Elimination Reactions
... • tertiary substrates go by E1 in polar solvents, with little or no base present! • typical polar solvents are water, ethanol, ...
... • tertiary substrates go by E1 in polar solvents, with little or no base present! • typical polar solvents are water, ethanol, ...
Review of Organic Chem II
... 3. The types of intermediates involved (cation, anion, or radical) should be consistent with the reaction classification above a. If the reaction is cationic, don’t show anionic intermediates b. If the reaction is anionic, don’t show cationic intermediates 4. Usually conditions are ionic. 5. Use a r ...
... 3. The types of intermediates involved (cation, anion, or radical) should be consistent with the reaction classification above a. If the reaction is cationic, don’t show anionic intermediates b. If the reaction is anionic, don’t show cationic intermediates 4. Usually conditions are ionic. 5. Use a r ...
chapter 4 -aromatic compounds
... • Organic compound that contains a benzene ring in its molecule is known as an aromatic compounds. • Sometimes called arenes. • Molecular formula: C6H6 • Represented as a regular hexagon containing an inscribed circle. ...
... • Organic compound that contains a benzene ring in its molecule is known as an aromatic compounds. • Sometimes called arenes. • Molecular formula: C6H6 • Represented as a regular hexagon containing an inscribed circle. ...
Slide 1
... • Organic compound that contains a benzene ring in its molecule is known as an aromatic compounds. • Sometimes called arenes. • Molecular formula: C6H6 • Represented as a regular hexagon containing an inscribed circle. ...
... • Organic compound that contains a benzene ring in its molecule is known as an aromatic compounds. • Sometimes called arenes. • Molecular formula: C6H6 • Represented as a regular hexagon containing an inscribed circle. ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... 1) As seen, alcohols do addition-elimination to alkanoyl halides to give esters 2) Acid catalyzed addition-elimination of alcohols to carboxylic acids is also useful 3) Esterification (and Ester Hydrolysis) Mechanism ...
... 1) As seen, alcohols do addition-elimination to alkanoyl halides to give esters 2) Acid catalyzed addition-elimination of alcohols to carboxylic acids is also useful 3) Esterification (and Ester Hydrolysis) Mechanism ...
File - Rasapalli Research Group
... Phenols are acidic in nature, and can be oxidized to quinones. 9. Alcohols upon reaction with HX provide alkyl halides. 10. An alkyl halide = an alkyl group with a halogen 11. Haloalkane Properties – Strongly affected by the C-X bond polarization and the polarizability of X. 12. Alcohols and alkyl h ...
... Phenols are acidic in nature, and can be oxidized to quinones. 9. Alcohols upon reaction with HX provide alkyl halides. 10. An alkyl halide = an alkyl group with a halogen 11. Haloalkane Properties – Strongly affected by the C-X bond polarization and the polarizability of X. 12. Alcohols and alkyl h ...
syllabus for two‐year four‐semester course in chemistry 2014
... Spectrophotometric, ion exchange and complexometric estimations. Identification of single organic liquid with one or more functional groups. Numerical, kinetic and equilibrium experiments. ...
... Spectrophotometric, ion exchange and complexometric estimations. Identification of single organic liquid with one or more functional groups. Numerical, kinetic and equilibrium experiments. ...
- Wiley Online Library
... usefulness of this procedure in the preparation of target compounds that rely on a-chlorocarbonyl compounds as intermediates. In conclusion, we report the first synthesis of a-chlorinated carbonyl compounds from secondary and primary allylic alcohols. A wide range of substrates were chlorinated in h ...
... usefulness of this procedure in the preparation of target compounds that rely on a-chlorocarbonyl compounds as intermediates. In conclusion, we report the first synthesis of a-chlorinated carbonyl compounds from secondary and primary allylic alcohols. A wide range of substrates were chlorinated in h ...
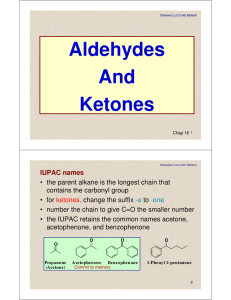
Aldehydes And Ketones
... or other Lewis acid to form a resonancestabilized cation-– protonation increases the electron deficiency of the carbonyl carbon and makes it more reactive toward nucleophiles R R ...
... or other Lewis acid to form a resonancestabilized cation-– protonation increases the electron deficiency of the carbonyl carbon and makes it more reactive toward nucleophiles R R ...