chapter 17 measuring the stars
... (including the Sun itself) ~The color of any 24, 000 K object glows white o White Dwarf: A dwarf star with sufficiently high surface temperature that it glows white ...
... (including the Sun itself) ~The color of any 24, 000 K object glows white o White Dwarf: A dwarf star with sufficiently high surface temperature that it glows white ...
Review 2
... How do we use the atomic emission and absorption spectra to find the composition of a star? How do we determine the rotation period of a star? How do we determine the distance to a star using Stellar Parallax? What is an H-R diagram and what information does it give us? A star when observed through ...
... How do we use the atomic emission and absorption spectra to find the composition of a star? How do we determine the rotation period of a star? How do we determine the distance to a star using Stellar Parallax? What is an H-R diagram and what information does it give us? A star when observed through ...
How Is a Star`s Color Related to Its Temperature?
... On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. You will see how star brightness, color, ...
... On a clear night you have surely noticed that some stars are brighter than others. But stars also have different colors. Rigel is blue, and Betelgeuse is red. Capella and our sun are yellow. In this activity you will make your own Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. You will see how star brightness, color, ...
Round 1
... A star becomes a red giant when this happens. (runs out of hydrogen to fuse in its core → leaves the main sequence) $1600 A Type 1a supernova occurs when a white dwarf’s mass exceeds this. (1.4 M ) $2000 This prevents the collapse of the star at the center of a planetary nebula. (electron ...
... A star becomes a red giant when this happens. (runs out of hydrogen to fuse in its core → leaves the main sequence) $1600 A Type 1a supernova occurs when a white dwarf’s mass exceeds this. (1.4 M ) $2000 This prevents the collapse of the star at the center of a planetary nebula. (electron ...
Astronomy Unit Test – Chapter 21
... 25. Predict what will happen when the sun runs out of fuel. 26. What is used to classify stars? 27. At which phase of the moon could a solar eclipse occur? 28. A star is twice as massive as the sun. How will its lifespan compare with the sun? 29. Some astronomers discover a galaxy that contains only ...
... 25. Predict what will happen when the sun runs out of fuel. 26. What is used to classify stars? 27. At which phase of the moon could a solar eclipse occur? 28. A star is twice as massive as the sun. How will its lifespan compare with the sun? 29. Some astronomers discover a galaxy that contains only ...
Sample exam 2
... 13. Suppose you are looking at the emission spectrum of gaseous helium. You dutifully write down the wavelengths of emission. You notice a power dial on the side of emission lamp and, just for fun, decide to turn up the power. The color of the helium lamp changes and you look through the spectroscop ...
... 13. Suppose you are looking at the emission spectrum of gaseous helium. You dutifully write down the wavelengths of emission. You notice a power dial on the side of emission lamp and, just for fun, decide to turn up the power. The color of the helium lamp changes and you look through the spectroscop ...
PPT - Mr.E Science
... universe began 15 to 20 billion years ago. Scientist have viewed thousands of galaxies and can measure the fact that all galaxies are moving away from each other. If you could run the film “backwards”, it would appear that all of the galaxies come together at a single incredibly dense point. Scienti ...
... universe began 15 to 20 billion years ago. Scientist have viewed thousands of galaxies and can measure the fact that all galaxies are moving away from each other. If you could run the film “backwards”, it would appear that all of the galaxies come together at a single incredibly dense point. Scienti ...
May 2016 night sky chart
... The Southern Cross is well placed for observation as it is now high in the south-east. The brightest star of the Cross, Acrux, is the closest to the horizon, while the next brightest, Beta Crucis or Mimosa, is to the east. Jupiter is located in the northern sky in the constellation of Leo and is dir ...
... The Southern Cross is well placed for observation as it is now high in the south-east. The brightest star of the Cross, Acrux, is the closest to the horizon, while the next brightest, Beta Crucis or Mimosa, is to the east. Jupiter is located in the northern sky in the constellation of Leo and is dir ...
Characteristics of stars
... • Many stars are about the size of the sun, which is a medium sized star. • White dwarfs are about the size of Earth. • Neutron stars are about 20KM (smallest) • Giant stars and super giant stars. If our sun were a super giant star it would fill our solar system as far out as Jupiter. ...
... • Many stars are about the size of the sun, which is a medium sized star. • White dwarfs are about the size of Earth. • Neutron stars are about 20KM (smallest) • Giant stars and super giant stars. If our sun were a super giant star it would fill our solar system as far out as Jupiter. ...
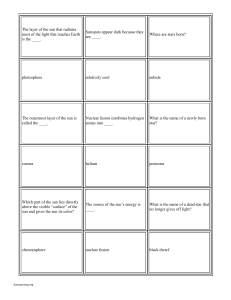
Star Game Cards
... What is the name of a dying star that has shrunk down to the size of a planet and no longer supports fusion? ...
... What is the name of a dying star that has shrunk down to the size of a planet and no longer supports fusion? ...
Astronomy
... • Commonly visualized as a baby bear with an unusually long tail (from being spun around the ...
... • Commonly visualized as a baby bear with an unusually long tail (from being spun around the ...
Chapter 20 The Universe
... Distance that light travels in 1 yr. ~10 billion km Sirius (Dog star) only 9 light years away Proxima Centauri (closest) 4.25 light yrs Other than sun Galaxy- large grouping of stars -our solar system is part of Milky Way Galaxy - what we see as the Milky Way is only the edge (spiral galaxy) ...
... Distance that light travels in 1 yr. ~10 billion km Sirius (Dog star) only 9 light years away Proxima Centauri (closest) 4.25 light yrs Other than sun Galaxy- large grouping of stars -our solar system is part of Milky Way Galaxy - what we see as the Milky Way is only the edge (spiral galaxy) ...
Compare the following sets of stars using the words: BRIGHTER or
... through waves 9. How do scientists know what elements are in stars? By looking at the star spectrums for known elements using a spectroscope. ...
... through waves 9. How do scientists know what elements are in stars? By looking at the star spectrums for known elements using a spectroscope. ...
Components of Universe
... Galaxy- Billions of stars bunched together. The Sun is a star in the Milky Way Galaxy. ...
... Galaxy- Billions of stars bunched together. The Sun is a star in the Milky Way Galaxy. ...
Stars and Moon Summative Review
... Identify the phases of the moon. How does the gravitational pull of the moon affect the Earth? (the side closest and the side farthest) What does a waxing moon indicate? Identify the cause of tides on Earth. Describe the effect that the elliptical orbit of the moon has on the Earth. ...
... Identify the phases of the moon. How does the gravitational pull of the moon affect the Earth? (the side closest and the side farthest) What does a waxing moon indicate? Identify the cause of tides on Earth. Describe the effect that the elliptical orbit of the moon has on the Earth. ...
The Life Cycle of a Star Webquest:
... 15. What is the scientific name for the twinkling of stars? ___________________________ 16. Why do stars twinkle? ____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 17. Why don’t planets twinkle? ________ ...
... 15. What is the scientific name for the twinkling of stars? ___________________________ 16. Why do stars twinkle? ____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 17. Why don’t planets twinkle? ________ ...
Ch. 25 Properties of Stars
... • Light-year – the distance light travels in one year (9.5 trillion kilometers) • We use this when determining astronomical distances since miles and kilometers would be way too small of a number • The next closest star after our sun, Proxima Centauri, is 4.3 light years away from our sun ...
... • Light-year – the distance light travels in one year (9.5 trillion kilometers) • We use this when determining astronomical distances since miles and kilometers would be way too small of a number • The next closest star after our sun, Proxima Centauri, is 4.3 light years away from our sun ...
Friday, August 29
... The Trouble with Angles • Angular size of an object cannot tell us its actual size – depends on how far away it is • Sun and Moon have very nearly the same angular size (30' = ½) when viewed from Earth ...
... The Trouble with Angles • Angular size of an object cannot tell us its actual size – depends on how far away it is • Sun and Moon have very nearly the same angular size (30' = ½) when viewed from Earth ...
Scientists classify stars by
... The gravity of a passing star or the shock wave from a nearby supernova may cause the nebula to contract. 1. Matter in the gas cloud will begin to come together into a dense region called a protostar. 2. As the protostar continues to condense, it heats up. 3. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass a ...
... The gravity of a passing star or the shock wave from a nearby supernova may cause the nebula to contract. 1. Matter in the gas cloud will begin to come together into a dense region called a protostar. 2. As the protostar continues to condense, it heats up. 3. Eventually, it reaches a critical mass a ...
Cosmology 2 - schoolphysics
... 1. Describe the model of the Universe proposed by Copernicus 2. If the time for Jupiter to make one orbit of the Sun is 11.86 years calculate the radius of its orbit. (Mass of the Sun = 2x1030 kg and G = 6.67x10-11 Nm2kg-2) 3. Write down Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion. 4. What piece of expe ...
... 1. Describe the model of the Universe proposed by Copernicus 2. If the time for Jupiter to make one orbit of the Sun is 11.86 years calculate the radius of its orbit. (Mass of the Sun = 2x1030 kg and G = 6.67x10-11 Nm2kg-2) 3. Write down Kepler’s three laws of planetary motion. 4. What piece of expe ...
A star is a - Trimble County Schools
... Appear to be tiny specks of white light Most vary in color and are much larger than Earth Motion • Stars move through the night sky towards the west • Stars rotate around the North Star, Polaris – _____________________________ = stars that circle around Polaris • Because of the earth’s rotation, som ...
... Appear to be tiny specks of white light Most vary in color and are much larger than Earth Motion • Stars move through the night sky towards the west • Stars rotate around the North Star, Polaris – _____________________________ = stars that circle around Polaris • Because of the earth’s rotation, som ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.