this article as a PDF
... then try 100x and 200x. The name "planetary" is misleading, as these objects are not planets at all but stars at the end of their life cycle. However, they do look something like cloudy planets, and this fact confused earlier observers whose incorrect naming convention has stayed with us to this day ...
... then try 100x and 200x. The name "planetary" is misleading, as these objects are not planets at all but stars at the end of their life cycle. However, they do look something like cloudy planets, and this fact confused earlier observers whose incorrect naming convention has stayed with us to this day ...
The Night Sky May 2016 - Bridgend Astronomical Society
... Algieba, which forms the base of the neck, is the second brightest star in Leo at magnitude 1.9. With a telescope it resolves into one of the most magnificent double stars in the sky - a pair of golden yellow stars! They orbit their common centre of gravity every 600 years. This lovely pair of orang ...
... Algieba, which forms the base of the neck, is the second brightest star in Leo at magnitude 1.9. With a telescope it resolves into one of the most magnificent double stars in the sky - a pair of golden yellow stars! They orbit their common centre of gravity every 600 years. This lovely pair of orang ...
AJAstroProject
... million ly away. • It is in the same group as M95 (Previous) and M96 not photographed. • In this exposure you can see two other galaxies, NGC3384 and NGC3379. • NGC3384 is in the Leo Group I and NGC3379 is a more distant galaxy. This was a 90sec exposure through the V-filter. ...
... million ly away. • It is in the same group as M95 (Previous) and M96 not photographed. • In this exposure you can see two other galaxies, NGC3384 and NGC3379. • NGC3384 is in the Leo Group I and NGC3379 is a more distant galaxy. This was a 90sec exposure through the V-filter. ...
W > 1 - The Open University
... NGC1502 (5.7) oc. A fine open cluster. Extending NW of this cluster is a line of 9th and 10th magnitude stars which form "Kemble's Cascade". A beautiful sight in binoculars or a low power wide-field eyepiece on small telescopes. NGC2403 (8.4) sg. Visible in large binoculars. It lies at a distance of ...
... NGC1502 (5.7) oc. A fine open cluster. Extending NW of this cluster is a line of 9th and 10th magnitude stars which form "Kemble's Cascade". A beautiful sight in binoculars or a low power wide-field eyepiece on small telescopes. NGC2403 (8.4) sg. Visible in large binoculars. It lies at a distance of ...
File
... 10. The region of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram that most stars fall within is the ______________________ . 11. A graph of stars showing surface temperature on the x-axis and absolute brightness on the y-axis is a(n) ________________________ . 12. ______________________ is often used to determine ...
... 10. The region of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram that most stars fall within is the ______________________ . 11. A graph of stars showing surface temperature on the x-axis and absolute brightness on the y-axis is a(n) ________________________ . 12. ______________________ is often used to determine ...
wk09noQ
... • The Zero Age Main Sequence (ZAMS) represents the onset or start of nuclear burning (fusion) • The properties of a star on the ZAMS are primarily determined by its mass, somewhat dependent on chemical composition (fraction of He and heavier elements) • The classification of stars in an HR diagram b ...
... • The Zero Age Main Sequence (ZAMS) represents the onset or start of nuclear burning (fusion) • The properties of a star on the ZAMS are primarily determined by its mass, somewhat dependent on chemical composition (fraction of He and heavier elements) • The classification of stars in an HR diagram b ...
Astronomy 100 Name(s):
... Once The Sky is open, go to Data → Location and confirm the location is Seattle, Washington (if not, you can choose this from the predefined list). Next go to Data → Time and set the time for 9 p.m. tonight. If you have time, you may wish to play with some of the following controls: on the second li ...
... Once The Sky is open, go to Data → Location and confirm the location is Seattle, Washington (if not, you can choose this from the predefined list). Next go to Data → Time and set the time for 9 p.m. tonight. If you have time, you may wish to play with some of the following controls: on the second li ...
What is a Star?
... same distance from Earth in the night sky. • How do we know that they are not? – Parallax • Is the apparent change in position of an object when you look at it from different positions. ...
... same distance from Earth in the night sky. • How do we know that they are not? – Parallax • Is the apparent change in position of an object when you look at it from different positions. ...
The magnitude scale, parallax, the parsec, and Cepheid distances
... – e.g. if f ranges from 101 to 1030 units ...
... – e.g. if f ranges from 101 to 1030 units ...
Magnitudes - Astronomy @ Walton High School
... We measure the brightness of a star by its magnitude. There are two types of magnitude: Apparent magnitude is how bright an object is to us on Earth. Absolute magnitude is how bright a star would appear in space from a certain distance. ...
... We measure the brightness of a star by its magnitude. There are two types of magnitude: Apparent magnitude is how bright an object is to us on Earth. Absolute magnitude is how bright a star would appear in space from a certain distance. ...
IB_Op_F_04 - Effectsmeister
... Which spectral class is most common? Which spectral class is the least common? In general, what is the relationship between the temperature of a star and its brightness? Most of the stars seem to be along a line from the upper left corner to the lower right corner of the HR Diagram. Stars which fall ...
... Which spectral class is most common? Which spectral class is the least common? In general, what is the relationship between the temperature of a star and its brightness? Most of the stars seem to be along a line from the upper left corner to the lower right corner of the HR Diagram. Stars which fall ...
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #20 Key
... Hubble was able to detect Cepheid variable stars within that “Nebula.” Then by observing their light curves and using the known period- luminosity relation for Cepheids, he obtained and compared the absolute magnitudes of these Cepheids with his observed apparent magnitudes, yielding a distance for ...
... Hubble was able to detect Cepheid variable stars within that “Nebula.” Then by observing their light curves and using the known period- luminosity relation for Cepheids, he obtained and compared the absolute magnitudes of these Cepheids with his observed apparent magnitudes, yielding a distance for ...
FINAL EXAM Name: ASTRONOMY II - 79202 Spring 1995
... to the known value of the sun’s age. Assume 1% efficiency to convert gravitational potential energy to luminosity. ...
... to the known value of the sun’s age. Assume 1% efficiency to convert gravitational potential energy to luminosity. ...
Absolute Magnitudes of Supernovae
... Figure 1: Six views of a distance galaxy with a supernova to the lower left of the galaxy. Notice the decreasing brightness and changing color of the supernova with time. (Hubble Space Telescope) ...
... Figure 1: Six views of a distance galaxy with a supernova to the lower left of the galaxy. Notice the decreasing brightness and changing color of the supernova with time. (Hubble Space Telescope) ...
Date_________________ TWINKLE, TWINKLE
... a star. The spectra of stars provide one basis for classifying stars. Stars have colors which you can notice if you let your eyes acclimate at night (red, orange, yellow, white, and blue). The major lines in a star's spectrum dictates the color. Stars of similar color share other characteristics tha ...
... a star. The spectra of stars provide one basis for classifying stars. Stars have colors which you can notice if you let your eyes acclimate at night (red, orange, yellow, white, and blue). The major lines in a star's spectrum dictates the color. Stars of similar color share other characteristics tha ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... become a red giant and expand in size to envelope the Earth. And surprisingly, the larger the mass of the star, the quicker it burns its fuel sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telescope pictures of a developing galactic nebula in our Milky Way Galaxy called N ...
... become a red giant and expand in size to envelope the Earth. And surprisingly, the larger the mass of the star, the quicker it burns its fuel sources and the shorter its lifespan. Also see and read about Hubble Space Telescope pictures of a developing galactic nebula in our Milky Way Galaxy called N ...
Astronomy 360 - indstate.edu
... This is the preferred coordinate system (Equatorial Coordinates) to pinpoint objects on the celestial sphere. Unlike the horizontal coordinate system, equatorial coordinates are independent of the observer's location and the time of the observation. This means that only one set of coordinates is re ...
... This is the preferred coordinate system (Equatorial Coordinates) to pinpoint objects on the celestial sphere. Unlike the horizontal coordinate system, equatorial coordinates are independent of the observer's location and the time of the observation. This means that only one set of coordinates is re ...
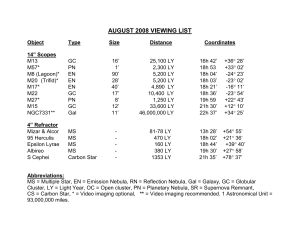
August
... star splits into a close binary. While some observers see color differences, most see the stars as two pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraor ...
... star splits into a close binary. While some observers see color differences, most see the stars as two pairs of white headlights oriented nearly perpendicular to each other. Albireo Beta Cygni, in the constellation Cygnus (SIG-nus) is probably not a true binary, but a visual double star with extraor ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 • In this class we will cover: Brief review
... Interlude: Naming stars Ordinary stars Greek letter (in order of brightness) then constellation e.g. α-Orionis is brightest star in Orion (aka Betelgeuse) δ-Cephei is fourth brightest star in Cepheus Variable stars Listed in order of discovery, starting with “R”, then “S” and on through “Z”, then “ ...
... Interlude: Naming stars Ordinary stars Greek letter (in order of brightness) then constellation e.g. α-Orionis is brightest star in Orion (aka Betelgeuse) δ-Cephei is fourth brightest star in Cepheus Variable stars Listed in order of discovery, starting with “R”, then “S” and on through “Z”, then “ ...
Stars and Galaxies
... When a star has used up its “stable” fuel, the force of fusion no longer balances with the force of gravity and the star loses its stability 1. when this occurs the core contracts in upon itself and becomes very hot causing the outer layers of the star to expand away from the core. 2. now this radia ...
... When a star has used up its “stable” fuel, the force of fusion no longer balances with the force of gravity and the star loses its stability 1. when this occurs the core contracts in upon itself and becomes very hot causing the outer layers of the star to expand away from the core. 2. now this radia ...
Stars - Haag
... (how bright it actually is) astronomers use the star’s apparent magnitude and it’s distance from earth. ...
... (how bright it actually is) astronomers use the star’s apparent magnitude and it’s distance from earth. ...
Document
... Recall that WIEN’s Law states that the wavelength of the blackbody peak is inversely proportional to temperature as λ = b/T where b = 2897768.5 nm·K ...
... Recall that WIEN’s Law states that the wavelength of the blackbody peak is inversely proportional to temperature as λ = b/T where b = 2897768.5 nm·K ...
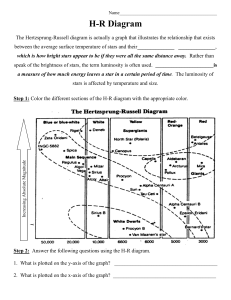
H-R Diagram Student
... 4. Name a star that is very dim and red. ____________________________________________ 5. Compare our sun to Alpha Centauri A in terms of brightness, color and surface temperature.___________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ ...
... 4. Name a star that is very dim and red. ____________________________________________ 5. Compare our sun to Alpha Centauri A in terms of brightness, color and surface temperature.___________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ ...
Star Gazing
... • Winter/Spring: Orion’s belt, left to Sirius, right to Aldebaran (Taurus) and Pleiades ...
... • Winter/Spring: Orion’s belt, left to Sirius, right to Aldebaran (Taurus) and Pleiades ...
Astronomy
... horizon to the location of an object (usually starting from the North pole and moving East; ...
... horizon to the location of an object (usually starting from the North pole and moving East; ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.