First Exam - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... 26. You look up in the night sky and see the planet Jupiter, the planet Mars, and the Moon very close together. You know that they are located in or close to one of the following. Which is it? (a) the ecliptic ∗ (b) the celestial equator (c) the zenith (d) the north celestial pole (e) the constellat ...
... 26. You look up in the night sky and see the planet Jupiter, the planet Mars, and the Moon very close together. You know that they are located in or close to one of the following. Which is it? (a) the ecliptic ∗ (b) the celestial equator (c) the zenith (d) the north celestial pole (e) the constellat ...
HR Diagram of a Star Cluster
... (or equivalently, color or spectral class). We will assume that every one of the stars on this photograph is a member of the cluster NGC 6819 and so we will assume that they all lie at about the same distance from us. Then we can use their apparent magnitude (V) in place of the (preferred) absolute ...
... (or equivalently, color or spectral class). We will assume that every one of the stars on this photograph is a member of the cluster NGC 6819 and so we will assume that they all lie at about the same distance from us. Then we can use their apparent magnitude (V) in place of the (preferred) absolute ...
Characteristics of Stars ppt.
... Some stars that appear as a single star from Earth are actually binary stars, which are two stars that rotate around a common center of mass. ...
... Some stars that appear as a single star from Earth are actually binary stars, which are two stars that rotate around a common center of mass. ...
What are constellations? - Red Hook Central Schools
... a white bull. He tricked Europa into climbing on his back. He then swam out to sea and carried her to Crete. In Egypt, the constellation was a reminder of Apis, the Bull of Memphis. He served as a servant to Osiris, god of the Sun. Just as famous as Taurus is the group of stars within it. The Pleiad ...
... a white bull. He tricked Europa into climbing on his back. He then swam out to sea and carried her to Crete. In Egypt, the constellation was a reminder of Apis, the Bull of Memphis. He served as a servant to Osiris, god of the Sun. Just as famous as Taurus is the group of stars within it. The Pleiad ...
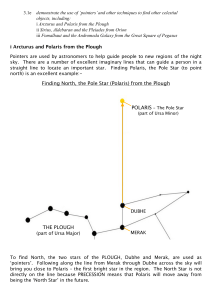
3.1e Finding Polaris and Sirius
... Star hopping is used to find the Andromeda Galaxy (M31). If you live where you have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Squar ...
... Star hopping is used to find the Andromeda Galaxy (M31). If you live where you have very dark skies, the Andromeda Galaxy is the furthest object that you can see with your naked eye – 2.4 million light years away! The galaxy appears as a small, white, fuzzy patch. When you have found the Great Squar ...
18.1 NOTES How are stars formed? Objective: Describe how stars
... A star is a big ball of gases that gives off heat and light. The Sun is only one of billions of stars that make up are galaxy, and there are billions of galaxies. Most stars appear to be white in color. However, there are blue, white, yellow, orange, and red stars. The color of a star determines how ...
... A star is a big ball of gases that gives off heat and light. The Sun is only one of billions of stars that make up are galaxy, and there are billions of galaxies. Most stars appear to be white in color. However, there are blue, white, yellow, orange, and red stars. The color of a star determines how ...
Lecture 13: The stars are suns
... Magnitude system was invented by Hipparchus (190-120 BC) – he ranked stars by their apparent brightness from ‘first magnitude’ (brightest) to ‘sixth magnitude’ (dimmest). Bright stars have low magnitudes (measure of faintness). A difference of 5 magnitudes corresponds to a factor of 100 in brightnes ...
... Magnitude system was invented by Hipparchus (190-120 BC) – he ranked stars by their apparent brightness from ‘first magnitude’ (brightest) to ‘sixth magnitude’ (dimmest). Bright stars have low magnitudes (measure of faintness). A difference of 5 magnitudes corresponds to a factor of 100 in brightnes ...
Stars
... mass increase, gravity begins to contract the cloud further. The temperature begins to rise and the cloud radiates heat (infrared). This is a Protostar (infant star). The gravity contraction continues, and the star reaches 10 million K. Hydrogen nuclei begin to fuse (join together). This is called N ...
... mass increase, gravity begins to contract the cloud further. The temperature begins to rise and the cloud radiates heat (infrared). This is a Protostar (infant star). The gravity contraction continues, and the star reaches 10 million K. Hydrogen nuclei begin to fuse (join together). This is called N ...
1. If a star`s temperature is doubled but radius is kept constant, by
... 1. If a star’s temperature is doubled but radius is kept constant, by how much does its luminosity go up by? 1a. Goes up by a factor of 24 = 16. 2. If a star’s temperature is increased by a factor of three, four, five and six, but in every case its radius is kept constant, what happens to its lumino ...
... 1. If a star’s temperature is doubled but radius is kept constant, by how much does its luminosity go up by? 1a. Goes up by a factor of 24 = 16. 2. If a star’s temperature is increased by a factor of three, four, five and six, but in every case its radius is kept constant, what happens to its lumino ...
Introduction to Stars: Their Properties
... 3. The Sun is the brightest star in the sky, with an apparent magnitude of about -26.5 Sirius is next in line, with an apparent magnitude of -1.5; how many times brighter is the Sun than Sirius? a) 25 ...
... 3. The Sun is the brightest star in the sky, with an apparent magnitude of about -26.5 Sirius is next in line, with an apparent magnitude of -1.5; how many times brighter is the Sun than Sirius? a) 25 ...
Where is the Sun in the Milk Way?
... • This equaDon shows the effect of the geometrical diluDon of the flux as a funcDon of distance from a star. • It’s also called the “Inverse-‐Square Law” ...
... • This equaDon shows the effect of the geometrical diluDon of the flux as a funcDon of distance from a star. • It’s also called the “Inverse-‐Square Law” ...
Starlight and What it Tells Us
... • How bright a star would be at a distance of 32.6 l.y. (10 parsecs) • Sun: 4.5 (inconspicuous naked-eye star) • Altair: 2.2 • Deneb: -7.1 (bright as crescent moon) – Note: Deneb - Altair about 10 magnitudes = 100 x 100 = 10,000 times ...
... • How bright a star would be at a distance of 32.6 l.y. (10 parsecs) • Sun: 4.5 (inconspicuous naked-eye star) • Altair: 2.2 • Deneb: -7.1 (bright as crescent moon) – Note: Deneb - Altair about 10 magnitudes = 100 x 100 = 10,000 times ...
P2_5 The Apparent Magnitude of α Orionis Supernova
... It has been found that when α Orionis becomes a supernova, it will be visible during the day. However, it will appear as a bright star rather than illuminating the Earth in the same way as the sun or moon. The moon has a mean apparent magnitude of -12.74 [6], and gives just enough light to help see ...
... It has been found that when α Orionis becomes a supernova, it will be visible during the day. However, it will appear as a bright star rather than illuminating the Earth in the same way as the sun or moon. The moon has a mean apparent magnitude of -12.74 [6], and gives just enough light to help see ...
Nov - Wadhurst Astronomical Society
... with Andromeda itself. This line will pass through Triangulum and then Aries. Drawing a line down from the two right hand stars in the Square of Pegasus southwards leads to Fomalhaut the brightest star in Pisces and fairly close to the horizon. About midway along this line from Pegasus to Fomalhaut ...
... with Andromeda itself. This line will pass through Triangulum and then Aries. Drawing a line down from the two right hand stars in the Square of Pegasus southwards leads to Fomalhaut the brightest star in Pisces and fairly close to the horizon. About midway along this line from Pegasus to Fomalhaut ...
How to Find the North Star ppt
... Dipper as shown, toward the Little Dipper. The North Star is located at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. The Polestar is the brightest of the Little Dipper stars. ...
... Dipper as shown, toward the Little Dipper. The North Star is located at the end of the handle of the Little Dipper. The Polestar is the brightest of the Little Dipper stars. ...
Earth Science, 10th edition Chapter 23: Beyond Our Solar System I
... I. Properties of stars A. Distance 1. Measuring a star's distance can be very difficult 2. Stellar parallax a. Used for measuring distance to a star b. Apparent shift in a star's position due to the orbital motion of Earth c. Measured as an angle d. Near stars have the largest parallax e. Largest pa ...
... I. Properties of stars A. Distance 1. Measuring a star's distance can be very difficult 2. Stellar parallax a. Used for measuring distance to a star b. Apparent shift in a star's position due to the orbital motion of Earth c. Measured as an angle d. Near stars have the largest parallax e. Largest pa ...
Measuring the ligth
... of 10 pc, one pc (parsec or second of parallax) is the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends and arc of one arc second and is more or less 3.26 light years. The absolute magnitude is related to the luminosity and it’s easy to prove knowing the Suns absolute magnitude and luminosity Mo and ...
... of 10 pc, one pc (parsec or second of parallax) is the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends and arc of one arc second and is more or less 3.26 light years. The absolute magnitude is related to the luminosity and it’s easy to prove knowing the Suns absolute magnitude and luminosity Mo and ...
ABSOLUTE AND APPARENT MAGNITUDES
... As a general (not vastly accurate, but close enough) rule of thumb, the highest apparent magnitude that the naked eye can see under ideal viewing conditions is about +6. Objects can cast visible shadows around an apparent magnitude -4 (you’d need a very dark night to see them though - they’d get pr ...
... As a general (not vastly accurate, but close enough) rule of thumb, the highest apparent magnitude that the naked eye can see under ideal viewing conditions is about +6. Objects can cast visible shadows around an apparent magnitude -4 (you’d need a very dark night to see them though - they’d get pr ...
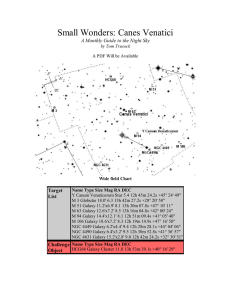
Small Wonders: Canes Venatici
... Canes Venatici is a somewhat small constellation, and may be difficult to find. Flanked on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the ...
... Canes Venatici is a somewhat small constellation, and may be difficult to find. Flanked on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the ...
File - 5th Grade Science Almost done!!!!!!!!!
... • The first thing the students do when they enter the room is write down the homework (see next slide) in stone-silence. • After about 20 to 30 seconds of silence I tell the students “Please begin the warm up.” • Please go through the ppt with the students. Students will have to write items in blue ...
... • The first thing the students do when they enter the room is write down the homework (see next slide) in stone-silence. • After about 20 to 30 seconds of silence I tell the students “Please begin the warm up.” • Please go through the ppt with the students. Students will have to write items in blue ...
Answers to Coursebook questions – Chapter E3
... The distance of star A is larger since its parallax is smaller. Since it appears brighter and it is further away it must have a larger luminosity than star B. ...
... The distance of star A is larger since its parallax is smaller. Since it appears brighter and it is further away it must have a larger luminosity than star B. ...
Introduction to Basic Stargazing Part I - Naples Free-Net
... in reality a very large pattern in the sky. Eighty-eight constellations cover the heavens from pole to pole of which around half are hidden from view at any given moment. On star charts you can often see a couple of solid lines, one is the ecliptic, the path the Sun follows across the sky each year. ...
... in reality a very large pattern in the sky. Eighty-eight constellations cover the heavens from pole to pole of which around half are hidden from view at any given moment. On star charts you can often see a couple of solid lines, one is the ecliptic, the path the Sun follows across the sky each year. ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.