb now rates a 1.26, and Betelgeuse rates .87. Hipparchus underestimated how bright the brightest were, so now we even use ne ...
... A 1st magnitude star is 100x brighter than a “6th ” Each order of magnitude is therefore 2.15 times brighter than the one below it. Magnitude is now given in decimal form. Deneb now rates a 1.26, and Betelgeuse rates .87. Hipparchus underestimated how bright the brightest were, so now we even use ne ...
AN INTRODUCTION TO ASTRONOMY Dr. Uri Griv Department of Physics, Ben-Gurion University
... • The responce of the human eye works on the basis of a geometric progression rather than an arithmetic progression • The modern magnitude classification: a difference of 5 magnitudes to equal exactly a factor of 100 in apparent brightness • If m1 and m2 are the apparent magnitudes with apparent bri ...
... • The responce of the human eye works on the basis of a geometric progression rather than an arithmetic progression • The modern magnitude classification: a difference of 5 magnitudes to equal exactly a factor of 100 in apparent brightness • If m1 and m2 are the apparent magnitudes with apparent bri ...
Beauty and the beast - University of Wyoming
... will disappear. The outer regions of your eye are good at detecting contrast (but not color), and this allows you to see fainter objects. Many more stars will be seen within the Pleiades with binoculars or a telescope. This open cluster contains over 1,000 stars in a region about 40 light years in d ...
... will disappear. The outer regions of your eye are good at detecting contrast (but not color), and this allows you to see fainter objects. Many more stars will be seen within the Pleiades with binoculars or a telescope. This open cluster contains over 1,000 stars in a region about 40 light years in d ...
I. Parallax
... has observed stars with magnitudes down to ____ at visible wavelengths and the Keck telescopes have located similarly faint stars in the infrared with _________________. F. There is a _________ difference in brightness for stars that differ by a _____________. For example, a star of magnitude 1 is 1 ...
... has observed stars with magnitudes down to ____ at visible wavelengths and the Keck telescopes have located similarly faint stars in the infrared with _________________. F. There is a _________ difference in brightness for stars that differ by a _____________. For example, a star of magnitude 1 is 1 ...
Stars and their Properties
... Cosmic horizon – Edge of the Observable Universe Age of the Universe is determined by the size of the Observable Universe (right now it’s between 14 and 15 billion years old) Astrometry – Measuring the distance of stars and how they move around Solar Neighborhood – Closest stars to the Sun If you kn ...
... Cosmic horizon – Edge of the Observable Universe Age of the Universe is determined by the size of the Observable Universe (right now it’s between 14 and 15 billion years old) Astrometry – Measuring the distance of stars and how they move around Solar Neighborhood – Closest stars to the Sun If you kn ...
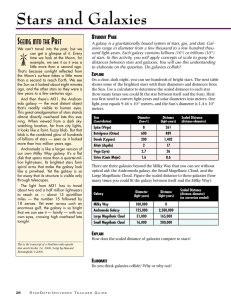
Astro 1 & 100 Levine Homework Stars Name:____________________________
... You may want to do the lecture-tutorial on pg 33, Apparent and Absolute Magnitude of Stars, prior to doing this portion of the homework, if you need a refresher on m and M. Ranking questions are 2 points each. Consider the following table of stars: ...
... You may want to do the lecture-tutorial on pg 33, Apparent and Absolute Magnitude of Stars, prior to doing this portion of the homework, if you need a refresher on m and M. Ranking questions are 2 points each. Consider the following table of stars: ...
CONSTELLATION CANES VENATICI the two hunting dogs Canes
... is Latin for "hunting dogs", and the constellation is often depicted in illustrations as representing the dogs of Boötes the Herdsman, a neighbouring constellation. Canes Venatici is bordered by Ursa Major to the north and west, Coma Berenices to the south, and Boötes to the east. The three-letter a ...
... is Latin for "hunting dogs", and the constellation is often depicted in illustrations as representing the dogs of Boötes the Herdsman, a neighbouring constellation. Canes Venatici is bordered by Ursa Major to the north and west, Coma Berenices to the south, and Boötes to the east. The three-letter a ...
PHYS 2410 General Astronomy Homework 5
... I. the latitude at which sunspots are visible at a given time. II. the number of sunspots that are visible at a given time. III. the rotation rate of the sun's equator at a given time. ...
... I. the latitude at which sunspots are visible at a given time. II. the number of sunspots that are visible at a given time. III. the rotation rate of the sun's equator at a given time. ...
Thursday October 1 - Montana State University
... What if all stars had the same luminosity? • Luminosity means total power output as light. • Determining their distance from us would be easy if they all were the same luminosity! ...
... What if all stars had the same luminosity? • Luminosity means total power output as light. • Determining their distance from us would be easy if they all were the same luminosity! ...
LIfe of a Star
... Hydrogen changes into helium which creates enormous amounts of energy The size of the star does not change much ...
... Hydrogen changes into helium which creates enormous amounts of energy The size of the star does not change much ...
3.6 spectral classes
... The method of parallax is used in measuring the distances to nearby stars. The position of a star is carefully determined relative to other stars. Six months later, when Earth’s revolution has carried telescopes halfway around the Sun, the star’s position is measured again. Nearby stars appear to sh ...
... The method of parallax is used in measuring the distances to nearby stars. The position of a star is carefully determined relative to other stars. Six months later, when Earth’s revolution has carried telescopes halfway around the Sun, the star’s position is measured again. Nearby stars appear to sh ...
The magnitudes of stars
... However this does not give a true impression of the actual brightness of a star. A nearby faint star may well look brighter than another star that is actually brighter but more distant. (A good example of this is shown by Rigel and Sirius in the following table. Sirius looks brighter than Rigel when ...
... However this does not give a true impression of the actual brightness of a star. A nearby faint star may well look brighter than another star that is actually brighter but more distant. (A good example of this is shown by Rigel and Sirius in the following table. Sirius looks brighter than Rigel when ...
STARS
... • Most stars are between 1 billion and 10 billion years old. Some stars may even be close to 13.7 billion years old—the observed age of the universe. The oldest star yet discovered, HE 1523-0901, is an estimated 13.2 billion years old. • The more massive the star, the shorter its lifespan, primarily ...
... • Most stars are between 1 billion and 10 billion years old. Some stars may even be close to 13.7 billion years old—the observed age of the universe. The oldest star yet discovered, HE 1523-0901, is an estimated 13.2 billion years old. • The more massive the star, the shorter its lifespan, primarily ...
HR-diagram - Bakersfield College
... would not be the same apparent magnitude WHY? • To compare absolute brightness • use a standard distance of 32.6 light-years away from earth ...
... would not be the same apparent magnitude WHY? • To compare absolute brightness • use a standard distance of 32.6 light-years away from earth ...
Mountain Skies - Pisgah Astronomical Research Institute
... in particular at the middle star and you will notice it is a bit fuzzy;; it is called the “smoking star” in some Native American traditions. A pair of binoculars or a telescope reveals this to be the beautiful “Great Nebula of Orion,” an immense cloud ...
... in particular at the middle star and you will notice it is a bit fuzzy;; it is called the “smoking star” in some Native American traditions. A pair of binoculars or a telescope reveals this to be the beautiful “Great Nebula of Orion,” an immense cloud ...
Characteristics of Stars Stars Analyzing Starlight Star Characteristics
... most common element - hydrogen second most common - helium ...
... most common element - hydrogen second most common - helium ...
Hertzsprung Russell diagram
... Russell first had the idea of plotting the absolute magnitude of a star against its spectral type. This type of diagram is known as a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. Since the original diagram was produced other quantities, the surface temperature and the luminosity compared with the Sun, have been add ...
... Russell first had the idea of plotting the absolute magnitude of a star against its spectral type. This type of diagram is known as a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. Since the original diagram was produced other quantities, the surface temperature and the luminosity compared with the Sun, have been add ...
star brightness
... Canis minoris (The Sm star of the constellation ion of Orion. near the great constellat ary stars, like our Sun, but bin Many stars are not single of sum the Their brightness is or multiple star systems. ponent stars. the brightness of the com n. htness in a regular patter Some stars change brig ...
... Canis minoris (The Sm star of the constellation ion of Orion. near the great constellat ary stars, like our Sun, but bin Many stars are not single of sum the Their brightness is or multiple star systems. ponent stars. the brightness of the com n. htness in a regular patter Some stars change brig ...