Unit 5: Chemical Kinetics and Equilibrium
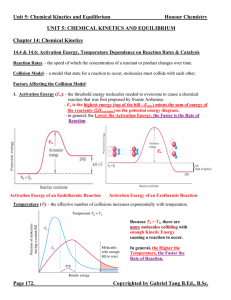
... constant with time (the Forward Reaction Rate = Reverse Reaction Rate). - the equilibrium state is dynamic (not static). Chemical species are continuously converting from reactants to products and vice versa. It appears that the reaction has stopped only because the rate of consumption = rate of pro ...
... constant with time (the Forward Reaction Rate = Reverse Reaction Rate). - the equilibrium state is dynamic (not static). Chemical species are continuously converting from reactants to products and vice versa. It appears that the reaction has stopped only because the rate of consumption = rate of pro ...
bonding
... E/Z System: For each carbon of the double bond, the groups are Assign a priority (high or low) according to a system of rules. Thus, the high priority groups can be on the same side or on opposite Sides of the double bond. If the high priority groups are on opposite sides then the double bond is des ...
... E/Z System: For each carbon of the double bond, the groups are Assign a priority (high or low) according to a system of rules. Thus, the high priority groups can be on the same side or on opposite Sides of the double bond. If the high priority groups are on opposite sides then the double bond is des ...
Functional Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids
... • Step 3: Make a new bond between a nucleophile and an electrophile. The ketone reacts with a second mole of Grignard reagent to give a second tetrahedral carbonyl addition intermediate. ...
... • Step 3: Make a new bond between a nucleophile and an electrophile. The ketone reacts with a second mole of Grignard reagent to give a second tetrahedral carbonyl addition intermediate. ...
Mechanism and Processing Parameters Affecting the Formation of
... and methanol are presented. Since sulfonic acids share common characteristics of extremely high acidity and low nucleophilicity, understanding of this model system is anticipated to be applicable to formation of sulfonate esters more generally. Two mechanistic pathways for sulfonate ester formation ...
... and methanol are presented. Since sulfonic acids share common characteristics of extremely high acidity and low nucleophilicity, understanding of this model system is anticipated to be applicable to formation of sulfonate esters more generally. Two mechanistic pathways for sulfonate ester formation ...
215-216 HH W12-notes
... b. Ring-opening reactions of epoxides: Epoxides are highly strained and easily undergo ring-opening reactions under both acidic and basic conditions. Acidic conditions: ring-opening reactions proceed rapidly at low temperatures (usually at room temp or below); elongated C-O bonds of the protonated, ...
... b. Ring-opening reactions of epoxides: Epoxides are highly strained and easily undergo ring-opening reactions under both acidic and basic conditions. Acidic conditions: ring-opening reactions proceed rapidly at low temperatures (usually at room temp or below); elongated C-O bonds of the protonated, ...
Student Study Guide Chemistry 534
... Gases play a very important role in our daily existence. Since we are surrounded by an ocean of gas called the atmosphere, many of the properties of gases are already familiar to us. We know that we can squeeze a balloon into a smaller shape and that perfume released into the corner of a room can, i ...
... Gases play a very important role in our daily existence. Since we are surrounded by an ocean of gas called the atmosphere, many of the properties of gases are already familiar to us. We know that we can squeeze a balloon into a smaller shape and that perfume released into the corner of a room can, i ...
Document
... Any property that only depends on object’s current state or condition Independence from method, path or mechanism by which change occurs is important feature of all state functions Some State functions, E, P, t, and V : ...
... Any property that only depends on object’s current state or condition Independence from method, path or mechanism by which change occurs is important feature of all state functions Some State functions, E, P, t, and V : ...
COURSES SCHEME & SYLLABUS
... Course Objective: To impart advanced knowledge of aromaticity, stereochemistry of organic compounds, pericyclic and photochemical reactions. Stereochemistry: Conformational analysis of Cycloalkanes and Decalins, Effect of conformation on reactivity, Conformation of sugars, Steric-strain due to unavo ...
... Course Objective: To impart advanced knowledge of aromaticity, stereochemistry of organic compounds, pericyclic and photochemical reactions. Stereochemistry: Conformational analysis of Cycloalkanes and Decalins, Effect of conformation on reactivity, Conformation of sugars, Steric-strain due to unavo ...
Review Packet Answers - Bremerton School District
... characteristics: start at 0 M, increase to 0.10 M, reach equilibrium at the same time [HI] reaches equilibrium 1 point for any two characteristics, 2 points for all three characteristics [H ][I ] (0.10)(0.10) ...
... characteristics: start at 0 M, increase to 0.10 M, reach equilibrium at the same time [HI] reaches equilibrium 1 point for any two characteristics, 2 points for all three characteristics [H ][I ] (0.10)(0.10) ...
course structure
... Optical activity in absence of chiral carbon (biphenyls, allenes and spirans), chirality due to helical shape. Stereochemistry of organo nitrogen-, sulfur- and phosphorus- compounds. Optical rotatory dispersion, circular dichroism, Cotton effect, axial haloketone rule, octant rule. Aromaticity in be ...
... Optical activity in absence of chiral carbon (biphenyls, allenes and spirans), chirality due to helical shape. Stereochemistry of organo nitrogen-, sulfur- and phosphorus- compounds. Optical rotatory dispersion, circular dichroism, Cotton effect, axial haloketone rule, octant rule. Aromaticity in be ...
Problem 28. TUNNELING IN CHEMISTRY
... Many chemical phenomena can be explained by physical theories. The main theory for chemistry is quantum mechanics, which gives the solid foundation for the observed chemical periodicity. One of the cornerstones of quantum mechanics is the superposition principle that says: “If a quantum system can b ...
... Many chemical phenomena can be explained by physical theories. The main theory for chemistry is quantum mechanics, which gives the solid foundation for the observed chemical periodicity. One of the cornerstones of quantum mechanics is the superposition principle that says: “If a quantum system can b ...