expected output
... information on trends, global and local distribution; Justification of importance of course. Biology of HIV/AIDS: Overview of immune system, natural immunity to HIV/AIDS; the AIDS Virus and its life Cycle, disease progression (epidemiology), transmission and diagnosis. Treatment and Management: Nutr ...
... information on trends, global and local distribution; Justification of importance of course. Biology of HIV/AIDS: Overview of immune system, natural immunity to HIV/AIDS; the AIDS Virus and its life Cycle, disease progression (epidemiology), transmission and diagnosis. Treatment and Management: Nutr ...
expected output
... information on trends, global and local distribution; Justification of importance of course Biology of HIV/AIDS: Overview of immune system, natural immunity to HIV/AIDS; the AIDS Virus and its life Cycle, disease progression (epidemiology), transmission and diagnosis. Treatment and Management: Nutri ...
... information on trends, global and local distribution; Justification of importance of course Biology of HIV/AIDS: Overview of immune system, natural immunity to HIV/AIDS; the AIDS Virus and its life Cycle, disease progression (epidemiology), transmission and diagnosis. Treatment and Management: Nutri ...
No Slide Title
... 5. The intermediate in Methyl Sulfoxide created by mixing LiAlH4 with argenine was next added dropwise at room temperature via a separatory funnel. 6. Mixture stirred for 12 hours at room temperature, diluted with diethyl ether, filtered and washed. The ether was then distilled from the filtrate to ...
... 5. The intermediate in Methyl Sulfoxide created by mixing LiAlH4 with argenine was next added dropwise at room temperature via a separatory funnel. 6. Mixture stirred for 12 hours at room temperature, diluted with diethyl ether, filtered and washed. The ether was then distilled from the filtrate to ...
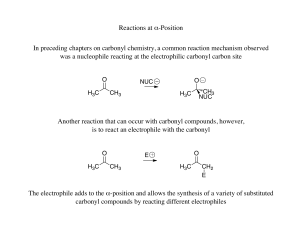
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones
... addition forming the conjugate acid of C=O Addition yields a hydroxy ether, called a hemiacetal (reversible); further reaction can occur Protonation of the OH and loss of water leads to an oxonium ion, R2C=OR+ to which a second alcohol adds to form the acetal ...
... addition forming the conjugate acid of C=O Addition yields a hydroxy ether, called a hemiacetal (reversible); further reaction can occur Protonation of the OH and loss of water leads to an oxonium ion, R2C=OR+ to which a second alcohol adds to form the acetal ...
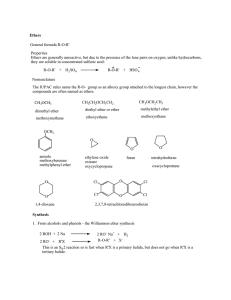
Ethers General formula R-O-R` Properties Ethers are generally
... R-O-R' + X 2 RO- + R'X This is an SN 2 reaction so is fast when R'X is a primary halide, but does not go when R'X is a tertiary halide. ...
... R-O-R' + X 2 RO- + R'X This is an SN 2 reaction so is fast when R'X is a primary halide, but does not go when R'X is a tertiary halide. ...
Unit-8-Alcohols-Aldehydes-Ketones
... Unit 8 - Organic Molecules III Alcohols, Thiols, Ethers, Aldehydes and Ketones In this unit we continue surveying some of the families of organic molecules that play important roles in biochemistry; looking both at their physical and chemical properties. The Group VIA elements, oxygen and sulfur, ty ...
... Unit 8 - Organic Molecules III Alcohols, Thiols, Ethers, Aldehydes and Ketones In this unit we continue surveying some of the families of organic molecules that play important roles in biochemistry; looking both at their physical and chemical properties. The Group VIA elements, oxygen and sulfur, ty ...
Ligand to Ligand Charge Transfer in
... electronegativities, has been developed,1 but the most common descriptions are based on HOMO-LUMO separations calculated by molecular orbital theory. An uncommon type of charge-transfer transition is ligand to ligand (LLCT) or interligand charge transfer. In comparison to the vast literature on MLCT ...
... electronegativities, has been developed,1 but the most common descriptions are based on HOMO-LUMO separations calculated by molecular orbital theory. An uncommon type of charge-transfer transition is ligand to ligand (LLCT) or interligand charge transfer. In comparison to the vast literature on MLCT ...
Sample Exercise 15.1 Writing Equilibrium
... Plan For equilibrium to be achieved, it must be possible for both the forward process and the reverse process to occur. For the forward process to occur, there must be some calcium carbonate present. For the reverse process to occur, there must be both calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. In both cases ...
... Plan For equilibrium to be achieved, it must be possible for both the forward process and the reverse process to occur. For the forward process to occur, there must be some calcium carbonate present. For the reverse process to occur, there must be both calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. In both cases ...
Ch25_outline-of-organic-nomenclature-1
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
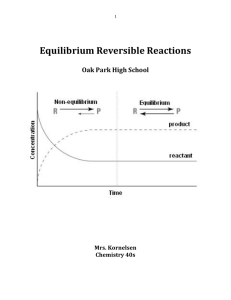
Equilibrium Reversible Reactions
... Are these the products or reactants? _____________________________________ In graph two which components start with a concentration of 0mol/L? _____________ Are these the products or reactants? _____________________________________ This shows that these two graphs represent the same chemical reactio ...
... Are these the products or reactants? _____________________________________ In graph two which components start with a concentration of 0mol/L? _____________ Are these the products or reactants? _____________________________________ This shows that these two graphs represent the same chemical reactio ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Studies toward the Stereoselective Synthesis of the
... protection of the secondary hydroxyl group as the benzyl ether and left the primary hydroxyl group, available after oxidation to the aldehyde, for a two-carbon chain extension to an α,βunsaturated ester. This ester in turn was reduced to an allylic alcohol which formed the starting material for a se ...
... protection of the secondary hydroxyl group as the benzyl ether and left the primary hydroxyl group, available after oxidation to the aldehyde, for a two-carbon chain extension to an α,βunsaturated ester. This ester in turn was reduced to an allylic alcohol which formed the starting material for a se ...