Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions
... Never change a subscript to balance an equation (You can only change coefficients) – If you change the subscript (formula) you are describing a different chemical. – H2O is a different compound than H2O2 Never put a coefficient in the middle of a formula; they must go only in the front ...
... Never change a subscript to balance an equation (You can only change coefficients) – If you change the subscript (formula) you are describing a different chemical. – H2O is a different compound than H2O2 Never put a coefficient in the middle of a formula; they must go only in the front ...
Thermochemistry
... Kinetic Energy: The energy an object has just by being in motion. KE=1/2 mv2 Potential Energy: The energy an object has because of its position and the forces acting on it. Such as the force of Gravity or the electrostatic force that arises between two charged particles. ...
... Kinetic Energy: The energy an object has just by being in motion. KE=1/2 mv2 Potential Energy: The energy an object has because of its position and the forces acting on it. Such as the force of Gravity or the electrostatic force that arises between two charged particles. ...
Ch 8 Notes: Chemical Equations and Reactions
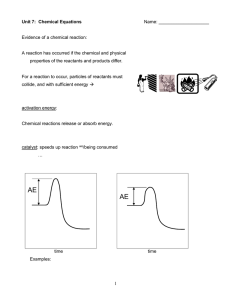
... Endothermic Reactions – when energy is absorbed or taken in during a chemical reaction. Energy is required when a compound is decomposed or breaks down; energy is a reactant and is written on the left of the arrow: 2H2O + energy 2H2 + O2 B. ...
... Endothermic Reactions – when energy is absorbed or taken in during a chemical reaction. Energy is required when a compound is decomposed or breaks down; energy is a reactant and is written on the left of the arrow: 2H2O + energy 2H2 + O2 B. ...
Determination of the reaction order Determination of the reaction
... experiments required much more sophisticated approach. These old methods are also very useful for analysis of kinetic data (small data sets) in text problem solving exercises. Hence, their application is essential for chemists. It is always useful to inspect the data carefully if any regularities di ...
... experiments required much more sophisticated approach. These old methods are also very useful for analysis of kinetic data (small data sets) in text problem solving exercises. Hence, their application is essential for chemists. It is always useful to inspect the data carefully if any regularities di ...
kinetics and equilibrium
... More exact definition- measure of the number of possible ways that the energy of a system can be distributed; related to the freedom of the system’s particles to move and the number of ways they can ...
... More exact definition- measure of the number of possible ways that the energy of a system can be distributed; related to the freedom of the system’s particles to move and the number of ways they can ...
Unit 3: Chemical Kinetics
... Increasing the number of collisions that have sufficient energy Increasing the number of collisions that have proper orientation. Before we look at these factors in depth, there are two more ...
... Increasing the number of collisions that have sufficient energy Increasing the number of collisions that have proper orientation. Before we look at these factors in depth, there are two more ...
NAME REVIEW 1: JUST THE BASICS ___1) In which material are
... 4) 1) isotopes are of the same element, but with different mass numbers. Thus they have the same symbol (due to the fact they have the same number of protons), but they have a different number of neutrons. 5) 2) mixture 6) 3) HClO 7) 1) Oxidation occurs at the anode only 8) 2) The products have high ...
... 4) 1) isotopes are of the same element, but with different mass numbers. Thus they have the same symbol (due to the fact they have the same number of protons), but they have a different number of neutrons. 5) 2) mixture 6) 3) HClO 7) 1) Oxidation occurs at the anode only 8) 2) The products have high ...
ANSWERS Concept Checks: Ch. 5 The Molecules of Life Concept
... 4. Which parts of an amino acid's structure are the same in all amino acids? Which part is unique? Central carbon is bonded to a hydrogen atom, an amino group, and a carboxyl group. The fourth bond is with a side or functional group that is unique to that amino acid. Concept Check 5.5 1. Explain the ...
... 4. Which parts of an amino acid's structure are the same in all amino acids? Which part is unique? Central carbon is bonded to a hydrogen atom, an amino group, and a carboxyl group. The fourth bond is with a side or functional group that is unique to that amino acid. Concept Check 5.5 1. Explain the ...
Chemistry: Selected Topics
... 1 Understanding the relation between reaction rate and reaction mechanism 2 Being able to develop the rate equation of a chemical reaction 3 Knowledge of the properties and synthesis of important types of inorganic polymers 4 Knowledge of the relation between chemical structure and properties of ...
... 1 Understanding the relation between reaction rate and reaction mechanism 2 Being able to develop the rate equation of a chemical reaction 3 Knowledge of the properties and synthesis of important types of inorganic polymers 4 Knowledge of the relation between chemical structure and properties of ...
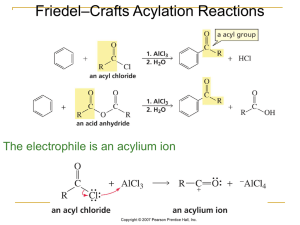
types of organic reactions
... One product will be there in greater amounts than the other and is called the major product (the other is called the minor product). To decide which is the major product, Markovnikov’s rule is used: The hydrogen atom of the addition reagent goes to the carbon atom of the double bond, that is attache ...
... One product will be there in greater amounts than the other and is called the major product (the other is called the minor product). To decide which is the major product, Markovnikov’s rule is used: The hydrogen atom of the addition reagent goes to the carbon atom of the double bond, that is attache ...
Thermochemistry Unit Review - WilsonSCH4U-03-2012
... Kinetic theory of Heat and Temperature All matter is made of uncountable numbers of particles. All particles are in constant motion. Even solid objects are in motion, even though we cannot detect motion. With two bodies in contact, energy will transfer from the body with the higher energy to the bod ...
... Kinetic theory of Heat and Temperature All matter is made of uncountable numbers of particles. All particles are in constant motion. Even solid objects are in motion, even though we cannot detect motion. With two bodies in contact, energy will transfer from the body with the higher energy to the bod ...
NCEA Level 2 Chemistry (91165) 2012 Assessment Schedule
... correct. • In (a) reagent 4 (H2) is correct. • In (a) reagent 3 (PCl3 / PCl5 / SOCl2) is correct. ...
... correct. • In (a) reagent 4 (H2) is correct. • In (a) reagent 3 (PCl3 / PCl5 / SOCl2) is correct. ...
Chemistry Crunch #12.2: Organic Reactions KEY Why? Learning
... 2. Describe what is going on between the molecules of pentene and hydrogen in this addition reaction. ...
... 2. Describe what is going on between the molecules of pentene and hydrogen in this addition reaction. ...