Name
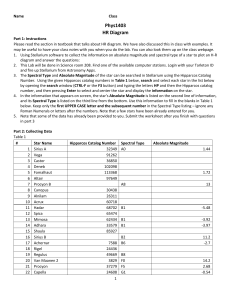
... Read the passage and study the table below. Then use a separate sheet of paper to answer the questions that follow. ...
... Read the passage and study the table below. Then use a separate sheet of paper to answer the questions that follow. ...
Review Day
... Corona: Only visible portion of the sun during an eclipse and the furthest layer from the core. ...
... Corona: Only visible portion of the sun during an eclipse and the furthest layer from the core. ...
Constellation
... pearls' surrounding an Exploding Star Two decades ago, astronomers spotted one of the brightest exploding stars in more than 400 years. This image shows the entire region around the supernova. The most prominent feature in the image is a ring with dozens of bright spots. A shock wave of material unl ...
... pearls' surrounding an Exploding Star Two decades ago, astronomers spotted one of the brightest exploding stars in more than 400 years. This image shows the entire region around the supernova. The most prominent feature in the image is a ring with dozens of bright spots. A shock wave of material unl ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Astronomy Project Purpose: To
... sun. Example: Betelgeuse is 38000 LSUN, and emits 1.4 x 1031 watts 3.) With the provided formula, determine the star’s radius, and find some way of comparing it to other objects in the solar system. Example: The radius of Betelgeuse is 380,000,000 km, which could fit the entire orbit of the inner pl ...
... sun. Example: Betelgeuse is 38000 LSUN, and emits 1.4 x 1031 watts 3.) With the provided formula, determine the star’s radius, and find some way of comparing it to other objects in the solar system. Example: The radius of Betelgeuse is 380,000,000 km, which could fit the entire orbit of the inner pl ...
Astronomy 1 Study Guide Key 16
... 7. A galaxy is a collection of stars. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way. 8. It has many solar systems with in its arms. At the center of our spiral galaxy is a black hole, so our galaxy is also called a quasar. Stars Be able to read an H-R diagram. ...
... 7. A galaxy is a collection of stars. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way. 8. It has many solar systems with in its arms. At the center of our spiral galaxy is a black hole, so our galaxy is also called a quasar. Stars Be able to read an H-R diagram. ...
Lab 1-2 : Vocabulary
... • Absolute - the magnitude of a star computed as if viewed from a distance of 32.6 light-years. • Apparent – a star’s brightness as it appears from Earth. The sun APPEARS brighter than the other stars because it is closer to us! ...
... • Absolute - the magnitude of a star computed as if viewed from a distance of 32.6 light-years. • Apparent – a star’s brightness as it appears from Earth. The sun APPEARS brighter than the other stars because it is closer to us! ...
The Ursa Major Moving Cluster, Collinder 285
... at 10 km/sec, and its spatial velocity relative to our Sun is about 46 km/s. This cluster is centered at a distance of about 75 light years from us (i.e., our solar system). As it is spread over a volume of 30 light years length and 18 light years width, it covers an enourmous portion of the sky, an ...
... at 10 km/sec, and its spatial velocity relative to our Sun is about 46 km/s. This cluster is centered at a distance of about 75 light years from us (i.e., our solar system). As it is spread over a volume of 30 light years length and 18 light years width, it covers an enourmous portion of the sky, an ...
mass per nucleon
... main sequence star (core Hydrogen burning) core Hydrogen exhausted (sub-giant) shell Hydrogen burning (red giant) core Helium burning (Helium Flash) shell Helium burning (double-shell burning red giant) planetary nebula white dwarf ...
... main sequence star (core Hydrogen burning) core Hydrogen exhausted (sub-giant) shell Hydrogen burning (red giant) core Helium burning (Helium Flash) shell Helium burning (double-shell burning red giant) planetary nebula white dwarf ...
H-R Diagram - Faculty Website Listing
... Please read the section in textbook that talks about HR diagram. We have also discussed this in class with examples. It may be useful to have your class notes with you when you do the lab. You can also look them up on the class webpage. 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on abso ...
... Please read the section in textbook that talks about HR diagram. We have also discussed this in class with examples. It may be useful to have your class notes with you when you do the lab. You can also look them up on the class webpage. 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on abso ...
molecular clouds
... Protostar Becomes A Star • Once sufficient temperature (>= 10 million degrees K) and pressure is reached in the core of the protostar, nuclear fusion begins and the protostar has now officially become a star ...
... Protostar Becomes A Star • Once sufficient temperature (>= 10 million degrees K) and pressure is reached in the core of the protostar, nuclear fusion begins and the protostar has now officially become a star ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. June 2005. A
... individual stars in a 4" (100mm) telescope. Increasing aperture brings greater rewards. lord Rosse and others using the 72" at Birr Castle in the 19th century observed three dark rifts radiating from the centre. later visual observers confirmed these. However with the advent of photography the rifts ...
... individual stars in a 4" (100mm) telescope. Increasing aperture brings greater rewards. lord Rosse and others using the 72" at Birr Castle in the 19th century observed three dark rifts radiating from the centre. later visual observers confirmed these. However with the advent of photography the rifts ...
less than 1 million years
... 1. Today, scientists have _________ about how stars evolve, what makes them different from one another, and how they _____. 2. When __________ fuel is depleted , a star loses its _________ ___________ status. (2 words) 3. This (depletion of star’s hydrogen) can take less than 1 million years for the ...
... 1. Today, scientists have _________ about how stars evolve, what makes them different from one another, and how they _____. 2. When __________ fuel is depleted , a star loses its _________ ___________ status. (2 words) 3. This (depletion of star’s hydrogen) can take less than 1 million years for the ...
Astronomy – Studying the Stars & Space
... between a star’s surface temperature and absolute magnitude • Shows how they are classified by brightness and temperature and how they change cool red to the right, bright stars over time ...
... between a star’s surface temperature and absolute magnitude • Shows how they are classified by brightness and temperature and how they change cool red to the right, bright stars over time ...
07-01TheColsmologicalDistanceLadder
... Cepheid Variables: How to measure the distance to a galaxy using Cepheid variable stars: 1. Find the Cepheid, measure its spectrum 2. Measure a couple periods, and its apparent magnitude m 3. Look up its absolute magnitude 4. Use M = m - 5 log10(d/10) to find d ...
... Cepheid Variables: How to measure the distance to a galaxy using Cepheid variable stars: 1. Find the Cepheid, measure its spectrum 2. Measure a couple periods, and its apparent magnitude m 3. Look up its absolute magnitude 4. Use M = m - 5 log10(d/10) to find d ...
Stars from Afar
... Stars can be classified in three ways: Size – How massive the star is Temperature – A stars color reveals its temperature. ...
... Stars can be classified in three ways: Size – How massive the star is Temperature – A stars color reveals its temperature. ...
Chapter 17 and 18 Vocabulary Quist
... 45. When a star explodes, it is said to have gone __________________ or _______________________ 46. A star that is very small and has so much gravity that electromagnetic energy cannot escape its surface is called a __________________________ 47. Stars are classified by there _______________________ ...
... 45. When a star explodes, it is said to have gone __________________ or _______________________ 46. A star that is very small and has so much gravity that electromagnetic energy cannot escape its surface is called a __________________________ 47. Stars are classified by there _______________________ ...
AN INTRODUCTION TO ASTRONOMY Dr. Uri Griv Department of Physics, Ben-Gurion University
... • Strictly speaking: L = (4πR2 )(σT 4 ) where R is the radius of a star. On the other hand, L = f · (4πr2 ) → T = (f r2 /R2 σ)1/4 • The basic idea of UBV Photometry is to measure the proportions of radiant energy put out by a thermal body at ultraviolet (U), blue (B), and visual (V) wavelength • fV ...
... • Strictly speaking: L = (4πR2 )(σT 4 ) where R is the radius of a star. On the other hand, L = f · (4πr2 ) → T = (f r2 /R2 σ)1/4 • The basic idea of UBV Photometry is to measure the proportions of radiant energy put out by a thermal body at ultraviolet (U), blue (B), and visual (V) wavelength • fV ...
Astronomy Lecture Notes: Stellar Nomenclature I Introduction
... 1. If one star is 1 magnitude brighter than another then that star is actually about 2.5 times brighter as measured in Watts/m2 by a photometer. 2. If one star is 5 magnitudes brighter than another then that star is actually exactly 100 times brighter as measured in Watts/m2 by a photometer. 3. Exam ...
... 1. If one star is 1 magnitude brighter than another then that star is actually about 2.5 times brighter as measured in Watts/m2 by a photometer. 2. If one star is 5 magnitudes brighter than another then that star is actually exactly 100 times brighter as measured in Watts/m2 by a photometer. 3. Exam ...
Stellar Magnitude, Distance, and Motion
... Actual star brightness The apparent magnitude that a star would have if it were (in our imagination) placed at a distance of 10 parsecs (which is 32.6 light years) from the Earth Used to describe luminosity - The amount of energy a star gives off each second The 20 Brightest Stars in the Sky C ...
... Actual star brightness The apparent magnitude that a star would have if it were (in our imagination) placed at a distance of 10 parsecs (which is 32.6 light years) from the Earth Used to describe luminosity - The amount of energy a star gives off each second The 20 Brightest Stars in the Sky C ...
9 spectroscopic parallax
... Absolute magnitude = how bright (what magnitude) a star would appear at 10 parsecs (32.6 light years) ...
... Absolute magnitude = how bright (what magnitude) a star would appear at 10 parsecs (32.6 light years) ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.