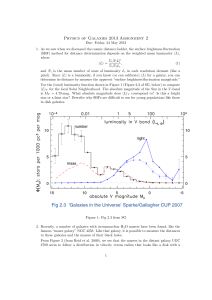
Problem Set 2
... one star moves back-and-forth across the sky in a straight line, meaning that its orbit is edge-on. We take spectra of this star to measure its radial velocity vr from the wavelength shift of its absorption lines, and we find that this repeats exactly each time the star is at the same point in the s ...
... one star moves back-and-forth across the sky in a straight line, meaning that its orbit is edge-on. We take spectra of this star to measure its radial velocity vr from the wavelength shift of its absorption lines, and we find that this repeats exactly each time the star is at the same point in the s ...
Astronomers classify stars according to their physical characteristics
... •A star’s _apparent_ brightness depends upon how bright it _actually is and its _distance_ from Earth. •A star’s actual brightness (or _absolute magnitude) usually depends on the star’s _size_ and temperature__. •Because stars with _more mass ___ have more __self _gravity, they tend to have _higher_ ...
... •A star’s _apparent_ brightness depends upon how bright it _actually is and its _distance_ from Earth. •A star’s actual brightness (or _absolute magnitude) usually depends on the star’s _size_ and temperature__. •Because stars with _more mass ___ have more __self _gravity, they tend to have _higher_ ...
Thought Question
... B. It would be -3 magnitudes brighter C. It would stay the same (its absolute magnitude is an intrinsic property of a star) ...
... B. It would be -3 magnitudes brighter C. It would stay the same (its absolute magnitude is an intrinsic property of a star) ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... Telescope pictures of a developing galactic nebula in our Milky Way Galaxy called NGC 3603. What is the next phase of our sun? ...
... Telescope pictures of a developing galactic nebula in our Milky Way Galaxy called NGC 3603. What is the next phase of our sun? ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... • Stars begin as a large cloud of gas and dust called a nebula • Once stars are formed they enter the main sequence stage. In this stage they continuously generate energy in the core through nuclear fusion. • Size, structure and composition change very little during this stage. ...
... • Stars begin as a large cloud of gas and dust called a nebula • Once stars are formed they enter the main sequence stage. In this stage they continuously generate energy in the core through nuclear fusion. • Size, structure and composition change very little during this stage. ...
PPT - University of Delaware
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
Astrophysics 11 - HR Diagram
... To recap: Analysis of absorption spectra gives clues as to the make up and surface temperature of stars. To know: How to draw a Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram The range on each axis. The position of white dwarfs, the main sequence and red giants ...
... To recap: Analysis of absorption spectra gives clues as to the make up and surface temperature of stars. To know: How to draw a Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram The range on each axis. The position of white dwarfs, the main sequence and red giants ...
Theoretical Modeling of Massive Stars Mr. Russell University of Delaware
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
... massive star(s) in our Milky Way Galaxy 10 M_sun Bipolar Nebula enshrouds star(s) from 1840’s “Giant Eruption” Very close so lots of data Data predicts system is actually a binary system with one star ~90 M_sun and the other ~30 M_sun Think it is in last stages of life before big star undergoes a su ...
Astronomy 2 Relativity and Gravitation
... - Since classification is based on the flux in different parts of the spectrum, one must beware of the effects of wavelength-dependent absorption (i.e. interstellar reddening) which would change the position of a star in the colour magnitude diagram depending on its distance as well as spectral type ...
... - Since classification is based on the flux in different parts of the spectrum, one must beware of the effects of wavelength-dependent absorption (i.e. interstellar reddening) which would change the position of a star in the colour magnitude diagram depending on its distance as well as spectral type ...
ppt
... objects actually are; it measures how bright they appear to us, which also depends on how close they are eg Sun has m = -26.74 • Absolute magnitude - measures how bright objects actually are -- it is defined as the apparent magnitude that an object would have if it were located at a distance of 10 p ...
... objects actually are; it measures how bright they appear to us, which also depends on how close they are eg Sun has m = -26.74 • Absolute magnitude - measures how bright objects actually are -- it is defined as the apparent magnitude that an object would have if it were located at a distance of 10 p ...
Chapter16
... spectral lines. solar motion — The motion of the Sun with respect to the nearby stars. spectral class — A categorization, based on the pattern of spectral lines of stars, that groups stars according to their surface temperatures. supergiant — An extremely luminous star of large size and mass. white ...
... spectral lines. solar motion — The motion of the Sun with respect to the nearby stars. spectral class — A categorization, based on the pattern of spectral lines of stars, that groups stars according to their surface temperatures. supergiant — An extremely luminous star of large size and mass. white ...
Measuring the Stars
... Apparent luminosity is measured using a magnitude scale, which is related to our perception. It is a logarithmic scale; a change of 5 in magnitude corresponds to a change of a factor of 100 in apparent ...
... Apparent luminosity is measured using a magnitude scale, which is related to our perception. It is a logarithmic scale; a change of 5 in magnitude corresponds to a change of a factor of 100 in apparent ...
Photometry
... an object. Often, we will want to know the number of photons at a specific wavelength. When this is the case, we can use special filters so that the only photons we see are of a particular wavelength. This wavelength is identified with a color. The number of photons observed can be converted into an ...
... an object. Often, we will want to know the number of photons at a specific wavelength. When this is the case, we can use special filters so that the only photons we see are of a particular wavelength. This wavelength is identified with a color. The number of photons observed can be converted into an ...
AST 112 – Activity #4 The Stellar Magnitude System
... The stellar magnitude system ranks stars according to their brightnesses. The original idea came from the ancient Greek scientist Hipparchus (c. 130 B.C.), who proclaimed the brightest stars to be of the first “magnitude”, the next brightest of the second magnitude, and so on down to 6th magnitude f ...
... The stellar magnitude system ranks stars according to their brightnesses. The original idea came from the ancient Greek scientist Hipparchus (c. 130 B.C.), who proclaimed the brightest stars to be of the first “magnitude”, the next brightest of the second magnitude, and so on down to 6th magnitude f ...
Wadhurst Astronomical Society Newsletter May 2017
... star reappears is recorded, although as Brian said, this is much more difficult to anticipate. A grazing occultation allows observations of the star as it passes behind mountains on the limb of the Moon from several positions at right angle to the path of the Moon and at the same time. These timings ...
... star reappears is recorded, although as Brian said, this is much more difficult to anticipate. A grazing occultation allows observations of the star as it passes behind mountains on the limb of the Moon from several positions at right angle to the path of the Moon and at the same time. These timings ...
Star Maps and Constellations
... •Lacaille extended Bayer's notation by using lower case (and some upper case) Latin letters. •John Flamsteed (1646-1719) First Royal Astronomer of England •Assigned stars “numbers”, starting with 1 in the west, and working eastward. •Hence Vega is ...
... •Lacaille extended Bayer's notation by using lower case (and some upper case) Latin letters. •John Flamsteed (1646-1719) First Royal Astronomer of England •Assigned stars “numbers”, starting with 1 in the west, and working eastward. •Hence Vega is ...
astronomy - Scioly.org
... 46. How much brighter is a -2 magnitude star than a +2 magnitude star? 47. RR Lyrae variable stars are typically _________ giant stars? (fill in the blank with a color) 48. Variable stars are stars in which the _______ changes over time. A. Size B. Color C. Shape D. brightness 49. A planet orbits th ...
... 46. How much brighter is a -2 magnitude star than a +2 magnitude star? 47. RR Lyrae variable stars are typically _________ giant stars? (fill in the blank with a color) 48. Variable stars are stars in which the _______ changes over time. A. Size B. Color C. Shape D. brightness 49. A planet orbits th ...
Ch.1, Sec.3 - Mapping the Stars
... planets and we use the lightyear to measure their distance from us - one light-year represents the distance light travels in 365 days (6 trillion miles @ 186,000 miles per second) ...
... planets and we use the lightyear to measure their distance from us - one light-year represents the distance light travels in 365 days (6 trillion miles @ 186,000 miles per second) ...
Brighter than the average star?
... Brighter than the average star? Many popular astronomy books start by explaining how small and unimportant our Solar System is. The famous ‘Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy’ begins by describing our own star with the words “Far out in the uncharted backwaters of the unfashionable end of the Western ...
... Brighter than the average star? Many popular astronomy books start by explaining how small and unimportant our Solar System is. The famous ‘Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy’ begins by describing our own star with the words “Far out in the uncharted backwaters of the unfashionable end of the Western ...
HR Diagram
... H-R Diagram Scientists began to learn about stars by observing properties of stars, including brightness and color. Astronomers tried to make sense of the star data by grouping together stars with similar properties. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram provides a way to group similar stars. The H-R dia ...
... H-R Diagram Scientists began to learn about stars by observing properties of stars, including brightness and color. Astronomers tried to make sense of the star data by grouping together stars with similar properties. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram provides a way to group similar stars. The H-R dia ...
Stars
... • DISTANCE – Measured in light-years • The distance which a ray of light would travel in one year • About 6,000,000,000,000 (6 trillion) miles • SPEED of LIGHT is ...
... • DISTANCE – Measured in light-years • The distance which a ray of light would travel in one year • About 6,000,000,000,000 (6 trillion) miles • SPEED of LIGHT is ...
Sky News – March 2015 The Realm of the Galaxies
... we can see deep into the sky without objects being obscured or dimmed by looking through our galaxy. In spring skies we are treated to views of the closest cluster of galaxies in Virgo of which our local group of galaxies are outlying members. Here galaxies are so numerous that they seem to outnumbe ...
... we can see deep into the sky without objects being obscured or dimmed by looking through our galaxy. In spring skies we are treated to views of the closest cluster of galaxies in Virgo of which our local group of galaxies are outlying members. Here galaxies are so numerous that they seem to outnumbe ...
SR Stellar Properties
... Name: ________________________________ Date: ___________________ Period: _________ H-R Diagram Scientists began to learn about stars by observing properties of stars, including brightness and color. Astronomers tried to make sense of the star data by grouping together stars with similar properties. ...
... Name: ________________________________ Date: ___________________ Period: _________ H-R Diagram Scientists began to learn about stars by observing properties of stars, including brightness and color. Astronomers tried to make sense of the star data by grouping together stars with similar properties. ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.