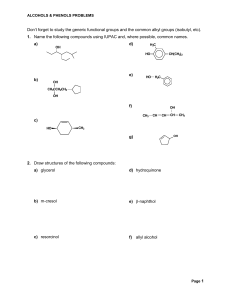
Don`t forget to study the generic functional groups and the common
... 11. Write equations to show how the following transformation can be carried out. More than one step may be necessary. There are marks assigned for each intermediate product (not charged transition states) and there are marks for the reagents used; so list them all. No marks are assigned for mechanis ...
... 11. Write equations to show how the following transformation can be carried out. More than one step may be necessary. There are marks assigned for each intermediate product (not charged transition states) and there are marks for the reagents used; so list them all. No marks are assigned for mechanis ...
CHEMISTRY 263
... 1. Stereochemistry – Walden Inversion (inversion of configuration) 2. Substitution of primary and secondary alkyl halides D. SN1 Reactions 1. Stereochemical Aspects (loss of stereochemistry via carbocations) 2. Substitution of tertiary alkyl halides and other tertiary carbons 3. Synthesis of alcohol ...
... 1. Stereochemistry – Walden Inversion (inversion of configuration) 2. Substitution of primary and secondary alkyl halides D. SN1 Reactions 1. Stereochemical Aspects (loss of stereochemistry via carbocations) 2. Substitution of tertiary alkyl halides and other tertiary carbons 3. Synthesis of alcohol ...
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
... (PLP), a derivative of vitamin B6, as a co-catalyst PLP is an aldehyde that readily forms imines from amino groups of substrates, such as amino acids The imine undergoes a proton shift that leads to the net conversion of the amino group of the substrate into a carbonyl group ...
... (PLP), a derivative of vitamin B6, as a co-catalyst PLP is an aldehyde that readily forms imines from amino groups of substrates, such as amino acids The imine undergoes a proton shift that leads to the net conversion of the amino group of the substrate into a carbonyl group ...
Chemistry Honours - SCS Autonomous College
... stability of Carbocations, Carbanions, Free radicals and Carbenes. Introduction to types of organic reactions and their mechanism: Addition, Elimination and Substitution reactions. CARBON-CARBON SIGMA BONDS: Chemistry of alkanes: Formation of alkanes, Wurtz Reaction, Wurtz-Fittig Reactions, Free rad ...
... stability of Carbocations, Carbanions, Free radicals and Carbenes. Introduction to types of organic reactions and their mechanism: Addition, Elimination and Substitution reactions. CARBON-CARBON SIGMA BONDS: Chemistry of alkanes: Formation of alkanes, Wurtz Reaction, Wurtz-Fittig Reactions, Free rad ...
Ch17 Lesson17_2
... 3 Evaluate Does the result make sense? • The temperature of the solution increases, which means that the reaction is exothermic, and thus the sign of ΔH should be negative. • About 4 J of heat raises the temperature of 1 g of water 1°C, so 200 J of heat is required to raise 50 g of water 1°C. Raisin ...
... 3 Evaluate Does the result make sense? • The temperature of the solution increases, which means that the reaction is exothermic, and thus the sign of ΔH should be negative. • About 4 J of heat raises the temperature of 1 g of water 1°C, so 200 J of heat is required to raise 50 g of water 1°C. Raisin ...
PDF File
... products (ImP and Pi) were separated by electrophoresis on 15% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels, and their ratios at each time point were quantitated with a Molecular Dynamics PhosphorImager. Data analysis was performed using Kaleidagraph (Synergy Software), and exponential fits to the data typical ...
... products (ImP and Pi) were separated by electrophoresis on 15% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gels, and their ratios at each time point were quantitated with a Molecular Dynamics PhosphorImager. Data analysis was performed using Kaleidagraph (Synergy Software), and exponential fits to the data typical ...
Chapter 20
... When an oxidizing agent such as Cu2+ is placed in direct contact with a reducing agent such as Zn, as shown in Interactive Figure 20.1.1, electrons can be transferred directly from the reducing agent to the oxidizing agent. We call this direct electron transfer because it occurs where the two specie ...
... When an oxidizing agent such as Cu2+ is placed in direct contact with a reducing agent such as Zn, as shown in Interactive Figure 20.1.1, electrons can be transferred directly from the reducing agent to the oxidizing agent. We call this direct electron transfer because it occurs where the two specie ...