Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... 1. Find the longest chain in the molecule. 2. Number the chain from the end nearest the first substituent encountered. 3. List the substituents as a prefix along with the number(s) of the carbon(s) to which they are attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Equilibrium
... The value of the equilibrium constant for any reaction can be determined by experiment. As detailed in the above section, the equilibrium position for a given reaction does not depend on the starting concentrations, so the equilibrium constant has the same value regardless of the initial amounts of ...
... The value of the equilibrium constant for any reaction can be determined by experiment. As detailed in the above section, the equilibrium position for a given reaction does not depend on the starting concentrations, so the equilibrium constant has the same value regardless of the initial amounts of ...
ethane - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... The resolution of a racemic mixture cannot be accomplished using standard physical means (e. g. distillation, recrystallization, or chromatography), because enantiomers have identical physical properties, except for the direction of rotation of plane polarized light. To distinguish between the compo ...
... The resolution of a racemic mixture cannot be accomplished using standard physical means (e. g. distillation, recrystallization, or chromatography), because enantiomers have identical physical properties, except for the direction of rotation of plane polarized light. To distinguish between the compo ...
AQA A-level Chemistry
... A reaction profile is a diagram of the enthalpy levels of the reactants and products in a chemical reaction. The vertical (y) axis is enthalpy but not ∆H. The horizontal (x) axis is progress of reaction, reaction coordinate or extent of reaction. Two horizontal lines are drawn and labelled with the ...
... A reaction profile is a diagram of the enthalpy levels of the reactants and products in a chemical reaction. The vertical (y) axis is enthalpy but not ∆H. The horizontal (x) axis is progress of reaction, reaction coordinate or extent of reaction. Two horizontal lines are drawn and labelled with the ...
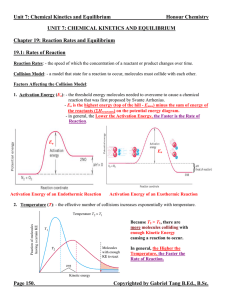
Unit 7 Reaction Rates and Equilibrium Notes
... 19.2A: Reversible Reactions Reversible Reactions: - reactions that can go from the right hand side of the equation (products) to the left hand side of the equation (reactants). Chemical Equilibrium: - the state at which the concentrations of all reactants and products remain constant with time (the ...
... 19.2A: Reversible Reactions Reversible Reactions: - reactions that can go from the right hand side of the equation (products) to the left hand side of the equation (reactants). Chemical Equilibrium: - the state at which the concentrations of all reactants and products remain constant with time (the ...
M.Sc. Chemistry (Two year Course)
... resolution, optical purity, prochirality, enantiotopic and diastereotopic atoms, groups and faces, asymmetric synthesis, cram’s rule and its modifications, prelog’s rule, conformational analysis of cycloalkanes (upto six membered rings), decalins, conformations of sugars, optical activity in absence ...
... resolution, optical purity, prochirality, enantiotopic and diastereotopic atoms, groups and faces, asymmetric synthesis, cram’s rule and its modifications, prelog’s rule, conformational analysis of cycloalkanes (upto six membered rings), decalins, conformations of sugars, optical activity in absence ...
Syllabus Advanced Level and Advanced Subsidiary Level
... questions testing such skills may be based on information which is unfamiliar to the candidate. In answering such questions, candidates are required to use principles and concepts that are within the syllabus and apply them in a logical, reasoned or deductive manner to a novel situation. Questions t ...
... questions testing such skills may be based on information which is unfamiliar to the candidate. In answering such questions, candidates are required to use principles and concepts that are within the syllabus and apply them in a logical, reasoned or deductive manner to a novel situation. Questions t ...
Reactions of Alcohols
... The –OH is a poor leaving group, but –OH2+ is an excellent leaving group, and once the -OH is protonated, the molecule may take part in a variety of substitution and/or elimination reactions. The nature of R determines whether the reactions proceed via SN1 or SN2 mechanisms. (If R is primary alkyl ...
... The –OH is a poor leaving group, but –OH2+ is an excellent leaving group, and once the -OH is protonated, the molecule may take part in a variety of substitution and/or elimination reactions. The nature of R determines whether the reactions proceed via SN1 or SN2 mechanisms. (If R is primary alkyl ...
Chemistry 180-213B Introductory Physical
... Carnot directed his attention to the point that, in the heat engine, work was done not at the expense of heat but in connection with the transfer of heat from a hot body to a cold body, and thus heat could not be used without a cold body, in analogy of water falling from a high reservoir to a low re ...
... Carnot directed his attention to the point that, in the heat engine, work was done not at the expense of heat but in connection with the transfer of heat from a hot body to a cold body, and thus heat could not be used without a cold body, in analogy of water falling from a high reservoir to a low re ...
THE TEACHING PROGRAM OF CHEMISTRY DEPARTMENT
... cleavage of a bond (homolytic and heterolytic). Homolytic and Heterolytic Bond Dissociation Enthalpies. The most important intermediates in organic chemistry. Formation of free radicals, triplet and singlet carbene, carbocation and their electronic structures. Carbocation Stability.Free Radical Subs ...
... cleavage of a bond (homolytic and heterolytic). Homolytic and Heterolytic Bond Dissociation Enthalpies. The most important intermediates in organic chemistry. Formation of free radicals, triplet and singlet carbene, carbocation and their electronic structures. Carbocation Stability.Free Radical Subs ...