Part 2 Answer Key
... Star Clusters are multiple star systems bound together by the force of gravity. Star Clusters can be divided into two main groups. One group is called Globular Clusters. They contain many stars and gravity holds them tightly together. They swarm just outside the galaxy and form a halo or bulge. We k ...
... Star Clusters are multiple star systems bound together by the force of gravity. Star Clusters can be divided into two main groups. One group is called Globular Clusters. They contain many stars and gravity holds them tightly together. They swarm just outside the galaxy and form a halo or bulge. We k ...
Scientists classify stars by
... Light A is brighter than light B. We see the apparent magnitude of the lights (how they look to us) If lights A and B were next to each other they would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is tr ...
... Light A is brighter than light B. We see the apparent magnitude of the lights (how they look to us) If lights A and B were next to each other they would look the same because the two lights are exactly the same. Their absolute magnitude is the same. Distance makes them look different. The same is tr ...
constellations are not real!
... per day. This apparent rotation of the celestial sphere presents us with an obvious means of defining a coordinate system for the surface of the celestial sphere - the extensions of the north pole (NP) and south pole (SP) of the Earth intersect with the north celestial pole (NCP) and the south celes ...
... per day. This apparent rotation of the celestial sphere presents us with an obvious means of defining a coordinate system for the surface of the celestial sphere - the extensions of the north pole (NP) and south pole (SP) of the Earth intersect with the north celestial pole (NCP) and the south celes ...
LIGO Star Chart
... shape. The best observations can be made from early September through December. ...
... shape. The best observations can be made from early September through December. ...
Document
... A standard candle can be any object (or class of object) that: a. Always has the same luminosity. b. Has some means of knowing its luminosity without first needing to know its distance. c. Can vary in brightness (as long as it always has the same average luminosity). d. Has a known absolute magnitud ...
... A standard candle can be any object (or class of object) that: a. Always has the same luminosity. b. Has some means of knowing its luminosity without first needing to know its distance. c. Can vary in brightness (as long as it always has the same average luminosity). d. Has a known absolute magnitud ...
doc - IAC
... They are certainly very special objects. Are these stars found in all kinds of galaxies? They can in principle be seen in any galaxy, but above all in galaxies with active star formation; in other words those in which stars are forming now. This occurs because in old galaxies, such as ellipticals, a ...
... They are certainly very special objects. Are these stars found in all kinds of galaxies? They can in principle be seen in any galaxy, but above all in galaxies with active star formation; in other words those in which stars are forming now. This occurs because in old galaxies, such as ellipticals, a ...
Proxima
... Centaurus is known as a “myth” constellation. It’s the 9th largest constellation in the sky Proxima is the 3rd star in Centaurus Contains 2 of the brightest stars (Alpha Centauri and Beta Centauri) It contains 11 stars ...
... Centaurus is known as a “myth” constellation. It’s the 9th largest constellation in the sky Proxima is the 3rd star in Centaurus Contains 2 of the brightest stars (Alpha Centauri and Beta Centauri) It contains 11 stars ...
E8B6_CRT_CR_MSTIPS_Final
... The accompanying picture shows the Milky Way Galaxy stretching from side-to-side across the mid-section of the photo. Each of the following statements accurately interprets information which can be observed in the photo EXCEPT A. more stars exist within the disk of the Milky Way Galaxy than are abov ...
... The accompanying picture shows the Milky Way Galaxy stretching from side-to-side across the mid-section of the photo. Each of the following statements accurately interprets information which can be observed in the photo EXCEPT A. more stars exist within the disk of the Milky Way Galaxy than are abov ...
Herzsprung-Russell Diagram
... The correlation between luminosity and spectral type also gives us further means to measure the distance to far away stars in our galaxy (Spectroscopic parallax) RUNG 4 Procedure: •Determine the star’s spectral type from spectroscopy and measure the star’s apparent brightness. •Use the main sequen ...
... The correlation between luminosity and spectral type also gives us further means to measure the distance to far away stars in our galaxy (Spectroscopic parallax) RUNG 4 Procedure: •Determine the star’s spectral type from spectroscopy and measure the star’s apparent brightness. •Use the main sequen ...
Stellarium Night Sky Search Key Commands Constellations buttons
... arrows will easily move your view in different directions.] ...
... arrows will easily move your view in different directions.] ...
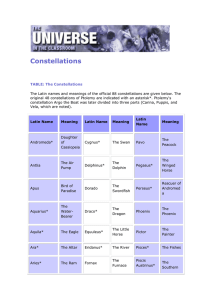
Clarice - Science A 2 Z
... rival of Mars” it is the thirteenth brightest star in the sky. • Antares is slowly evaporating due to fierce winds that blow from it’s surface. • The Polynesians saw Scorpius as a simple fishhook. http://www.barransclass.com/astr1070/const/Yoneguchi/Scorpius.jpg ...
... rival of Mars” it is the thirteenth brightest star in the sky. • Antares is slowly evaporating due to fierce winds that blow from it’s surface. • The Polynesians saw Scorpius as a simple fishhook. http://www.barransclass.com/astr1070/const/Yoneguchi/Scorpius.jpg ...
Diapositiva 1
... the brightest star Theta-1 Orionis C powers the complex star forming region's entire visible glow. About three million years old, the Orion Nebula Cluster was even more compact in its younger years and a recent dinamical study indicates that runaway stllar colosion at an earlier age may have formed ...
... the brightest star Theta-1 Orionis C powers the complex star forming region's entire visible glow. About three million years old, the Orion Nebula Cluster was even more compact in its younger years and a recent dinamical study indicates that runaway stllar colosion at an earlier age may have formed ...
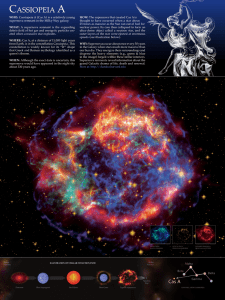
cassiopeia a - Chandra X
... debris field of hot gas and energetic particles created when a massive star explodes. WHERE: Cas A, at a distance of 11,000 light years from Earth, is in the constellation Cassiopeia. This constellation is widely known for its “W” shape that Greek and Roman mythology identified as a queen’s throne. ...
... debris field of hot gas and energetic particles created when a massive star explodes. WHERE: Cas A, at a distance of 11,000 light years from Earth, is in the constellation Cassiopeia. This constellation is widely known for its “W” shape that Greek and Roman mythology identified as a queen’s throne. ...
Orion - CSIC
... inches of string trailing off from the cotton ball. Place cardboard so that the long side is facing you. That side will be called the "front". For each star, measure as far along the front edge from the right hand corner as indicated by the number in the column marked "Measurement from Right". Then, ...
... inches of string trailing off from the cotton ball. Place cardboard so that the long side is facing you. That side will be called the "front". For each star, measure as far along the front edge from the right hand corner as indicated by the number in the column marked "Measurement from Right". Then, ...
Document
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are ...
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are ...
Chapter 10: Measuring the Stars - Otto
... • Expanded beyond stars visible to naked eye • One magnitude difference is 2.5X in brightness • A 1st magnitude star is 2.5X brighter than a 2nd magnitude star • Full moon has an apparent magnitude of -12.5 • Faintest objects visible by Hubble or Keck telescopes are apparent magnitude 30 ...
... • Expanded beyond stars visible to naked eye • One magnitude difference is 2.5X in brightness • A 1st magnitude star is 2.5X brighter than a 2nd magnitude star • Full moon has an apparent magnitude of -12.5 • Faintest objects visible by Hubble or Keck telescopes are apparent magnitude 30 ...
Stars
... When seen from the Earth, most stars appear as small points of light because they are very far away. They do not move. The Earth rotates, so we are the ones moving. ...
... When seen from the Earth, most stars appear as small points of light because they are very far away. They do not move. The Earth rotates, so we are the ones moving. ...
Notes - Bill Wolf
... preserved the original magnitude scale, though it is worthy of note that since 2.5125 ≈ 100, a magnitude difference of 5 yields a brightness ratio of 100. What do we mean by “brightness,” anyway? It’s exactly what we talked about in Astro 1: it’s the flux that reaches our eyes here at earth. Absolut ...
... preserved the original magnitude scale, though it is worthy of note that since 2.5125 ≈ 100, a magnitude difference of 5 yields a brightness ratio of 100. What do we mean by “brightness,” anyway? It’s exactly what we talked about in Astro 1: it’s the flux that reaches our eyes here at earth. Absolut ...
Astro 1 & 100 Levine Homework Stars Name:____________________________
... You may want to do the lecture-tutorial on pg 33, Apparent and Absolute Magnitude of Stars, prior to doing this portion of the homework, if you need a refresher on m and M. Ranking questions are 2 points each. Consider the following table of stars: ...
... You may want to do the lecture-tutorial on pg 33, Apparent and Absolute Magnitude of Stars, prior to doing this portion of the homework, if you need a refresher on m and M. Ranking questions are 2 points each. Consider the following table of stars: ...
cancer, la constelac..
... Cancer, and this is why the Tropic of Cancer was named so (In the present day the sun now reaches the solstice point near the star eta () Geminorum.) To find Cancer in the sky look between Gemini and Leo, although you may need a dark sky to see all it's stars. According to Greek mythology Cancer wa ...
... Cancer, and this is why the Tropic of Cancer was named so (In the present day the sun now reaches the solstice point near the star eta () Geminorum.) To find Cancer in the sky look between Gemini and Leo, although you may need a dark sky to see all it's stars. According to Greek mythology Cancer wa ...
Homework PHY121 (Astronomy
... Moon and the Sun. Since our (real) equatorial system is defined by Earth’s rotation and by the apparent motions it incurs on the stars, the “equatorial coordinate system” for our hypothetical, still standing Earth would be quite different. Our (real) celestial poles are defined in such a way, that t ...
... Moon and the Sun. Since our (real) equatorial system is defined by Earth’s rotation and by the apparent motions it incurs on the stars, the “equatorial coordinate system” for our hypothetical, still standing Earth would be quite different. Our (real) celestial poles are defined in such a way, that t ...
20081 Study Guide_77-120
... Answers to Analysis and Conclusions 1. The plate does not actually change position, although it does appear to move when it is viewed from different locations. 2. The apparent change in position of the plate is greater at short distances than it is farther away because the angle formed by the observ ...
... Answers to Analysis and Conclusions 1. The plate does not actually change position, although it does appear to move when it is viewed from different locations. 2. The apparent change in position of the plate is greater at short distances than it is farther away because the angle formed by the observ ...
Session Two - A Sidewalk Astronomer in Charlottetown
... difference is that a star is a point of light, whereas a galaxy has a larger apparent surface area. The entire luminosity of the object is summed over it's area. The magnitude is then the same as a point source like a star emitting the luminosity. Therefore, large objects appear dimmer than stars th ...
... difference is that a star is a point of light, whereas a galaxy has a larger apparent surface area. The entire luminosity of the object is summed over it's area. The magnitude is then the same as a point source like a star emitting the luminosity. Therefore, large objects appear dimmer than stars th ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... • A clue: Compare brightness of our sun to brightness of stars . . . It’s the difference between night and day! ...
... • A clue: Compare brightness of our sun to brightness of stars . . . It’s the difference between night and day! ...
Aries (constellation)
Aries is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere between Pisces to the west and Taurus to the east. The name Aries is Latin for ram, and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♈), representing a ram's horns. It is one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is a mid-sized constellation, ranking 39th overall size, with an area of 441 square degrees (1.1% of the celestial sphere).Although Aries came to represent specifically the ram whose fleece became the Golden Fleece of Ancient Greek mythology, it has represented a ram since late Babylonian times. Before that, the stars of Aries formed a farmhand. Different cultures have incorporated the stars of Aries into different constellations including twin inspectors in China and a porpoise in the Marshall Islands. Aries is a relatively dim constellation, possessing only four bright stars: Hamal (Alpha Arietis, second magnitude), Sheratan (Beta Arietis, third magnitude), Mesarthim (Gamma Arietis, fourth magnitude), and 41 Arietis (also fourth magnitude). The few deep-sky objects within the constellation are quite faint and include several pairs of interacting galaxies. Several meteor showers appear to radiate from Aries, including the Daytime Arietids and the Epsilon Arietids.