Name: Period : ______ The Universe – Life and Death of a Star How
... 26. While our Sun is a cosmic loner, more than half of all stars are part of _______________________. 27. When a white dwarf pulls in enough material from its companion star and explodes, it is known as a Type 1-A _________________________. 28. Although a supernova is very bright, the visible light ...
... 26. While our Sun is a cosmic loner, more than half of all stars are part of _______________________. 27. When a white dwarf pulls in enough material from its companion star and explodes, it is known as a Type 1-A _________________________. 28. Although a supernova is very bright, the visible light ...
Stellar Magnitude, Distance, and Motion
... Actual star brightness The apparent magnitude that a star would have if it were (in our imagination) placed at a distance of 10 parsecs (which is 32.6 light years) from the Earth Used to describe luminosity - The amount of energy a star gives off each second The 20 Brightest Stars in the Sky C ...
... Actual star brightness The apparent magnitude that a star would have if it were (in our imagination) placed at a distance of 10 parsecs (which is 32.6 light years) from the Earth Used to describe luminosity - The amount of energy a star gives off each second The 20 Brightest Stars in the Sky C ...
Chapter 28 Stars and Galaxies Reading Guide
... 16. We are not able to visit distant stars, yet we can determine how far away they are. How do parallax and math help us do this? A nearby star's apparent movement against the background of more distant stars as the Earth revolves around the Sun is referred to as stellar parallax. Nearby objects hav ...
... 16. We are not able to visit distant stars, yet we can determine how far away they are. How do parallax and math help us do this? A nearby star's apparent movement against the background of more distant stars as the Earth revolves around the Sun is referred to as stellar parallax. Nearby objects hav ...
Lecture 13: The stars are suns
... Magnitude system was invented by Hipparchus (190-120 BC) – he ranked stars by their apparent brightness from ‘first magnitude’ (brightest) to ‘sixth magnitude’ (dimmest). Bright stars have low magnitudes (measure of faintness). A difference of 5 magnitudes corresponds to a factor of 100 in brightnes ...
... Magnitude system was invented by Hipparchus (190-120 BC) – he ranked stars by their apparent brightness from ‘first magnitude’ (brightest) to ‘sixth magnitude’ (dimmest). Bright stars have low magnitudes (measure of faintness). A difference of 5 magnitudes corresponds to a factor of 100 in brightnes ...
Johnathan - WordPress.com
... Auriga is located north of the celestial equator. Its name is the Latin word for "charioteer", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent in the northern Hemisphere winter sky, along with the five other constellations that have ...
... Auriga is located north of the celestial equator. Its name is the Latin word for "charioteer", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent in the northern Hemisphere winter sky, along with the five other constellations that have ...
Problem Sheet for Introduction to Astrophysics
... a) If you could stand on the event horizon of a one-solar-mass black hole (M=1.991030 kg), what is the tidal force acting on you? (Assume your weight is 70kg and your height is 2 m) b) If you could stand on the event horizon of a 109 solar mass black hole, what is the tidal force acting on you (the ...
... a) If you could stand on the event horizon of a one-solar-mass black hole (M=1.991030 kg), what is the tidal force acting on you? (Assume your weight is 70kg and your height is 2 m) b) If you could stand on the event horizon of a 109 solar mass black hole, what is the tidal force acting on you (the ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... The Heavens Are Not Changeless • The Stars Move – Most of our constellations would have been unrecognizable to Neanderthal Man ...
... The Heavens Are Not Changeless • The Stars Move – Most of our constellations would have been unrecognizable to Neanderthal Man ...
Worksheet: Stars and the HR Diagram
... Background: The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were al the same distance away. Rather than speak of the br ...
... Background: The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were al the same distance away. Rather than speak of the br ...
Due Date: Thursday, November 16, 2006
... 3. Is this statement sensible? Why, or why not? (20pt) If the Sun had been born as a high-mass star some 4.6 billion years ago, rather than as a low mass star, the planet Jupiter would probably have Earth-like conditions today, while earth would be hot like Venus. If the Sun was formed as a high-mas ...
... 3. Is this statement sensible? Why, or why not? (20pt) If the Sun had been born as a high-mass star some 4.6 billion years ago, rather than as a low mass star, the planet Jupiter would probably have Earth-like conditions today, while earth would be hot like Venus. If the Sun was formed as a high-mas ...
PPT - University of Delaware
... way to feed large sources of energy and mass into the interstellar medium. • So, everything we are made of comes from stars, their winds, and their deaths. WR wind bubble NGC 2359 ...
... way to feed large sources of energy and mass into the interstellar medium. • So, everything we are made of comes from stars, their winds, and their deaths. WR wind bubble NGC 2359 ...
The Life Cycle of a Star Webquest
... 15. What is the scientific name for the twinkling of stars? ___________________________ 16. Why do stars twinkle? ____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 17. Why don’t planets twinkle? ________ ...
... 15. What is the scientific name for the twinkling of stars? ___________________________ 16. Why do stars twinkle? ____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 17. Why don’t planets twinkle? ________ ...
The Life of a Star
... • Begin as a ball of gas and dust. • Go from there to mainsequence, red-giant or supergiant, then to white dwarf. • Or be a massive star that goes from main-sequence to supernova to neutron star (perhaps pulsar) and perhaps becomes a black hole. ...
... • Begin as a ball of gas and dust. • Go from there to mainsequence, red-giant or supergiant, then to white dwarf. • Or be a massive star that goes from main-sequence to supernova to neutron star (perhaps pulsar) and perhaps becomes a black hole. ...
Light from stars part II
... Flux: the total light Energy emitted by one square meter of an object every second ...
... Flux: the total light Energy emitted by one square meter of an object every second ...
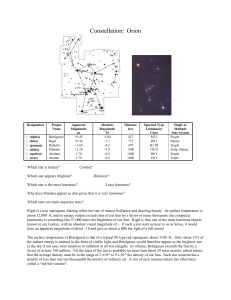
Orion
... Why does Mintaka appear so dim given that it is very luminous? Which stars are main sequence stars? Rigel is a true supergiant, blazing white-hot star of intense brilliance and dazzling beauty. Its surface temperature is about 12,000 K and its energy output exceeds that of our Sun by a factor of ma ...
... Why does Mintaka appear so dim given that it is very luminous? Which stars are main sequence stars? Rigel is a true supergiant, blazing white-hot star of intense brilliance and dazzling beauty. Its surface temperature is about 12,000 K and its energy output exceeds that of our Sun by a factor of ma ...
CHAPTER 2 NOTES (STARS AND GALAXIES)
... to Earth Constellations- groups of stars in which people at one time thought they saw imaginary figures of animals and people: ex Ursa Minor (Little Bear)- containing the Polaris (North Star) Orion (Hunter)- containing the bright supergiant stars, Betelgeuse and Rigel Siruis (Dog Star)- middle sized ...
... to Earth Constellations- groups of stars in which people at one time thought they saw imaginary figures of animals and people: ex Ursa Minor (Little Bear)- containing the Polaris (North Star) Orion (Hunter)- containing the bright supergiant stars, Betelgeuse and Rigel Siruis (Dog Star)- middle sized ...
Astronomy 120
... (a) Capella and the sun have roughly the same surface temperature. Which star is larger? (b) Regulus and Capella have about the same luminosity. Which star is larger? (c) Vega and Sirius have about the same surface temperature. Which star is more luminous? (d) Which star would appear redder, Vega or ...
... (a) Capella and the sun have roughly the same surface temperature. Which star is larger? (b) Regulus and Capella have about the same luminosity. Which star is larger? (c) Vega and Sirius have about the same surface temperature. Which star is more luminous? (d) Which star would appear redder, Vega or ...
Document
... Mizar, 88 light years distant, is the middle star in the handle of the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too ...
... Mizar, 88 light years distant, is the middle star in the handle of the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too ...
Stars
... Mizar, 88 light years distant, is the middle star in the handle of the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too ...
... Mizar, 88 light years distant, is the middle star in the handle of the Big Dipper. It was the first binary star system to be imaged with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too ...
Friday, August 28 - Otterbein University
... The Trouble with Angles • Angular size of an object cannot tell us its actual size – depends on how far away it is • Sun and Moon have very nearly the same angular size (30' = ½) when viewed from Earth ...
... The Trouble with Angles • Angular size of an object cannot tell us its actual size – depends on how far away it is • Sun and Moon have very nearly the same angular size (30' = ½) when viewed from Earth ...
Level 6 Stars and Constellations
... Stars Are very far away from Earth. The closest Star is about 23.5 trillion miles away. ...
... Stars Are very far away from Earth. The closest Star is about 23.5 trillion miles away. ...
Chapter 16 Lesson 2: What is a Star
... this star during the day because its light prevents other stars from being seen. II. Brightness, Color and Temperature of Stars a. The Sun is the closest star to Earth that’s why it appears brighter than any other star and is the only star to supply energy to the earth. b. The brightest and the brig ...
... this star during the day because its light prevents other stars from being seen. II. Brightness, Color and Temperature of Stars a. The Sun is the closest star to Earth that’s why it appears brighter than any other star and is the only star to supply energy to the earth. b. The brightest and the brig ...
Unit 3 - Section 9.2 2011 Star Characteristics0
... 1. The figure displays the spectral patterns for five elements. What do the patterns tell you? 2. There is also a spectral pattern for the Sun. What is the elemental composition of the Sun? 3. There are three “mystery stars.” Using a ruler, line up the spectral patterns of the elements to the myster ...
... 1. The figure displays the spectral patterns for five elements. What do the patterns tell you? 2. There is also a spectral pattern for the Sun. What is the elemental composition of the Sun? 3. There are three “mystery stars.” Using a ruler, line up the spectral patterns of the elements to the myster ...
d 2
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
Stars
... When seen from the Earth, most stars appear as small points of light because they are very far away. They do not move. The Earth rotates, so we are the ones moving. ...
... When seen from the Earth, most stars appear as small points of light because they are very far away. They do not move. The Earth rotates, so we are the ones moving. ...