Parallax, Apparent Magnitude and Absolute Magnitude
... nearby star observed six months apart. As the Earth orbits the Sun, its line of sight towards the star changes, which makes the star’s position shift against the (more distant) background stars (see Figure 2). Because the stars are so far away, this shift is tiny – even the nearest star, Proxima Cen ...
... nearby star observed six months apart. As the Earth orbits the Sun, its line of sight towards the star changes, which makes the star’s position shift against the (more distant) background stars (see Figure 2). Because the stars are so far away, this shift is tiny – even the nearest star, Proxima Cen ...
Kinds of Stars
... size. Include blue-white RIGEL, Whiteyellow CANOPUS, red SuperGiants ANTARES & BETELGUESE. REDSUPERGIANTS- Largest of all stars ...
... size. Include blue-white RIGEL, Whiteyellow CANOPUS, red SuperGiants ANTARES & BETELGUESE. REDSUPERGIANTS- Largest of all stars ...
solution
... for visual (the visible range includes visual and spans B V G R) which lets light in the range 551 nm ± 88 nm through. So for a star to be bright at U and V, but dim at B, means that the spectrum has a big dip in it in-between the two bands. This is very unlikely, since stars are blackbody radiators ...
... for visual (the visible range includes visual and spans B V G R) which lets light in the range 551 nm ± 88 nm through. So for a star to be bright at U and V, but dim at B, means that the spectrum has a big dip in it in-between the two bands. This is very unlikely, since stars are blackbody radiators ...
Astronomy 114 Problem Set # 7 Due: 30 Apr 2007 SOLUTIONS 1
... from very nearby standard candles. One example is the Cepheid Variable that we often use to determine the distance of galaxies. By accurately measuring the parallax of nearby Cepheid Variables we can then determine the correlation between their luminosity and luminosity variability period. Using thi ...
... from very nearby standard candles. One example is the Cepheid Variable that we often use to determine the distance of galaxies. By accurately measuring the parallax of nearby Cepheid Variables we can then determine the correlation between their luminosity and luminosity variability period. Using thi ...
20 Stars/Distances/Magnitudes
... 3. You see a star in the night sky, and you look up its distance to be 10 parsecs. What would you expect to observe for a parallax angle for this star? ...
... 3. You see a star in the night sky, and you look up its distance to be 10 parsecs. What would you expect to observe for a parallax angle for this star? ...
Chapter 15 part 1
... Barnard’s Star. Its parallax is 0.55'', so it lies at a distance of 1.8 pc, or 6.0 light-years. ...
... Barnard’s Star. Its parallax is 0.55'', so it lies at a distance of 1.8 pc, or 6.0 light-years. ...
29.2 Measuring the Stars - Mr. Tobin`s Earth Science Class
... distances between stars are measured. Students will be able to distinguish between brightness and luminosity. Students will be able to identify properties used to classify stars. ...
... distances between stars are measured. Students will be able to distinguish between brightness and luminosity. Students will be able to identify properties used to classify stars. ...
The Stars
... • What is the difference between apparent and absolute magnitude? • What two factors cause luminosity to increase? • What are the spectral classes? • Why is a blue star more luminous than a yellow star of the same size? • What does the H-R diagram show us about most stars (main sequence stars)? • Wh ...
... • What is the difference between apparent and absolute magnitude? • What two factors cause luminosity to increase? • What are the spectral classes? • Why is a blue star more luminous than a yellow star of the same size? • What does the H-R diagram show us about most stars (main sequence stars)? • Wh ...
Sample final exam
... 10. In the space within 20 ly of the Sun, there are few (choose one): OBA class stars ...
... 10. In the space within 20 ly of the Sun, there are few (choose one): OBA class stars ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... 4. Large, massive stars will have a _____________ main sequence stage while less massive stars will have a _________ main sequence stage. 5. What is a red giant? ...
... 4. Large, massive stars will have a _____________ main sequence stage while less massive stars will have a _________ main sequence stage. 5. What is a red giant? ...
11.3.1 Grade 6 Standard 4 Unit Test Astronomy Multiple Choice 1
... Betelgeuse Polaris (North Star) Sirius (Dog Star) ...
... Betelgeuse Polaris (North Star) Sirius (Dog Star) ...
Telescopes (continued). Properties of Stars.
... Measuring the Apparent Brightness Stars emit radiation of all wavelengths. No detector is sensitive to the entire spectrum. Usually we measure apparent brightness in a small range of the complete spectrum. Eyes are sensitive to visible light. When we measure the apparent brightness in the visible r ...
... Measuring the Apparent Brightness Stars emit radiation of all wavelengths. No detector is sensitive to the entire spectrum. Usually we measure apparent brightness in a small range of the complete spectrum. Eyes are sensitive to visible light. When we measure the apparent brightness in the visible r ...
HR Diagram
... It has been shown through observational data of many stars that the more massive a star, the more luminous it is. If you observe the H-R diagram on the cover of the lab, it is clear that there are fewer luminous stars as compared to the less luminous ones. In terms of the diagram, there are more sta ...
... It has been shown through observational data of many stars that the more massive a star, the more luminous it is. If you observe the H-R diagram on the cover of the lab, it is clear that there are fewer luminous stars as compared to the less luminous ones. In terms of the diagram, there are more sta ...
Big bang and Stars
... their original mass After they spend their life as main sequence star …. Sun size > expand to red giant in about 5 ...
... their original mass After they spend their life as main sequence star …. Sun size > expand to red giant in about 5 ...
E3 – Stellar distances
... • At distances greater than Mpc, neither parallax nor spectroscopic parallax can be relied upon to measure the distance to a star. • When we observe another galaxy, all of the stars in that galaxy are approximately the same distance away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known ...
... • At distances greater than Mpc, neither parallax nor spectroscopic parallax can be relied upon to measure the distance to a star. • When we observe another galaxy, all of the stars in that galaxy are approximately the same distance away from the earth. What we really need is a light source of known ...
ppt
... pinwheel (we’ll see other examples). Structure difficult to detect because we live inside galaxy – literally can’t see the forest for the trees… Careful measurement reveals spiral arms, and shows that the disk is rotating differentially. ...
... pinwheel (we’ll see other examples). Structure difficult to detect because we live inside galaxy – literally can’t see the forest for the trees… Careful measurement reveals spiral arms, and shows that the disk is rotating differentially. ...
Patterns in the Sky
... mythical monsters, and animals. - Uras Major is the constellation that the Big Dipper is found. - There are 88 constellations recognized. - Different cultures named the same constellations differently as they used their imagination to group the stars. - Orion (a great hunter), named by the Greeks, w ...
... mythical monsters, and animals. - Uras Major is the constellation that the Big Dipper is found. - There are 88 constellations recognized. - Different cultures named the same constellations differently as they used their imagination to group the stars. - Orion (a great hunter), named by the Greeks, w ...
Project Packet - Montville.net
... 1. Time of year when it is visible 2. What direction you should look and at what time 3. How high above the horizon you should look. Part 2 1. What does your constellation look like? 2. Draw a diagram or include an image in the space on the results pages. Part 3 Look up what stars are in your conste ...
... 1. Time of year when it is visible 2. What direction you should look and at what time 3. How high above the horizon you should look. Part 2 1. What does your constellation look like? 2. Draw a diagram or include an image in the space on the results pages. Part 3 Look up what stars are in your conste ...
Startalk
... A big glowing ball of gas! Contains mainly H and He They have a core that is dense and super hot! Nuclear fusion is the source of their energy! ...
... A big glowing ball of gas! Contains mainly H and He They have a core that is dense and super hot! Nuclear fusion is the source of their energy! ...
Stars: flux, luminosity, color, and temperature
... This is the same way your eye determines color, but the bands are different. ...
... This is the same way your eye determines color, but the bands are different. ...
Friday, Oct. 10
... In traveling a distance of 1 pc from a star, light spreads out over some area. When the light has traveled a distance of 2 pc from the star, it has spread out over 4 times as much area. Since the flux of starlight is the power emitted divided by the area it has spread over, the flux is 4 times small ...
... In traveling a distance of 1 pc from a star, light spreads out over some area. When the light has traveled a distance of 2 pc from the star, it has spread out over 4 times as much area. Since the flux of starlight is the power emitted divided by the area it has spread over, the flux is 4 times small ...
Astrology, calendars and the dating of Christian festivals.
... Napoleon’s naval forces; however the star would never have been seen from that position. The precise South Celestial Pole can be found easily using Canopus and another star Achernar with a magnitude of 0.50 which can be easily seen with the naked eye. Make an imaginary equilateral triangle and place ...
... Napoleon’s naval forces; however the star would never have been seen from that position. The precise South Celestial Pole can be found easily using Canopus and another star Achernar with a magnitude of 0.50 which can be easily seen with the naked eye. Make an imaginary equilateral triangle and place ...
+(J - cloudfront.net
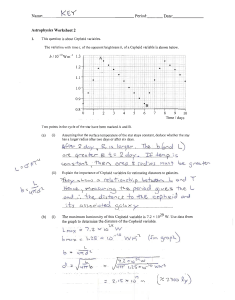
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.