Distance to Stars
... • The brightness a star would appear if it was set at a standard distance from Earth. – Astronomers calculate the stars apparent magnitude and it’s distance from Earth. – Then calculate the brightness if it were a standard distance from Earth. ...
... • The brightness a star would appear if it was set at a standard distance from Earth. – Astronomers calculate the stars apparent magnitude and it’s distance from Earth. – Then calculate the brightness if it were a standard distance from Earth. ...
Making H-R Diagrams - PLC-METS
... Making an H-R Diagram BACKGOUND INFORMATION: Stars in the sky are not created equal and are composed of different materials, different temperatures, different brightness, different sizes, and different distances from Earth. A star’s mass dictates how bright it will be, how long it will live, its tem ...
... Making an H-R Diagram BACKGOUND INFORMATION: Stars in the sky are not created equal and are composed of different materials, different temperatures, different brightness, different sizes, and different distances from Earth. A star’s mass dictates how bright it will be, how long it will live, its tem ...
Stars - Mc Guckin Science
... Life Cycle of Stars • Matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. • If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the univer ...
... Life Cycle of Stars • Matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. • If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the univer ...
Chapter 1 Vocabulary – The Puzzled of Matter
... Black Hole – an object whose surface gravity is so great that no even electromagnetic waves can escape from it Constellation – a group of stars that appears to from a pattern as seen from Earth Star System – a group of two or more stars held together by gravity Binary Star – a star system with two s ...
... Black Hole – an object whose surface gravity is so great that no even electromagnetic waves can escape from it Constellation – a group of stars that appears to from a pattern as seen from Earth Star System – a group of two or more stars held together by gravity Binary Star – a star system with two s ...
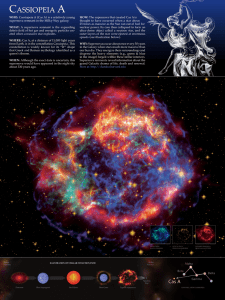
cassiopeia a - Chandra X
... WHO: Cassiopeia A (Cas A) is a relatively young supernova remnant in the Milky Way galaxy. WHAT: A supernova remnant is the expanding debris field of hot gas and energetic particles created when a massive star explodes. WHERE: Cas A, at a distance of 11,000 light years from Earth, is in the constell ...
... WHO: Cassiopeia A (Cas A) is a relatively young supernova remnant in the Milky Way galaxy. WHAT: A supernova remnant is the expanding debris field of hot gas and energetic particles created when a massive star explodes. WHERE: Cas A, at a distance of 11,000 light years from Earth, is in the constell ...
here - Lund Observatory
... 1.15. Determine if the star is a supergiant, a giant or a main-sequence star (dwarf). The visual extinction is three times the colour excess B-V. In thr direction of the star the visual extinction, AV, can be assumed to be given by AV = a ⋅ r, where r is the distance to the star and a = 0.003 magnit ...
... 1.15. Determine if the star is a supergiant, a giant or a main-sequence star (dwarf). The visual extinction is three times the colour excess B-V. In thr direction of the star the visual extinction, AV, can be assumed to be given by AV = a ⋅ r, where r is the distance to the star and a = 0.003 magnit ...
Stars, Constellations, and Quasars
... the equinoxes, there are 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of darkness at every location on Earth. This is because the Earth’s axis points neither toward nor away from the Sun. The Sun is directly overhead at the equator during equinoxes. ...
... the equinoxes, there are 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of darkness at every location on Earth. This is because the Earth’s axis points neither toward nor away from the Sun. The Sun is directly overhead at the equator during equinoxes. ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... • A clue: Compare brightness of our sun to brightness of stars . . . It’s the difference between night and day! ...
... • A clue: Compare brightness of our sun to brightness of stars . . . It’s the difference between night and day! ...
Birth of Stars
... stars in the sky at a time. The most common known star is the Sun. 9000 billion stars have formed over 13.7 billion years. Space is filled with interstellar matter, (matter occurring between the stars of our Galaxy) made up of gas. ...
... stars in the sky at a time. The most common known star is the Sun. 9000 billion stars have formed over 13.7 billion years. Space is filled with interstellar matter, (matter occurring between the stars of our Galaxy) made up of gas. ...
The 22 First Magnitude Stars
... • Usually assigned in order of apparent brightness, but not always • If more needed, lowercase Roman (a - z) and then uppercase Roman (A - Q) [these are not in use anymore] ...
... • Usually assigned in order of apparent brightness, but not always • If more needed, lowercase Roman (a - z) and then uppercase Roman (A - Q) [these are not in use anymore] ...
Telescopes (continued). Properties of Stars.
... Spectral Type The surface temperature also determines the line spectrum of a star. Hot stars display lines of highly ionized elements, while cool stars show molecular lines. Stars are classified by assigning a spectral type. The hottest stars are called spectral type O, followed by B, A, F, G, K, M ...
... Spectral Type The surface temperature also determines the line spectrum of a star. Hot stars display lines of highly ionized elements, while cool stars show molecular lines. Stars are classified by assigning a spectral type. The hottest stars are called spectral type O, followed by B, A, F, G, K, M ...
Characteristics of stars
... • Many stars are about the size of the sun, which is a medium sized star. • White dwarfs are about the size of Earth. • Neutron stars are about 20KM (smallest) • Giant stars and super giant stars. If our sun were a super giant star it would fill our solar system as far out as Jupiter. ...
... • Many stars are about the size of the sun, which is a medium sized star. • White dwarfs are about the size of Earth. • Neutron stars are about 20KM (smallest) • Giant stars and super giant stars. If our sun were a super giant star it would fill our solar system as far out as Jupiter. ...
Observing Information for Waddesdon, 4th October 2014
... This is an asterism of three bright stars, Deneb, Vega and Altair. It is easily visible with the unaided eye and is useful for locating other objects at this time of year. Deneb is the bright star that’s very high to the SE. It’s the brightest star in the constellation Cygnus. It is 1400 light years ...
... This is an asterism of three bright stars, Deneb, Vega and Altair. It is easily visible with the unaided eye and is useful for locating other objects at this time of year. Deneb is the bright star that’s very high to the SE. It’s the brightest star in the constellation Cygnus. It is 1400 light years ...
11.1 Stars - St John Brebeuf
... It is estimated there are more stars in the universe than there are grains of sand on all the beaches on Earth. By peering through the interstellar matter (dust and gases), astronomers can observe the birth of stars. ...
... It is estimated there are more stars in the universe than there are grains of sand on all the beaches on Earth. By peering through the interstellar matter (dust and gases), astronomers can observe the birth of stars. ...
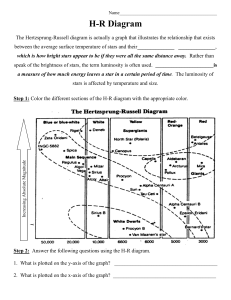
H-R Diagram Student
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightne ...
... The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their______________ ______________, which is how bright stars appear to be if they were all the same distance away. Rather than speak of the brightne ...
Magnitude Scale
... – The smaller (or more negative) the number, the more blue (and hot) the star. ...
... – The smaller (or more negative) the number, the more blue (and hot) the star. ...
Review Game
... 38) An object compacted to such a small size that light cannot escape from its gravitational field is called a: 39) The spherical surface of space which defines the "surface" of a black hole is the: 40) White dwarfs, like Sirius B, would be found to the ________ on the H-R diagram. 41) A red supergi ...
... 38) An object compacted to such a small size that light cannot escape from its gravitational field is called a: 39) The spherical surface of space which defines the "surface" of a black hole is the: 40) White dwarfs, like Sirius B, would be found to the ________ on the H-R diagram. 41) A red supergi ...
From the Everett and Seattle Astronomical
... There are several types of nebulae. Emission nebulae are clouds of high temperature gas. The atoms in the cloud are energized by ultraviolet light from a nearby star and emit radiation as they fall back into lower energy states. Emission nebulae are sites of recent and ongoing star formation. The Or ...
... There are several types of nebulae. Emission nebulae are clouds of high temperature gas. The atoms in the cloud are energized by ultraviolet light from a nearby star and emit radiation as they fall back into lower energy states. Emission nebulae are sites of recent and ongoing star formation. The Or ...
Stars
... Color of Stars • Look at the candle and Bunsen burner. Which is hotter? • The blue flame of the Bunsen burner is much hotter than the yellow flame of the candle. • Stars are different colors too, so we know they are different ...
... Color of Stars • Look at the candle and Bunsen burner. Which is hotter? • The blue flame of the Bunsen burner is much hotter than the yellow flame of the candle. • Stars are different colors too, so we know they are different ...
What`s Up - April 2016
... same distance, Canopus would appear far brighter than Sirius. Canopus is 15000 times as luminous as the sun, a rare yellow-white supergiant 313 light years away. If placed at the center of our solar system, its surface would be three quarters of the distance from the centre to the orbit of Mercury, ...
... same distance, Canopus would appear far brighter than Sirius. Canopus is 15000 times as luminous as the sun, a rare yellow-white supergiant 313 light years away. If placed at the center of our solar system, its surface would be three quarters of the distance from the centre to the orbit of Mercury, ...
The Life Cycle of a Star and the Hertzsprung
... Graphing or plotting data is an essential tool used by scientists. In attempting to make sense of data and see if two quantities are related we can plot them and seek trends. One of the most useful and powerful plots in astronomy is the Hertzsprung - Russell diagram (H-R diagram). The Hertzsprung - ...
... Graphing or plotting data is an essential tool used by scientists. In attempting to make sense of data and see if two quantities are related we can plot them and seek trends. One of the most useful and powerful plots in astronomy is the Hertzsprung - Russell diagram (H-R diagram). The Hertzsprung - ...
Document
... 2. On the next page you will find a listing of the nearest, brightest, and other stars, as well as their surface temperatures and absolute magnitude. On your H-R diagram, plot the absolute magnitude vs. surface temperature for all of the stars listed. Use an * to label the location of the Sun. 3. ...
... 2. On the next page you will find a listing of the nearest, brightest, and other stars, as well as their surface temperatures and absolute magnitude. On your H-R diagram, plot the absolute magnitude vs. surface temperature for all of the stars listed. Use an * to label the location of the Sun. 3. ...
Space Science Unit
... • Stars stay in this part of their life cycle for a long time; most of their “lives” ...
... • Stars stay in this part of their life cycle for a long time; most of their “lives” ...
Merak
... How Far Away: 62 light years away How Bright: About 50 times brighter than the Sun Where to View: In the constellation Ursa Major. When to View:All year round in the Northern Hemisphere ...
... How Far Away: 62 light years away How Bright: About 50 times brighter than the Sun Where to View: In the constellation Ursa Major. When to View:All year round in the Northern Hemisphere ...