Groups of Stars
... • Many stars exist in groups of two or more stars that are held close together because of gravity • More than half of all stars are members of star systems • Is our Sun part of a star system? ...
... • Many stars exist in groups of two or more stars that are held close together because of gravity • More than half of all stars are members of star systems • Is our Sun part of a star system? ...
Characteristics of stars powerpoint
... • The distance that light travels in one year • It travels about 9.5 million million km • Travels at a speed of 300,000 km per second ...
... • The distance that light travels in one year • It travels about 9.5 million million km • Travels at a speed of 300,000 km per second ...
How Is a Star`s Color Related to Its Temperature?
... 3. Stars with surface temperatures up to 3,500 K are red. Shade a vertical band from 2000 K to 3500 K a light red. 4. Shade other color bands as follows: Stars up to 5000 K are orange-red, up to 6000 K yellow-white, up to 7500 K blue-white, and up to 40,000 K blue. 5. Look for patterns in your graph ...
... 3. Stars with surface temperatures up to 3,500 K are red. Shade a vertical band from 2000 K to 3500 K a light red. 4. Shade other color bands as follows: Stars up to 5000 K are orange-red, up to 6000 K yellow-white, up to 7500 K blue-white, and up to 40,000 K blue. 5. Look for patterns in your graph ...
The Milky Way
... They were believed to represent great heroes and mythological figures. Their position in the sky seemed to tell stories that were handed down from generation to generation over thousands of years. Different cultures grouped stars differently. Example: The Pawnee Indians knew the constellation Scorpi ...
... They were believed to represent great heroes and mythological figures. Their position in the sky seemed to tell stories that were handed down from generation to generation over thousands of years. Different cultures grouped stars differently. Example: The Pawnee Indians knew the constellation Scorpi ...
The HR Diagram
... –HR Diagram • 90% of stars are found on a diagonal line called the main sequence • Hotter on the left cooler on the right • Brighter at top dimmer at bottom ...
... –HR Diagram • 90% of stars are found on a diagonal line called the main sequence • Hotter on the left cooler on the right • Brighter at top dimmer at bottom ...
The Family of Stars
... that a star would have if it were at a distance of 10 pc. If we know a star’s absolute magnitude, we can infer its distance by comparing absolute and apparent magnitudes. ...
... that a star would have if it were at a distance of 10 pc. If we know a star’s absolute magnitude, we can infer its distance by comparing absolute and apparent magnitudes. ...
Stars - Images
... Ways of tracking where the constellations are located during the different seasons of the year. Remember as the earth revolves around the sun, it also rotates causing the stars to “shift” in the ...
... Ways of tracking where the constellations are located during the different seasons of the year. Remember as the earth revolves around the sun, it also rotates causing the stars to “shift” in the ...
White Dwarfs - Astronomy - The University of Texas at Austin
... is still here 10-100 billion of them (~ 100 billion stars total) Most are dim, undiscovered, see only those nearby, none naked eye Sirius, brightest star in the sky, has a white dwarf companion. Can’t see the white dwarf with the naked eye, too small, dim, but Sirius is easy if you look for it at th ...
... is still here 10-100 billion of them (~ 100 billion stars total) Most are dim, undiscovered, see only those nearby, none naked eye Sirius, brightest star in the sky, has a white dwarf companion. Can’t see the white dwarf with the naked eye, too small, dim, but Sirius is easy if you look for it at th ...
Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... The apparent brightness of the Sun is 1400 W m–2 and that of star X is L 8.1 × 10–8 W M–2 The ratio of luminosities is X 12 . Calculate the distance to star X Le in pc. ...
... The apparent brightness of the Sun is 1400 W m–2 and that of star X is L 8.1 × 10–8 W M–2 The ratio of luminosities is X 12 . Calculate the distance to star X Le in pc. ...
Locating Objects in Space
... Red Supergiant: larger and more luminous Supernova: star that blows off its outer shell into interstellar space, luminosity soars & may outshine entire ...
... Red Supergiant: larger and more luminous Supernova: star that blows off its outer shell into interstellar space, luminosity soars & may outshine entire ...
Lab 1-2 : Vocabulary
... • Absolute - the magnitude of a star computed as if viewed from a distance of 32.6 light-years. • Apparent – a star’s brightness as it appears from Earth. The sun APPEARS brighter than the other stars because it is closer to us! ...
... • Absolute - the magnitude of a star computed as if viewed from a distance of 32.6 light-years. • Apparent – a star’s brightness as it appears from Earth. The sun APPEARS brighter than the other stars because it is closer to us! ...
The HR Diagram Interpreted (PowerPoint version)
... The HR Diagram Interpreted: Properties of Stars ...
... The HR Diagram Interpreted: Properties of Stars ...
The HR Diagram Interpreted: Properties of Stars
... The HR Diagram Interpreted: Properties of Stars ...
... The HR Diagram Interpreted: Properties of Stars ...
The Life Cycle of a Star Webquest:
... 15. What is the scientific name for the twinkling of stars? ___________________________ 16. Why do stars twinkle? ____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 17. Why don’t planets twinkle? ________ ...
... 15. What is the scientific name for the twinkling of stars? ___________________________ 16. Why do stars twinkle? ____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 17. Why don’t planets twinkle? ________ ...
The Night Sky 12-07
... Moon slowly wanes it passes near Saturn on the 16th & 17th. A very low thin crescent is to the lower right of Venus on the 23rd. ...
... Moon slowly wanes it passes near Saturn on the 16th & 17th. A very low thin crescent is to the lower right of Venus on the 23rd. ...
Mountain Skies February 8 2016 - Pisgah Astronomical Research
... the most spectacular constellation in the entire sky and, as we’ve seen in past columns, can be used to find other objects and patterns in the sky. Orion can be found high in the east as the sky darkens. The three stars in a row marking his belt are fairly obvious. To the north of these are two more ...
... the most spectacular constellation in the entire sky and, as we’ve seen in past columns, can be used to find other objects and patterns in the sky. Orion can be found high in the east as the sky darkens. The three stars in a row marking his belt are fairly obvious. To the north of these are two more ...
Size Color and Temperature
... Betelgeuse (BEET-uhl-JOOZ) is more than 600 times greater in diameter than the Sun. If Betelgeuse replaced the Sun, it would fill space in our solar system well beyond Earth’s orbit. Because giant and supergiant stars have such huge surface areas to give off light, they are very bright. Betelgeuse i ...
... Betelgeuse (BEET-uhl-JOOZ) is more than 600 times greater in diameter than the Sun. If Betelgeuse replaced the Sun, it would fill space in our solar system well beyond Earth’s orbit. Because giant and supergiant stars have such huge surface areas to give off light, they are very bright. Betelgeuse i ...
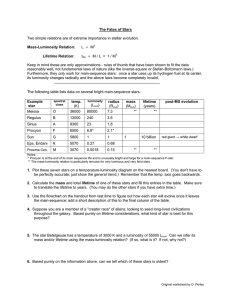
The Fates of Stars Mass-Luminosity Relation: Lifetime Relation:
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
source
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
Chapter 1 Starts and Galaxies
... Giant star- star with a diameter about 10 to 100 times as large as the sun Supergiant star- star with a diameter up to 1000 times the diameter of the sun; largest of all stars White dwarf- small dense star Neutron star- smallest of all stars ...
... Giant star- star with a diameter about 10 to 100 times as large as the sun Supergiant star- star with a diameter up to 1000 times the diameter of the sun; largest of all stars White dwarf- small dense star Neutron star- smallest of all stars ...
25 Study Guide
... • Binary stars can be used to determine stellar mass. • The nearest stars have the largest parallax angles, while those of distant stars are too small to measure. • Three factors control the apparent brightness of a star as seen from Earth: how big it is, how hot it is, and how far away it is. • A H ...
... • Binary stars can be used to determine stellar mass. • The nearest stars have the largest parallax angles, while those of distant stars are too small to measure. • Three factors control the apparent brightness of a star as seen from Earth: how big it is, how hot it is, and how far away it is. • A H ...
chap17_s05_probs
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...