Constellation Information
... The night skies of winter are famously bright with stars. People often think this is because the air is especially clear at this time of year. Its true dry winter air is more transparent than the humid hazes of summer, but theres a more important reason why we see brighter stars now. They really a ...
... The night skies of winter are famously bright with stars. People often think this is because the air is especially clear at this time of year. Its true dry winter air is more transparent than the humid hazes of summer, but theres a more important reason why we see brighter stars now. They really a ...
Additional Images
... the stars reached its Roche volume) eclipsing binary of a cream-white color. The brightness varies from 3.4 mag to 4.3 mag every twelve days and 22 hours. One of the two stars of this system is filling its Roche surface and ellipsoidally deformed. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of this class of eclipsi ...
... the stars reached its Roche volume) eclipsing binary of a cream-white color. The brightness varies from 3.4 mag to 4.3 mag every twelve days and 22 hours. One of the two stars of this system is filling its Roche surface and ellipsoidally deformed. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of this class of eclipsi ...
Chapter 1 Daily Note Sheets Completed Power Point
... 8. What is the celestial sphere ? • Imaginary ball around the Earth that the stars can be found upon. ...
... 8. What is the celestial sphere ? • Imaginary ball around the Earth that the stars can be found upon. ...
Figures I through VII in Section 1 on the following sheet
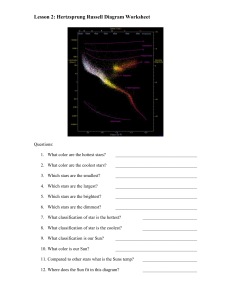
... Of stars C and E in figure X, which is more likely to have produced the spectrum in figure II (_4_)? Why (_5_)? Of the stars labeled on figure X: Which two are the two hottest (_6_)? Which are the two brightest (_7_)? Which has the largest radius (_8_)? Which is most like our sun (_9_)? Approximatel ...
... Of stars C and E in figure X, which is more likely to have produced the spectrum in figure II (_4_)? Why (_5_)? Of the stars labeled on figure X: Which two are the two hottest (_6_)? Which are the two brightest (_7_)? Which has the largest radius (_8_)? Which is most like our sun (_9_)? Approximatel ...
The Milky Way
... Constellations The stars in constellations are not physically close to each other in space. They were believed to represent great heroes and mythological figures. Their position in the sky seemed to tell stories that were handed down from generation to generation over thousands of years. Different ...
... Constellations The stars in constellations are not physically close to each other in space. They were believed to represent great heroes and mythological figures. Their position in the sky seemed to tell stories that were handed down from generation to generation over thousands of years. Different ...
Solutions to problems
... the luminosity vs. temperature of each. Temperature (spectral type) is on the horizontal axis (increasing to left) and luminosity is on the vertical axis. Accordingly, a star in the upper left is hotter and brighter than a star in the lower right. Note: When stars are plotted in this way, they fall ...
... the luminosity vs. temperature of each. Temperature (spectral type) is on the horizontal axis (increasing to left) and luminosity is on the vertical axis. Accordingly, a star in the upper left is hotter and brighter than a star in the lower right. Note: When stars are plotted in this way, they fall ...
d 2
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... Fusion of heavier elements Makes the star expand more Can be the size of our solar system (WOW!) ...
... Fusion of heavier elements Makes the star expand more Can be the size of our solar system (WOW!) ...
Name____________________________________________
... __3__ Our Solar System __2___ The Milky Way __1__ The Universe 3. What is a galaxy? A huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters, dust, and gas bound together by gravity. 4. What does an elliptical galaxy look like? Round or flattened ball; smashed circle 5. The Milky Way Galaxy is just ...
... __3__ Our Solar System __2___ The Milky Way __1__ The Universe 3. What is a galaxy? A huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters, dust, and gas bound together by gravity. 4. What does an elliptical galaxy look like? Round or flattened ball; smashed circle 5. The Milky Way Galaxy is just ...
Lab Document - University of Iowa Astronomy and Astrophysics
... (8) Now let’s try and find a “Deep Sky” object using the Pocket Sky Atlas. We will look at the object M13 in the constellation of Hercules. Using the Star Wheel and SC1 chart, find Hercules. Both the Star Wheel and the SC1 indicate where M13 is located. The Pocket Sky Atlas has a more detailed map o ...
... (8) Now let’s try and find a “Deep Sky” object using the Pocket Sky Atlas. We will look at the object M13 in the constellation of Hercules. Using the Star Wheel and SC1 chart, find Hercules. Both the Star Wheel and the SC1 indicate where M13 is located. The Pocket Sky Atlas has a more detailed map o ...
Questions for The Elements: Forged in Stars
... 2. What percent of each of these two elements do they have? 3. What happens to Hydrogen atoms in a star’s core? 4. For about what percent of a star’s life does it do this? 5. What happens when a star runs out of Hydrogen to use as fuel for fusion? 6. If you fuse three Helium atoms together, what ele ...
... 2. What percent of each of these two elements do they have? 3. What happens to Hydrogen atoms in a star’s core? 4. For about what percent of a star’s life does it do this? 5. What happens when a star runs out of Hydrogen to use as fuel for fusion? 6. If you fuse three Helium atoms together, what ele ...
Star Classification
... The first people to combine a camera with a spectroscope were the father and son team of John and Henry Draper in the 1870s. Their work was carried on by Edward C. Pickering who, by 1918, had listed the spectra of over 200000 stars. Using details about luminosity and composition, stars are classifie ...
... The first people to combine a camera with a spectroscope were the father and son team of John and Henry Draper in the 1870s. Their work was carried on by Edward C. Pickering who, by 1918, had listed the spectra of over 200000 stars. Using details about luminosity and composition, stars are classifie ...
1 - WordPress.com
... 1. What nuclear process combines two atomic nuclei to form one heavier element? ...
... 1. What nuclear process combines two atomic nuclei to form one heavier element? ...
astronomy final exam - Physics and Astronomy
... A star spends most of its lifetime undergoing what process? A pulsar is believed to be what kind of object? Where were the heavy elements in our bodies formed? The turn-off point on the H-R diagram of a star cluster will tell us what property about the cluster? A 21-centimeter photon comes from what ...
... A star spends most of its lifetime undergoing what process? A pulsar is believed to be what kind of object? Where were the heavy elements in our bodies formed? The turn-off point on the H-R diagram of a star cluster will tell us what property about the cluster? A 21-centimeter photon comes from what ...
Chapter 25 - OG
... Red Supergiant - core contracts – causes temp to increase then COOLS Supernova : outer portion of star explodes (def = huge explosion that destroys a star) ▪ Neutron Star – consists only of Neutrons in dense core ▪ Black Hole – core collapses until there is no volume – gravity so great nothing c ...
... Red Supergiant - core contracts – causes temp to increase then COOLS Supernova : outer portion of star explodes (def = huge explosion that destroys a star) ▪ Neutron Star – consists only of Neutrons in dense core ▪ Black Hole – core collapses until there is no volume – gravity so great nothing c ...
Place the stars in the proper sequence, following the
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
Can We Make A Star?
... move so that the gasses will react with each other • Then we just sit way back and wait until the gasses explode into a fireball ...
... move so that the gasses will react with each other • Then we just sit way back and wait until the gasses explode into a fireball ...
Lab 21.1 Classifying Stars
... Groups of two (maximum), but each person does the lab. Note the position of the Sun: temperature = 5,000C Plot the 36 closest stars on the graph paper and mark each star’s location with a small “x”. Plot the 20 brightest stars on the graph paper and mark each star’s location with a small “o”. Using ...
... Groups of two (maximum), but each person does the lab. Note the position of the Sun: temperature = 5,000C Plot the 36 closest stars on the graph paper and mark each star’s location with a small “x”. Plot the 20 brightest stars on the graph paper and mark each star’s location with a small “o”. Using ...
25 Study Guide
... 10,000 light-years thick at the nucleus. • In addition to shape and size, one of the major differences among different types of galaxies is the age of their stars. • The red shifts of distant galaxies indicate that the universe is expanding. • The big bang theory states that at one time, the entire ...
... 10,000 light-years thick at the nucleus. • In addition to shape and size, one of the major differences among different types of galaxies is the age of their stars. • The red shifts of distant galaxies indicate that the universe is expanding. • The big bang theory states that at one time, the entire ...
Document
... USING KEY TERMS The statements below are false. For each statement, replace the underlined term to make a true statement. ...
... USING KEY TERMS The statements below are false. For each statement, replace the underlined term to make a true statement. ...
Monday, April 15
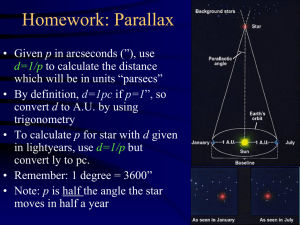
... • Then do the following Gedankenexperiment: – In your mind, put the star from its actual position to a position 10 pc away – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its a ...
... • Then do the following Gedankenexperiment: – In your mind, put the star from its actual position to a position 10 pc away – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its a ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... formed iron, no more reactions can occur, and the core violently collapses in on itself Supernova ...
... formed iron, no more reactions can occur, and the core violently collapses in on itself Supernova ...
Scientists classify stars by
... The gravity of a passing star or the shock wave from a nearby supernova may cause the nebula to contract. 1. Matter in the gas cloud will begin to come together into a dense region called a protostar. 2. As the protostar continues to condense, it heats up. 3. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass a ...
... The gravity of a passing star or the shock wave from a nearby supernova may cause the nebula to contract. 1. Matter in the gas cloud will begin to come together into a dense region called a protostar. 2. As the protostar continues to condense, it heats up. 3. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass a ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.