Lesson 2 Power Notes Outline
... When astronomers use the word luminosity, they mean the actual brightness of a star. They measure it on a scale called absolute magnitude. ...
... When astronomers use the word luminosity, they mean the actual brightness of a star. They measure it on a scale called absolute magnitude. ...
File
... properties that allow us to determine distances to far away galaxies. We call these stellar candles • One of these candles is a type of variable star called a cepheid variable. • Variable stars are stars that pulsate, changing their size and temperature (and therefore their brightness) in a predicta ...
... properties that allow us to determine distances to far away galaxies. We call these stellar candles • One of these candles is a type of variable star called a cepheid variable. • Variable stars are stars that pulsate, changing their size and temperature (and therefore their brightness) in a predicta ...
Constellations
... from those seen by the ancient Greeks, the Babylonians, and the people of other cultures, even though they were all looking at the same stars in the night sky. Interestingly, though, different cultures often made the same basic groupings of stars, despite widely varying interpretations of what they ...
... from those seen by the ancient Greeks, the Babylonians, and the people of other cultures, even though they were all looking at the same stars in the night sky. Interestingly, though, different cultures often made the same basic groupings of stars, despite widely varying interpretations of what they ...
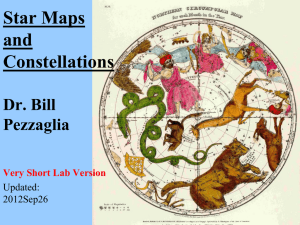
Star Maps and Constellations
... •For example, Alpha Centauri (abbreviated α-Cen) is the brightest star in the constellation Centaurus, while Beta Centauri or "β-Cen" is the second brightest. •However, in some cases (n.b. Ursa Major), Bayer named the stars not in order of brightness, but in order of location. ...
... •For example, Alpha Centauri (abbreviated α-Cen) is the brightest star in the constellation Centaurus, while Beta Centauri or "β-Cen" is the second brightest. •However, in some cases (n.b. Ursa Major), Bayer named the stars not in order of brightness, but in order of location. ...
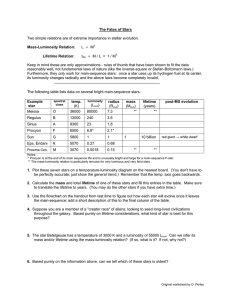
Calculating_Main_Sequence_Lifetimes_StudentGuide
... At the beginning of the twentieth century two astronomers, the Danish E. Hertzsprung and the American H. N. Russell, established a correlation between two important stellar parameters: brightness and color. Since ancient times, the brightness of a star is indicated by "magnitudes": 1, 2 and so on, w ...
... At the beginning of the twentieth century two astronomers, the Danish E. Hertzsprung and the American H. N. Russell, established a correlation between two important stellar parameters: brightness and color. Since ancient times, the brightness of a star is indicated by "magnitudes": 1, 2 and so on, w ...
Unit 11 Vocabulary
... 3. protostar - a very young star that is still gathering mass from its parent molecular cloud. This is the earliest phase in the process of a star’s evolution. 4. main sequence star - stars that are fusing hydrogen atoms to form helium atoms in their cores. Most of the stars in the universe are main ...
... 3. protostar - a very young star that is still gathering mass from its parent molecular cloud. This is the earliest phase in the process of a star’s evolution. 4. main sequence star - stars that are fusing hydrogen atoms to form helium atoms in their cores. Most of the stars in the universe are main ...
STARS AND CONSTELLATIONS
... - Used to find North Star. The North Star is about six times the distance between bowl stars (pointer stars) - Two galaxies and one planetary nebula are found in the Big Dipper. The planetary nebula is the Owl Nebula, (a star explodes shedding it’s outer layer of gases). - In Greek mythology the Big ...
... - Used to find North Star. The North Star is about six times the distance between bowl stars (pointer stars) - Two galaxies and one planetary nebula are found in the Big Dipper. The planetary nebula is the Owl Nebula, (a star explodes shedding it’s outer layer of gases). - In Greek mythology the Big ...
Phobos
... This star is the famous Castor, the horseman. There is some idea that either this star or Pollux has changed in brightness over the past few hundred years because Castor is no longer the brighter of the two. Instead it is now ranked as the 23rd brightest star in the sky or perhaps we should say brig ...
... This star is the famous Castor, the horseman. There is some idea that either this star or Pollux has changed in brightness over the past few hundred years because Castor is no longer the brighter of the two. Instead it is now ranked as the 23rd brightest star in the sky or perhaps we should say brig ...
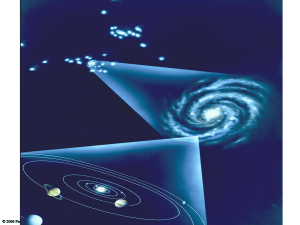
The hierarchical structure of the Universe (go from little to large)
... The Big Dipper is closer than Orion because the Big Dipper looks larger in the sky. ...
... The Big Dipper is closer than Orion because the Big Dipper looks larger in the sky. ...
Calculating Main Sequence Lifetimes
... At the beginning of the twentieth century two astronomers, the Danish E. Hertzsprung and the American H. N. Russell, established a correlation between two important stellar parameters: brightness and color. Since ancient times, the brightness of a star is indicated by "magnitudes": 1, 2 and so on, w ...
... At the beginning of the twentieth century two astronomers, the Danish E. Hertzsprung and the American H. N. Russell, established a correlation between two important stellar parameters: brightness and color. Since ancient times, the brightness of a star is indicated by "magnitudes": 1, 2 and so on, w ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black ...
... neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the universe. What is left behind is an intense region of gravity called a black ...
Sky Watching Talk
... of stars all in roughly the same direction from Earth, BUT …. Each has its own different distance from the Earth – Therefore, NOT grouped together is space ...
... of stars all in roughly the same direction from Earth, BUT …. Each has its own different distance from the Earth – Therefore, NOT grouped together is space ...
Johnathan - WordPress.com
... star in the night sky, with a visual magnitude of 0.13. Rigel is a triple star system. The primary star (Rigel A) is a bluewhite supergiant around 120,000 times as luminous as the Sun. It has exhausted its core hydrogen and swollen out to 79 times the Sun's radius. An Alpha Cygni variable, it puls ...
... star in the night sky, with a visual magnitude of 0.13. Rigel is a triple star system. The primary star (Rigel A) is a bluewhite supergiant around 120,000 times as luminous as the Sun. It has exhausted its core hydrogen and swollen out to 79 times the Sun's radius. An Alpha Cygni variable, it puls ...
Constellations
... if they were all the same distance from earth. All stars place 32.6 LY from the sun Our sun abs. Mag = 4.8 Negative is brighter ...
... if they were all the same distance from earth. All stars place 32.6 LY from the sun Our sun abs. Mag = 4.8 Negative is brighter ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explo ...
... E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explo ...
Lec12
... squeezed as they move into spiral arms 2. Squeezing of clouds triggers star formation 3. Young stars flow out of spiral arms ...
... squeezed as they move into spiral arms 2. Squeezing of clouds triggers star formation 3. Young stars flow out of spiral arms ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explo ...
... E = MC2 and learn how mass in the form of hydrogen atoms is converted to helium and causes a release of energy that makes stars shine. 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explo ...
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop\Lecture 15.wpd
... to the astronomer we need to know how far away a star or galaxy is. Example: If you look at the sky, Sirius is brighter than Betelgeuse. But Betelgeuse is actually 300 times more luminous or brighter than Sirius. That is, Betelgeuse actually emits far more energy than Sirius. The reason is that Bete ...
... to the astronomer we need to know how far away a star or galaxy is. Example: If you look at the sky, Sirius is brighter than Betelgeuse. But Betelgeuse is actually 300 times more luminous or brighter than Sirius. That is, Betelgeuse actually emits far more energy than Sirius. The reason is that Bete ...
using a cepheid variable to determine distance
... 4. Distance modulus ( m - M ) = _________ 5. Distance to the Cepheid ( r ) = _______ parsecs Distance to the Cepheid ( r ) = _______light years ...
... 4. Distance modulus ( m - M ) = _________ 5. Distance to the Cepheid ( r ) = _______ parsecs Distance to the Cepheid ( r ) = _______light years ...
Nov13Guide - East-View
... High in the sky looking southwards, the square of Pegasus is still the group of stars which catches the eye, but the square is joined to the east by the ancient constellation of Andromeda. Andromeda was the mythological daughter of Queen Cassiopeia and King Cepheus who was rescued from Cetus, the se ...
... High in the sky looking southwards, the square of Pegasus is still the group of stars which catches the eye, but the square is joined to the east by the ancient constellation of Andromeda. Andromeda was the mythological daughter of Queen Cassiopeia and King Cepheus who was rescued from Cetus, the se ...
Stars
... Life Cycle of Stars • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the univ ...
... Life Cycle of Stars • The matter inside the star will be compressed so tightly that its atoms are compacted into a dense shell of neutrons. If the remaining mass of the star is more than about three times that of the Sun, it will collapse so completely that it will literally disappear from the univ ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.