Life Cycle of Stars
... • 1. DISTANCE – Measured in light-years • The distance which a ray of light would travel in one year • About 6,000,000,000,000 (6 trillion) miles • 186,000 miles per second ...
... • 1. DISTANCE – Measured in light-years • The distance which a ray of light would travel in one year • About 6,000,000,000,000 (6 trillion) miles • 186,000 miles per second ...
Night Sky Checklist October–November
... Perseus, the Hero, saved Andromeda’s life during one of many adventures. The meteors of the Perseid meteor shower in August seem to come from this constellation. Stars (The stars on the checklist are easily visible to the unaided eye except in the most light polluted parts of cities.) Alpheratz is ...
... Perseus, the Hero, saved Andromeda’s life during one of many adventures. The meteors of the Perseid meteor shower in August seem to come from this constellation. Stars (The stars on the checklist are easily visible to the unaided eye except in the most light polluted parts of cities.) Alpheratz is ...
Inverse Square Law
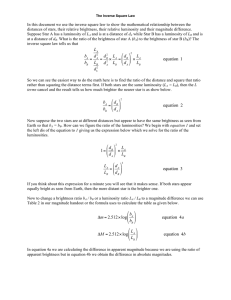
... Suppose Star A has a luminosity of LA and is at a distance of dA while Star B has a luminosity of LB and is at a distance of dB. What is the ratio of the brightness of star A (bA) to the brightness of star B (bB)? The inverse square law tells us that ...
... Suppose Star A has a luminosity of LA and is at a distance of dA while Star B has a luminosity of LB and is at a distance of dB. What is the ratio of the brightness of star A (bA) to the brightness of star B (bB)? The inverse square law tells us that ...
Astronomy 20 Homework # 2
... Handed out on October 8, 2004 Due in class on Friday, October 15, 2004 1. What are the apparent bolometric magnitudes of: (a) a Sun-like star 50 pc away? (b) a 100 Watt lightbulb 10 km away? (c) a galaxy containing ∼ 3 × 1010 stars of an average luminosity ∼ 0.5L⊙ 20 Mpc away? (d) A quasar with lumi ...
... Handed out on October 8, 2004 Due in class on Friday, October 15, 2004 1. What are the apparent bolometric magnitudes of: (a) a Sun-like star 50 pc away? (b) a 100 Watt lightbulb 10 km away? (c) a galaxy containing ∼ 3 × 1010 stars of an average luminosity ∼ 0.5L⊙ 20 Mpc away? (d) A quasar with lumi ...
If you wish to a copy of this months Night Sky News
... prominent and brilliant star, Regulus, lying within half a degree of the ecliptic at some 85 light-years distance. In this position it is occulted occasionally by the Moon. It is a blue-white star of spectral type B7, radiating about 130 times as much light as the Sun and seen from Earth at magnitud ...
... prominent and brilliant star, Regulus, lying within half a degree of the ecliptic at some 85 light-years distance. In this position it is occulted occasionally by the Moon. It is a blue-white star of spectral type B7, radiating about 130 times as much light as the Sun and seen from Earth at magnitud ...
Document
... This also means that if you know the distance to a star (d), and the apparent magnitude (which you can measure by the size of an image on a photograph), then you can use this equation to find distance... Example if you are intersted. Star A has a magnitude of 5 and an absolte magnitude of 12. Thus: ...
... This also means that if you know the distance to a star (d), and the apparent magnitude (which you can measure by the size of an image on a photograph), then you can use this equation to find distance... Example if you are intersted. Star A has a magnitude of 5 and an absolte magnitude of 12. Thus: ...
Worksheet: Stars and the HR Diagram
... Background: The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were al the same distance away. Rather than speak of the br ...
... Background: The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is actually a graph that illustrates the relationship that exists between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude, which is how bright they would appear to be if they were al the same distance away. Rather than speak of the br ...
SSG Coordinators will be at the Cronan Ranch observing site at 5
... scopes in the 4” range under medium to high magnification may glimpse a faint dust lane and some surface mottling. Cassiopeia (S&T Pocket Sky Atlas – pg 1 – 3) This constellation is one of the most recognized in the sky due to its prominent M (or W) asterism. Cassiopeia is also a circumpolar constel ...
... scopes in the 4” range under medium to high magnification may glimpse a faint dust lane and some surface mottling. Cassiopeia (S&T Pocket Sky Atlas – pg 1 – 3) This constellation is one of the most recognized in the sky due to its prominent M (or W) asterism. Cassiopeia is also a circumpolar constel ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... Click Stars: Lights in the Sky and write out the questions and answers to the following on a sheet of white construction paper to be turned in. Be sure your name and period are on it. 1) What is the name of the brightest star in our night sky? What is the name of the brightest star in all of the kno ...
... Click Stars: Lights in the Sky and write out the questions and answers to the following on a sheet of white construction paper to be turned in. Be sure your name and period are on it. 1) What is the name of the brightest star in our night sky? What is the name of the brightest star in all of the kno ...
E3 – Stellar distances
... • At distances greater than Mpc, neither parallax nor spectroscopic parallax can be relied upon to measure the distance to a star. • When we observe another galaxy, all of the stars in that galaxy are approximately the same distance away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known ...
... • At distances greater than Mpc, neither parallax nor spectroscopic parallax can be relied upon to measure the distance to a star. • When we observe another galaxy, all of the stars in that galaxy are approximately the same distance away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known ...
The Night Sky This Month - Usk Astronomical Society
... Venus is in the west in the evening twilight throughout the month and is unfavourable. Mars is just west of south at dusk throughout this month and is poorly placed for observation. In the first days of the month, however it makes a near-equilateral triangle with Saturn and Antares, but low down. Ju ...
... Venus is in the west in the evening twilight throughout the month and is unfavourable. Mars is just west of south at dusk throughout this month and is poorly placed for observation. In the first days of the month, however it makes a near-equilateral triangle with Saturn and Antares, but low down. Ju ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... brilliant objects in their home galaxies, visible from millions or even billions of light-years away. Supernovae are of several distinct types, as is evident from their spectra—the graphs astronomers plot showing the distribution of colors of the supernova light. One major category is core-collapse ...
... brilliant objects in their home galaxies, visible from millions or even billions of light-years away. Supernovae are of several distinct types, as is evident from their spectra—the graphs astronomers plot showing the distribution of colors of the supernova light. One major category is core-collapse ...
Benchmark lesson
... gas and the helium gas that makes up the Sun. During the reaction, called nuclear fusion, large amounts of energy are given off in the form of light and heat. Many schools and community buildings in Florida use this energy to heat water. The energy from the heated water is used to make electricity. ...
... gas and the helium gas that makes up the Sun. During the reaction, called nuclear fusion, large amounts of energy are given off in the form of light and heat. Many schools and community buildings in Florida use this energy to heat water. The energy from the heated water is used to make electricity. ...
Chapter 28 – Stars and Galaxies
... 1. The actual brightness of the star is luminosity 2. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star would be more luminous 3. If the same size, hotter one would be brighter 4. Types of magnitude a. Absolute – as if all stars were same distance from earth b. Apparent – as they appea ...
... 1. The actual brightness of the star is luminosity 2. If two stars have the same surface temperature, the larger star would be more luminous 3. If the same size, hotter one would be brighter 4. Types of magnitude a. Absolute – as if all stars were same distance from earth b. Apparent – as they appea ...
Astro 1 & 100 Levine Homework Stars Name:____________________________
... 1. Rank these stars in order of luminosity, from brightest to dimmest : Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Dimmest Or, all have the same luminosity ______________ 2. Rank these stars in order of apparent brightness, from brightest to dimmest: Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ __ ...
... 1. Rank these stars in order of luminosity, from brightest to dimmest : Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ ______ Dimmest Or, all have the same luminosity ______________ 2. Rank these stars in order of apparent brightness, from brightest to dimmest: Brightest ______ ______ ______ ______ __ ...
Galaxies - C. Levesque
... • The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy • Our solar system is located on the Orion Arm of the Milky Way Galaxy ...
... • The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy • Our solar system is located on the Orion Arm of the Milky Way Galaxy ...
absolute magnitude
... – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
... – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
chapter-30-pp
... Giant stars can be 1,000 times the diameter of our sun. Most stars that are visible from Earth are medium sized stars and similar to our sun. ...
... Giant stars can be 1,000 times the diameter of our sun. Most stars that are visible from Earth are medium sized stars and similar to our sun. ...
stars - allenscience
... The largest stars shed their layers in a massive explosion called a Supernova. The end result is also a planetary nebula. Supernova are so bright that they can outshine an entire galaxy for a period of time. ...
... The largest stars shed their layers in a massive explosion called a Supernova. The end result is also a planetary nebula. Supernova are so bright that they can outshine an entire galaxy for a period of time. ...
Stars
... • The distance which a ray of light would travel in one ‘Earth’ year • About 6,000,000,000,000 (6 trillion) miles • 186,000 miles per second ...
... • The distance which a ray of light would travel in one ‘Earth’ year • About 6,000,000,000,000 (6 trillion) miles • 186,000 miles per second ...
CYGNUS CONSTELLATION, the Swan Cygnus is
... Alpha Cygni, called Deneb, is the brightest star in Cygnus. It is a white supergiant star of spectral type A2Iae that varies between magnitudes 1.21 and 1.29, one of the largest and most luminous A-class stars known. It is located about 3200 light-years away (an A-type star is a main-sequence (hydro ...
... Alpha Cygni, called Deneb, is the brightest star in Cygnus. It is a white supergiant star of spectral type A2Iae that varies between magnitudes 1.21 and 1.29, one of the largest and most luminous A-class stars known. It is located about 3200 light-years away (an A-type star is a main-sequence (hydro ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. September
... star charts or those such as available from the Variable Star Section of the BAA. The Section operates a “mentor” system where novices to variable star observation are given guidance and support. ...
... star charts or those such as available from the Variable Star Section of the BAA. The Section operates a “mentor” system where novices to variable star observation are given guidance and support. ...
lifedeath - University of Glasgow
... Hydrogen fusion – fuelling a star’s nuclear furnace H = Hydrogen He = Helium ...
... Hydrogen fusion – fuelling a star’s nuclear furnace H = Hydrogen He = Helium ...
Scientists classify stars by
... Light A is brighter than light B. We see the apparent magnitude of the lights (how they look to us) If lights A and B were next to each other they would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is tr ...
... Light A is brighter than light B. We see the apparent magnitude of the lights (how they look to us) If lights A and B were next to each other they would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is tr ...
Pretest
... measures how far light travels through space in one year. 12. The distance that a star so far away would appear to move when seen from opposite sides of Earth’s orbit would be too small to measure accurately. 13. A star is born when nuclear fusion begins. 14. Most star formation takes place in the s ...
... measures how far light travels through space in one year. 12. The distance that a star so far away would appear to move when seen from opposite sides of Earth’s orbit would be too small to measure accurately. 13. A star is born when nuclear fusion begins. 14. Most star formation takes place in the s ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.