How do stars form?
... and the H-R Diagram • What happens when a star exhausts its nuclear fuel? • Depends on size • Star core collapses on itself, but heats the outer envelope. • Result may be: White dwarf, white dwarf with planetary nebula, red giant, neutron star or black hole. ...
... and the H-R Diagram • What happens when a star exhausts its nuclear fuel? • Depends on size • Star core collapses on itself, but heats the outer envelope. • Result may be: White dwarf, white dwarf with planetary nebula, red giant, neutron star or black hole. ...
Stars and the Sun
... – Big enough to swallow first 3 planets – Uses He other elements for about 10 million years ...
... – Big enough to swallow first 3 planets – Uses He other elements for about 10 million years ...
Feb 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and cloud bands, easily visible at 50x. It is posof the globulars that can be seen in the sky are part of our Milky sible to see the moons with well-focused binoculars. Saturn is Way Galaxy, and there are about 200 of ...
... tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and cloud bands, easily visible at 50x. It is posof the globulars that can be seen in the sky are part of our Milky sible to see the moons with well-focused binoculars. Saturn is Way Galaxy, and there are about 200 of ...
ASTR100 Homework #5 Solutions Chapter 11 #29, 31 Due
... Also the more massive a white dwarf is, the smaller it is! This is because the more mass a white dwarf has, the more its electrons must squeeze together to maintain enough outward pressure to support the extra mass. There is a limit on the amount of mass a white dwarf can have, however. This limit i ...
... Also the more massive a white dwarf is, the smaller it is! This is because the more mass a white dwarf has, the more its electrons must squeeze together to maintain enough outward pressure to support the extra mass. There is a limit on the amount of mass a white dwarf can have, however. This limit i ...
Review Quiz No. 22
... the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a white dwarf. the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a neutron star. the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a black hole. a neutron star is tidally disrupted by a ...
... the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a white dwarf. the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a neutron star. the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a black hole. a neutron star is tidally disrupted by a ...
Chapter 21
... The sun is a medium-sized star. Stars that are much larger than the sun are called ______________ or __________________. Composition – The chemical composition of most stars is about 73 % ______________ and 25 % ____________________. How can astronomers infer which elements are found in stars? ___ ...
... The sun is a medium-sized star. Stars that are much larger than the sun are called ______________ or __________________. Composition – The chemical composition of most stars is about 73 % ______________ and 25 % ____________________. How can astronomers infer which elements are found in stars? ___ ...
t2 images part 1
... proportional to their distance from each other: v=H* d Where H is the Hubble Constant If the Universe is expanding, it stands that at some point in the past everything in the Universe was all concentrated at the same point and began expanding outward. This point in time is called the “Big Ba ...
... proportional to their distance from each other: v=H* d Where H is the Hubble Constant If the Universe is expanding, it stands that at some point in the past everything in the Universe was all concentrated at the same point and began expanding outward. This point in time is called the “Big Ba ...
Earth Science 11 Chapter 28 Answers: 28.1 1. All are forms of
... 1. Galaxies are natural groupings of stars in space, whereas constellations are not. A constellation is a group of stars that appear to be together as viewed from Earth. 2. A light-year is the distance a ray of light travels in one year, equal to 9.5 x 1012 kilometers. A parsec equals 3.258 light ye ...
... 1. Galaxies are natural groupings of stars in space, whereas constellations are not. A constellation is a group of stars that appear to be together as viewed from Earth. 2. A light-year is the distance a ray of light travels in one year, equal to 9.5 x 1012 kilometers. A parsec equals 3.258 light ye ...
1. If a star`s temperature is doubled but radius is kept constant, by
... 1. If a star’s temperature is doubled but radius is kept constant, by how much does its luminosity go up by? 1a. Goes up by a factor of 24 = 16. 2. If a star’s temperature is increased by a factor of three, four, five and six, but in every case its radius is kept constant, what happens to its lumino ...
... 1. If a star’s temperature is doubled but radius is kept constant, by how much does its luminosity go up by? 1a. Goes up by a factor of 24 = 16. 2. If a star’s temperature is increased by a factor of three, four, five and six, but in every case its radius is kept constant, what happens to its lumino ...
Codes of Life
... • Once the fusion reactions start a main sequence star, like our Sun, is formed. • In these reactions atoms of hydrogen are fused together to form helium with vast amounts of heat and light given out. ...
... • Once the fusion reactions start a main sequence star, like our Sun, is formed. • In these reactions atoms of hydrogen are fused together to form helium with vast amounts of heat and light given out. ...
BAS Visit to the Norman Lockyer Observatory, October 2015
... variable star that serves as a prototype for an entire class of variables, the Mira variables. There are between 6,000 to 7,000 known stars belonging to this group. They are all red giants whose surfaces oscillate in such a way as to cause variations in brightness over periods ranging from 80 to 1,0 ...
... variable star that serves as a prototype for an entire class of variables, the Mira variables. There are between 6,000 to 7,000 known stars belonging to this group. They are all red giants whose surfaces oscillate in such a way as to cause variations in brightness over periods ranging from 80 to 1,0 ...
Supernovae - Cloudfront.net
... the amount of energy created in a Type Ia Supernova is always about the same. Thus its luminosity is always the same. A Type Ia Supernova in another galaxy is thus a good standard candle to use to find the distance to the galaxy ...
... the amount of energy created in a Type Ia Supernova is always about the same. Thus its luminosity is always the same. A Type Ia Supernova in another galaxy is thus a good standard candle to use to find the distance to the galaxy ...
SIERRA STAR GAZERS
... dark lanes that roughly split the glowing cloud into three major (some say four) portions. As with M8, OIII and Deep Sky filters work well here. Messier 54 is a small globular cluster that is about 70,000 light years away, placing it as the most distant of all the Messier globulars. With a combined ...
... dark lanes that roughly split the glowing cloud into three major (some say four) portions. As with M8, OIII and Deep Sky filters work well here. Messier 54 is a small globular cluster that is about 70,000 light years away, placing it as the most distant of all the Messier globulars. With a combined ...
The Danger of Deadly Cosmic Explosions
... – 4 million x sun • Maybe still dangerous at 7000 light years • Fortunately not pointed at us, we think. • Other stars old too… ...
... – 4 million x sun • Maybe still dangerous at 7000 light years • Fortunately not pointed at us, we think. • Other stars old too… ...
Phys 100 – Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for
... Planets are larger than stars. Planets reflect light while stars produce their own light. Stars move faster in the sky than planets. Planets are brighter than stars. ...
... Planets are larger than stars. Planets reflect light while stars produce their own light. Stars move faster in the sky than planets. Planets are brighter than stars. ...
KEY Unit 10‐11 Test Review: Characteristics of the Universe
... HOT MAIN SEQUENCE STAR 8. The Sun‛s luminosity and temperature place it in the middle of the _ MAIN SEQUENCE_ area of the HR diagram. ...
... HOT MAIN SEQUENCE STAR 8. The Sun‛s luminosity and temperature place it in the middle of the _ MAIN SEQUENCE_ area of the HR diagram. ...
Lifecycle of a Star
... Super dense core of a star left over after a supernova. Only 5 to 15 MILES in diameter, but have a mass 1.5 – 2 times that of the Sun. ...
... Super dense core of a star left over after a supernova. Only 5 to 15 MILES in diameter, but have a mass 1.5 – 2 times that of the Sun. ...
Astronomy Tour
... dust that is a “tail” Scientists believe that these originate from a large region filled with comet cores called the Oort cloud. ...
... dust that is a “tail” Scientists believe that these originate from a large region filled with comet cores called the Oort cloud. ...
here - Boise State University
... 10. Explain the relationship between star size and true brightness: Which size stars are the brightest???? Which size stars dim and not as bright???? 11. List another term scientist’s use to describe the true brightness of a star: 12. What do all stars form in? 13. What is a nebula? 14. What is the ...
... 10. Explain the relationship between star size and true brightness: Which size stars are the brightest???? Which size stars dim and not as bright???? 11. List another term scientist’s use to describe the true brightness of a star: 12. What do all stars form in? 13. What is a nebula? 14. What is the ...
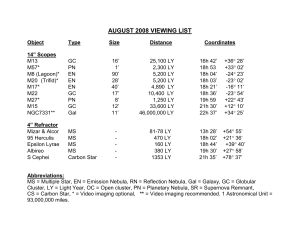
August
... M13 At a distance of 25,100 light years, this globular cluster in the constellation Hercules (HER-cueleez) is about 145 light years in diameter. The age of M13 has been estimated at over 10 billion years. It contains over 300,000 stars. At the center, stars are about 500 times more concentrated than ...
... M13 At a distance of 25,100 light years, this globular cluster in the constellation Hercules (HER-cueleez) is about 145 light years in diameter. The age of M13 has been estimated at over 10 billion years. It contains over 300,000 stars. At the center, stars are about 500 times more concentrated than ...
Project topics
... 2. Electromagnetic spectrum and its importance in astronomy. 3. Spectroscopes and the spectrums of stars. Include information about a spectroscope, spectrums of different gases, the Doppler Effect with emphases on what a”red shift” is, and how Edwin Hubble used the” red shift” to determine stellar d ...
... 2. Electromagnetic spectrum and its importance in astronomy. 3. Spectroscopes and the spectrums of stars. Include information about a spectroscope, spectrums of different gases, the Doppler Effect with emphases on what a”red shift” is, and how Edwin Hubble used the” red shift” to determine stellar d ...
Astronomy Galaxies & The Universe
... uses data from lots of stars, so there are lots of dots. The position of each dot on the diagram corresponds to the star's luminosity and its temperature The vertical position represents the star's luminosity (absolute magnitude). The horizontal position represents the star's surface temperature ...
... uses data from lots of stars, so there are lots of dots. The position of each dot on the diagram corresponds to the star's luminosity and its temperature The vertical position represents the star's luminosity (absolute magnitude). The horizontal position represents the star's surface temperature ...
Mars Project
... All star start their lives as a dense part of a nebula. (A big cloud of gas and dust spread out in space.) in the dense part of the nebula the gas and dust becomes so dense and hot that a star is born. ...
... All star start their lives as a dense part of a nebula. (A big cloud of gas and dust spread out in space.) in the dense part of the nebula the gas and dust becomes so dense and hot that a star is born. ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.